Abstract
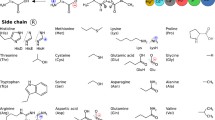
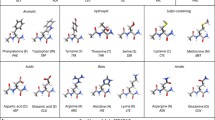
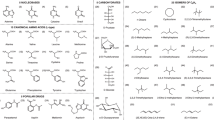
The binding energies of thirty-six hydrogen-bonded peptide-base complexes, including the peptide backbone-ase complexes and amino acid side chain-base complexes, are evaluated using the analytic potential energy function established in our lab recently and compared with those obtained from MP2, AMBER99, OPLSAA/L, and CHARMM27 calculations. The comparison indicates that the analytic potential energy function yields the binding energies for these complexes as reasonable as MP2 does, much better than the force fields do. The individual N-H…O=C, N-H…N, C-H…O=C, and C-H…N attractive interaction energies and C=O…O=C, N-H…H-N, C-H…H-N, and C-H…H-C repulsive interaction energies, which cannot be easily obtained from ab initio calculations, are calculated using the dipole-dipole interaction term of the analytic potential energy function. The individual N-H…O=C, C-H…O=C, C-H…N attractive interactions are about −5.3±1.8, −1.2±0.4, and −0.8 kcal/mol, respectively, the individual N-H…N could be as strong as aboutt -8.1 kcal/mol or as weak as −1.0 kcal/mol, while the individual C=O…O=C, N-H…H-N, C-H…H-N, and C-H…H-C repulsive interactions are about 1.8±1.1, 1.7±0.6, 0.6±0.3, and 0.35±0.15 kcal/mol. These data are helpful for the rational design of new strategies for molecular recognition or supramolecular assemblies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hobza P, Šponer J. Structure, energetics, and dynamics of the nucleic acid base pairs: Nonempirical ab initio calculations. Chem Rev, 1999, 99(11): 3247–3276
Šponer J, Leszczynski J, Hobza P. Electronic properties, hydrogen bonding, stacking, and cation binding of DNA and RNA bases. Biopolymers, 2002, 61(1): 3–31
Mohajeri A, Nobandegani FF. Detection and evaluation of hydrogen bond strength in nucleic acid base pairs. J Phys Chem A, 2008, 112(2): 281–295
DeChancie J, Houk KN. The origins of femtomolar protein-ligand binding: Hydrogen-bond cooperativity and desolvation energetics in the biotin-(strept)avidin binding site. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129(17): 5419–5429
Wieczorek R, Dannenberg JJ. H-bonding cooperativity and energetics of α-helix formation of five 17-amino acid peptides. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125(27): 8124–8129
Wieczorek R, Dannenberg JJ. Comparison of fully optimized α- and 310-helices with extended β-strands. An oniom density functional theory study. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(43): 14198–14205
Salvador P, Kobko N, Wieczorek R, Dannenberg JJ. Calculation trans-hydrogen-bond 13C-15N three-bond and other scalar J-couplings in cooperative peptide models. A density functional theory study. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(43): 14190–14197
Tong Y, Mei Y, Li YL, Ji CG, Zhang JZH. Electrostatic polarization makes a substantial contribution to the free energy of avidin-biotin binding. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132(14): 5137–5142
Lejeune D, Delsaux N, Charloteaux B, Thomas A, Brasseur R. Protein-nucleic acid recognition: statistical analysis of atomic interactions and influence of DNA structure. Prot Struct Funct Bioinfor, 2005, 61(2): 258–271
Seeman NC, Rosenberg JM, Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA, 1976, 73(3): 804–808
Cheng AC, Chen WW, Fuhrmann CN, Frankel AD. Recognition of nucleic acid bases and base-pairs by hydrogen bonding to amino acid side-chains. J Mol Biol, 2003, 327(4): 781–796
Cheng AC, Frankel AD. Ab initio interaction energies of hydrogen-bonded amino acid side chain-nucleic acid base interactions. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(2): 434–435
Jeong E, Kim H, Lee SW, Han K. Discovering the interaction propensities of amino acids and nucleotides from protein-RNA complexes. Mol Cells, 2003, 16(2): 161–167
Hunter KC, Millen AL, Wetmore SD. Effects of hydrogen-bonding and stacking interactions with amino acids on the acidity of uracil. J Phys Chem B, 2007, 111(7): 1858–1871
Dunning TH Jr. A road map for the calculation of molecular binding energies. J Phys Chem A, 2000, 104(40): 9062–9080
Šponer J, Jurečka P, Hobza P. Accurate interaction energies of hydrogen-bonded nucleic acid base pairs. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(32): 10142–10151
Dabkowska I, Jurečka P, Hobza P. On geometries of stacked and H-bonded nucleic acid base pairs determined at various DFT, MP2, and CCSD(T) levels up to the CCSD(T)/complete basis set limit level. J Chem Phys, 2005, 122(20): 204322
