Abstract
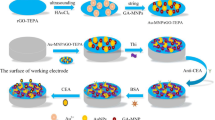
A sensitive electrochemical immunoassay system for the detection of a protein tumor biomarker through a dual amplified strategy was reported. Firstly, this protocol involves in the electropolymerization of o-aminobenzoic acid (o-ABA) on a glass carbon electrode (GCE). Subsequently, capture anti-CEA (Ab1) is covalently linked to poly(o-ABA) (PAB) film, via N-(3-dimethylamminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), and N-hydroxysulfosuccinimid sodium salt (NHS) activation of the carboxyl groups and surface blocking with ethanolamine. Later, the target, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), is sandwiched between an electrode surface confined Ab1 and the alkaline phosphatase-labeled signal anti-CEA antibodies conjugated with gold nanoparticles (Ab2-ALP-AuNP bioconjugates). The dual biocatalytic signal amplification for CEA monitoring is achieved by coupling the numerous enzymes loaded on the AuNPs with redox-recycling of the enzymatic products in the presence of the secondary enzyme and the corresponding substrate. The novel dramatic signal amplification strategy, exhibits a good linearity at the studied concentration range from 0.005 to 50 ng mL−1 towards CEA with a detection limit of 2 pg mL−1 (S/N=3). There is a 5–100-fold improvement in detection limit compared to other similar studies. The developed dual signal amplified strategy shows good selectivity, regeneration, stability and acceptable reproducibility. Therefore, the signal amplification approach holds great potential applications in detection of ultra-trace protein biomarkers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu J, Fu Z, Yan F, Ju H. Biomedical and clinical applications of immunoassays and immunosensors for tumor markers. Trends Anal Chem, 2007, 26(7): 679–688
Kawabata T, Watanabe M, Nakamura K, Satomura S. Liquid-phase binding assay of α-fetoprotein using DNA-coupled antibody and capillary chip electrophoresis. Anal Chem, 2005, 77(17): 5579–5582
Li X, Yang X, Zhang S. Electrochemical enzyme immunoassay using model labels. Trends Anal Chem, 2008, 27(6): 543–553
Aguilar Z, Vandaveer W, Fritsch I. Self-contained microelectrochemical immunoassay for small volumes using mouse IgG as a model system. Anal Chem, 2002, 74(14): 3321–3329
Xiang Y, Zhang Y, Chang Y, Chai Y, