Abstract
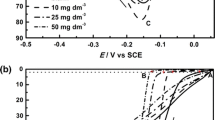
The effect of two alklpyridinium hydrosulfate based ionic liquids (ILs) including N-butylpyridinium hydrogen sulfate (Bpy-HSO4) and N-hexylpyridinium hydrogen sulfate (HpyHSO4) as additives on the nucleation and growth of copper from acidic sulfate bath was investigated using cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometric and scanning electron microscopy techniques. Results from cyclic voltammetry indicated that the two studied additives had a blocking effect on copper electrodeposition process and this effect initiated by HpyHSO4 was more pronounced in comparison to BpyHSO4. Dimensionless chronoamperometric current-time transients for the electrodeposition of copper from the bath free of additives were in good accord with the theoretical transients for the limiting case of instantaneous three-dimensional nucleation with diffusion-controlled growth of the nuclei. However, the instantaneous nucleation mechanism observed in the additive-free bath was changed to a more progressive one when additives were present in the bath. Surface morphology analysis indicated that alklpyridinium hydrosulfate ILs can induce the formation of leveled and finer grained deposits by the adsorption of additive at the first stages of deposition process, leading to decrease of the nucleation and growth rate of nuclei.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pasquale MA, Gassa LM, Arvia AJ. Copper electrodeposition from an acidic plating bath containing accelerating and inhibiting organic additives. Electrochim Acta, 2008, 53: 5891–5904
Bonou L, Eyraud M, Denoyel R, Massiani Y. Influence of additives on Cu electrodeposition mechanisms in acid solution: Direct current study supported by non-electrochemical measurements. Electrochim Acta, 2002, 47: 4139–4148
Oniciu L, Muresan L. Some fundamental aspects of levelling and brightening in metal electrodeposition. J Appl Electrochem, 1991, 21: 565–574
MacKinnon DJ, Brannen JM. Evaluation of organic additives as levelling agents for zinc electrowinning from chloride electrolytes. J Appl Electrochem, 1982, 12: 21–31
Michailova E, Peykova M, Stoychev D, Milchev A. On the role of surface active agents in the nucleation step of metal electrodeposition on a foreign substrate. J Electroanal Chem, 1994, 366: 195–202
Budevski E, Staikov G, Lorenz WJ. Electrochemical phase formation and growth. New York: VCH, 1996
Sun M, O’Keefe TJ. The effect of additives on the nucleation and growth of copper onto stainless steel cathodes. Metal Trans B, 1992, 23B: 591–599
Fabricius G, Kontturi K, Sundholm G. Influence of thiourea on the nucleation of copper from acid sulphate solutions. Electrochim Acta, 1994, 39: 2353–2357
Hölzle MH, Apsel CW, Will T, Kolb DM. Copper deposition onto Au (111) in the presence of thiourea. J Electrochem Soc, 1995, 142: 3741–3749
Tarallo A, Heerman L. Influence of thiourea on the nucleation of copper on polycrystalline platinum. J App Electrochem. 1999, 29: 585–591
Kapočius V, Karpavičien V, Steponavičius A. Electrochemical processes at a platinum electrode in CuSO4 solutions in the UPD region and at initial electrocrystallization stages: Effect of polyethylene glycol. Russian J Electrochem. 2002, 38: 274–279
Nichols RJ, Beckmann W, Meyer H. An in situ scanning tunnelling microscopy study of bulk copper deposition and the influence of an organic additive. J Electroanal Chem, 1992, 330: 381–394
Grujicic D, Pesic B. Electrodeposition of copper: The nucleation mechanisms. Electrochim Acta, 2002, 47: 2901–2912
Gladysz O, Los P. The electrochemical nucleation of copper on disc-shaped ultramicroelectrode in industrial electrolyte. Electrochim Acta, 2008, 54: 801–807
Zhang QB, Hua YX, Wang YT, Lu HJ, Zhang XY. Effects of ionic liquid additive [BMIM]HSO4 on copper electrodeposition from acidic sulfate electrolyte. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 98: 291–297
Zhang QB, Hua YX. Influence of alkylpyridinium ionic liquids on copper electrodeposition from acidic sulfate electrolyte. J Cent South Univ T, 2013, 20(8): 2096–2102
Fletcher S. Some new formulae applicable to electrochemical nucleation/growth/collision. Electrochim Acta, 1983, 28: 917–923
Zhang QB, Hua YX. Alkylimidazolium ionic liquids on the corrosion inhibition of copper in sulfuric acid solution. Acta Phys-Chim Sin, 2011, 27: 655–663
Pitner WR, Hussey CL. Electrodeposition of zinc from the lewis acidic aluminum chloride-1-methyl-3-ethylimidazolium chloride room temperature molten salt. J Electrochem Soc, 1997, 144: 3095–3103
Scharifker BR, Hills G. Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation. Electrochim Acta, 1983, 28: 879–889
Raeissi K, Saatchi A, Golozar MA. Effect of nucleation mode on the morphology and texture of electrodeposited zinc. J Appl Electrochem, 2003, 33: 635–642
Zhang QB, Hua YX. Effects of [HMIM]HSO4 and [OMIM]HSO4 on the electrodeposition of zinc from sulfate electrolytes. J Appl Electrochem, 2009, 39: 1185–1192
Scharifker BR, Mostany J. Three-dimensional nucleation with diffusion controlled growth: Part I. Number density of active sites and nucleation rates per site. J Electroanal Chem, 1984, 177: 13–23
Alvarez AE, Salinas DR. Nucleation and growth of Zn on HOPG in the presence of gelatine as additive. J Electroanal Chem, 2004, 566: 393–400
Milchev A, Stoyanov S, Kaischev R. Atomistic theory of electrolytic nucleation: I. Thin Solid Films, 1974, 22: 255–265
Milchev A, Stoyanov S. Classical and atomistic models of electrolytic nucleation: Comparison with experimental data. J Electroanal Chem, 1976, 72: 33–43
Milchev A, Tsakova V. Theory of progressive nucleation and growth accounting for the ohmic drop in the electrolyte. I. J Appl Electrochem, 1990, 20: 301–306
Michailova E, Vitanova I, Stoychev D, Milchev A. Initial stages of copper electrodeposition in the presence of organic additives. Electrochim Acta, 1993, 38: 2455–2458
Deutscher RL, Fletcher S. Nucleation on active sites: Part IV. Invention of an electronic method of counting the number of crystals as a function of time; and the discovery of nucleation rate dispersion. J Electroanal Chem, 1988, 239: 17–54
Budevski E, Staikov G, Lorenz WJ. Electrocrystallization: Nucleation and growth phenomena. Electrochim Acta, 2000, 45: 2559–2574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Hua, Y. & Wang, R. Initial stages of copper electrodeposition from acidic sulfate solution in the presence of alklpyridinium hydrosulfate ionic liquids. Sci. China Chem. 56, 1586–1592 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4947-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4947-0