Riley KE, Pitoňák M, Černý J, Hobza P. On the structure and geometry of biomolecular binding motifs(hydrogen-bonding, stacking, X-H…π): WFT and DFT calculations. J Chem Theory Comput, 2010, 6(1): 66–80
Rejnek J, Hobza P. Hydrogen-bonded nucleic acid base pairs containing unusual base tautomers: complete basis set calculations at the MP2 and CCSD(T) levels. J Phys Chem B, 2007, 111(3): 641–645
Vargas R, Garza J, Friesner RA, Stern H, Hay BP, Dixon DA. Strength of the N-H…O=C and C-H…O=C bonds in formamide and N-methylacetamide dimmers. J Phys Chem A, 2001, 105(20): 4963–4968
Asensio A, Kobko N, Dannenberg JJ. Cooperative hydrogen-bonding in adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine base pairs. Density functional theory and møller-plesset molecular orbital study. J Phys Chem A, 2003, 107(33): 6441–6443
Scheiner S. Relative strengths of NH…O and CH…O hydrogen bonds between polypeptide chain segments. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109(33): 16132–16141
Scheiner S. Contributions of NH…O and CH…O hydrogen bonds to the stability of β-sheets in proteins. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 110(37): 18670–18679
Chin W, Piuzzi F, Dimicoli I, Mons M. Probing the competition between secondary structures and local preferences in gas phase isolated peptide backbones. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2006, 8(9): 1033–1048
Sun CL, Jiang XN, Wang CS. An analytic potential energy function for the amide-amide and amide-water intermolecular hydrogen bonds in peptides. J Comput Chem, 2009, 30(15): 2567–2575
Li Y, Jiang XN, Wang CS. Rapid evaluation of the binding energies in hydrogen-bonded amide-thymine and amide-uracil dimers in gas phase. J Comput Chem, 2011, 32(5): 953–966
Li Y, Wang CS. Rapid evaluation of the binding energies between peptide amide and DNA base. J Comput Chem, 2011, 32(13): 2765–2772
Wang CS, Sun CL. Investigation on the individual contributions of N-H…O=C and C-H…O=C interactions to the binding energies of β-sheet models. J Comput Chem, 2010, 31(5): 1036–1044
Jiang XN, Wang CS. Rapid prediction of the hydrogen bond cooperativity in N-methylacetamide chains. ChemPhysChem, 2009, 10(18): 3330–3336
Jiang XN, Sun CL, Wang CS. A scheme for rapid prediction of cooperativity in hydrogen bond chains of formamides, acetamides, and N-methylformamides. J Comput Chem, 2010, 31(7): 1410–1420
Boys SF, Bernardi F. The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol Phys, 1970, 19(4): 553–566
Simon S, Duran M, Dannenberg JJ. How does basis set superposition error change the potential surfaces for hydrogen-bonded dimers. J Chem Phys, 1996, 105(24): 11024–11031
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Montgomery JA. Jr., T. V, Kudin KN, Burant JC, Millam JM, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Barone V, Mennucci B, Cossi M, Scalmani G, Rega N, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Klene M, Li X, Knox JE, Hratchian HP, Cross JB, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Ayala PY, Morokuma K, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Zakrzewski VG, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Strain MC, Farkas O, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cui Q, Baboul AG, Clifford S, Cioslowski J, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Gonzalez C, Pople JA: Gaussian 03. Revision B. 02. Pittsburgh(PA): Gaussian, Inc. 2003
Cornell WD, Cieplak P, Bayly CI, Gould IR, Merz KM Jr, Ferguson DM, Spellmeyer DC, Fox T, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA. A second generation force field for the simulation of proteins, nucleic acids, and organic molecules. J Am Chem Soc, 1995, 117(19): 5179–5197
Kaminsky GA, Friesner RA, Tirado-Rives J, Jorgensen WL. Evaluation and reparametrization of the OPLS-AA field for proteins via comparison with accurate quantum chemical calculations on peptides. J Phys Chem B, 2001, 105(28): 6474–6487
MacKerell AD, Jr, Bashford D, Bellott M, Dunbrack RL Jr, Evanseck JD, Field MJ, Fischer S, Gao J, Guo H, Ha S, Joseph-McCarthy D, Kuchnir L, Kuczera K, Lau FTK, Mattos C, Michnick S, Ngo T, Nguyen DT, Prodhom B, Reiher WE, III, Roux B, Schlenkrich M, Smith JC, Stote R, Straub J, Watanabe M, Wiorkiewicz-Kuczera J, Yin D, Karplus M. All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J Phys Chem B, 1998, 102(18): 3586–3616
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Li, Y. & Wang, C. Rapid and accurate evaluation of the binding energies and the individual N-H···O=C, N-H···N, C-H···O=C, and C-H···N interaction energies for hydrogen-bonded peptide-base complexes. Sci. China Chem. 56, 238–248 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4715-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4715-6