Abstract
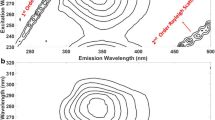
A novel method applying simple, rapid, effective and inexpensive excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with second-order calibration method for simultaneous determination of ethoxyquin (EQ) and tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) contents in biological fluid samples was developed. After a simple data preprocessing that was to insert zeros below the first-order Rayleigh scattering, the second-order calibration method based on the alternating normalization-weighed error (ANWE) algorithm was used to deal with EEM data. Via the introduced “second-order advantage”, the individual concentrations of the analytes of interest could be obtained even in the presence of uncalibrated interferences. The experimental concentration ranges for the analytes were as follows: EQ, from 4.58 to 20.6 μg mL−1 in plasma and from 6.87 to 20.6 μg mL−1 in urine; TBHQ, from 4.49 to 20.2 μg mL−1 in plasma and from 6.73 to 22.4 μg mL−1 in urine. The recoveries from spiked biological fluid samples were in the ranges of 92.8%–106.2% for EQ and 94.6%–107.2% for TBHQ. These results demonstrate that the three-dimensional EEM fluorescence with second-order calibration method is a powerful tool for obtaining both EQ and TBHQ quantitative results in plasma and urine samples, and could be applied to more complex matrices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karovičová J, Šimko P. Determination of synthetic phenolic antioxidants in food by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A, 2000, 882(1–2): 271–281
Yankah VV, Ushio H, Ohshima T, Koizumi C. Quantitative determination of butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, and tert-butyl hydroquinone in oils, foods, and biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection. Lipids, 1998, 33(11): 1139–1145
Blaszczyk A, Skolimowski J. Apoptosis and cytotoxicity caused by ethoxyquin salts in human lymphocytes in vitro. Food Chem, 2007, 105(3): 1159–1163
Dolatabadi JEN, Kashanian S. A review on DNA interaction with synthetic phenolic food additives. Food Res Int, 2010, 43(5): 1223–1230
Melton SL. Methodology for following lipid oxidation in muscle foods. Food Technol, 1983, 37(7): 105–111
Bohne VJB, Lundebye AK, Hamre K. Accumulation and depuration of the synthetic antioxidant ethoxyquin in the muscle of Atlantic salmon. Food Chem Toxicol, 2008, 46(5): 1834–1843
BŁaszczyk A, Skolimowski J. Apootosis and cytotoxicity caused by ethoxyquin and two of its salts. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2005, 10(1): 15–21
Alanko K, Jolanki R, Estlander T, Kanerva L. Occupational “multivitamin allergy” caused by the antioxidant ethoxyquin. Contact Dermatitis, 1998, 39(5): 263–264
Dzanis DA. Safety of ethoxyquin in dog foods. J Nutr, 1991, 121(Suppl. 11): S163–S164
Rubel DM, Freeman S. Allergic contact dermatitis to ethoxyquin in a farmer handling chicken feeds. Australas J Dermatol, 1998, 39(2): 89–91
Blaszczyk A. DNA damage induced by ethoxyquin in human peripheral lymphocytes. Toxicol Lett, 2006, 163(1): 77–83
Manson M, Green J, Driver H. Ethoxyquin alone induces preneoplastic changes in rat kidney whilst preventing induction of such lesions in liver by aflatoxin B1. Carcinog, 1987, 8(5): 723–728
Hernández M, Reyes J, Gómez-Lojero C, Sayavedra M, Meléndez E. Inhibition of the renal uptake of paminohippurate and tetraethylammonium by the antioxidant ethoxyquin in the rat. Food Chem Toxicol, 1993, 31(5): 363–367
Reyes JL, Hernández ME, Meléndez E, Gómez-Lojero C. Inhibitory effect of the antioxidant ethoxyquin on electron transport in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem Pharmacol, 1995, 49(3): 283–289
Okubo T, Nagai F, Ushiyama K, Kano I. Contribution of oxygen radicals to DNA cleavage by quinone compounds derived from phenolic antioxidants, tert-butylhydroquinone and 2,5-di-tert-butylhydroquinone. Toxicol Lett, 1997, 90(1): 11–18
Nagai F, Okubo T, Ushiyama K, Satoh K, Kano I. Formation of hydroxydeoxyguanosine in calf thymus DNA treated with tertbutylhydroquinone, a major metabolite of butylated hydroxyanisole. Toxicol Lett, 1996, 89(2): 163–167
Ding T, Shen CY, Jiang Y, Yao YG, Tao J, Zhao HM, Shen WJ, Xu JZ, Yao RR. Determination of Ethoxyquin Residues in Fruits by HPLC-MS/MS. J Chin Mass Spectrom Soc, 2009, 30(5): 307–310
Lu YJ, Cheng J, Jiang JS. Determination of Tertiary Butylhydroquinone in Foods by HPLC. Mod Sci Instrum, 2008, 5: 58–60
André C, Castanheira I, Cruz J, Paseiro P, Sanches-Silva A. Analytical strategies to evaluate antioxidants in food: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol, 2010, 21(5): 229–246
Noel Robledo S, Alicia Zón M, Daniel Ceballos C, Fernández H. Qualitative and quantitative electroanalysis of synthetic phenolic antioxidant mixtures in edible oils based on their acid-base properties. Food Chem, 2011, 127(3): 1361–1369
Hao PP, Sun WL, Huang W, Ni JR. Metabolic pathways of tertiary butylhydroquinone in rats. J Toxicol, 2007, 21(1): 30–32
Guan YQ, Chu QC, Fu L, Ye JN. Determination of phenolic antioxidants by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography with electrochemical detection. Food Chem, 2006, 94(1): 157–162.
Yang MH, Lin HJ, Choong YM. A rapid gas chromatographic meth od for direct determination of BHA, BHT and TBHQ in edible oils and fats. Food Res Int, 2002, 35(7): 627–633
Guo L, Xie MY, Yan AP, Wan YQ, Wu YM. Simultaneous determination of five synthetic antioxidants in edible vegetable oil by GC-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2006, 386(6): 1881–1887
Huang W, Gu YC, Niu H. Determination of tertiary-butylhydroquinone and its metabolites in rat serum by liquid chromatographyion trap mass spectrometry. Lipids, 2008, 43(3): 281–288
Kmellar B, Pareja L, Ferrer C, Fodor P, Fernández-Alba AR. Study of the effects of operational parameters on multiresidue pesticide analysis by LC-MS/MS. Talanta, 2011, 84(2): 262–273
Kowalski BR, Seasholtz MB. Recent developments in multivariate calibration. J Chemom, 1991, 5(3): 129–145
Booksh KS, Kowalski BR. Theory of analytical chemistry. Anal Chem, 1994, 66(15): 782A–791A
Xia AL, Wu HL, Zhu SH, Han QJ, Zhang Y, Yu RQ. Determination of psoralen in human plasma using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence coupled to second-order calibration. Anal Sci, 2008, 24(9): 1171–1176
Thygesen LG, Rinnan A, Barsberg S, Moller JKS. Stabilizing the PARAFAC decomposition of fluorescence spectra by insertion of zeros outside the data area. Chemom Intell Lab Syst, 2004, 71(2): 97–106
Li YN, Wu HL, Nie JF, Li SF, Yu YJ, Zhang SR, Yu RQ. Interference-free determination of abscisic acid and gibberellin in plant samples using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence based on oxidation derivatization coupled with second-order calibration methods. Anal Methods, 2009, 1: 115–122
Wang XM, Wu HL, Nie JF, Li YN, Yu YJ, Yu RQ. Rapid determination of thiabendazole in orange extract using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and second-order calibration based on alternating trilinear decomposition/alternating normalization-weighted error algorithms. Sci China Chem, 2008, 51(8): 729–735
Harshman RA. Foundations of the PARAFAC procedure: Models and conditions for an explanatory multimodal factor analysis. UCLA Working Papers in Phonetics, 1970, 16: 1–84
Carroll JD, Chang JJ. Analysis of individual differences in multidimensional scaling via an n-way generalization of ‘Eckart-Young’ decomposition. Psychometrika, 1970, 35(3): 283–319
Bro R, Kiers HAL. A new efficient method for determining the number of components in PARAFAC models. J Chemom, 2003, 17(5): 274–286
Olivieri AC, Faber NKM. A closed-form expression for computing the sensitivity in second-order bilinear calibration. J Chemom, 2005, 19(11–12): 583–592
Olivieri AC. Computing sensitivity and selectivity in parallel factor analysis and related multiway techniques: the need for further developments in net analyte signal theory. Anal Chem, 2005, 77(15): 4936–4946
Boqué R, Ferré J, Faber NKM, Rius FX. Limit of detection estimator for second-order bilinear calibration. Anal Chim Acta, 2002, 451(2): 313–321
Lorber A. Error propagation and figures of merit for quantification by solving matrix equations. Anal Chem, 1986, 58(6): 1167–1172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wu, H., Wang, J. et al. Chemometrics-assisted excitation-emission fluorescence spectroscopy for simultaneous determination of ethoxyquin and tert-butylhydroquinone in biological fluid samples. Sci. China Chem. 56, 664–671 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4765-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4765-9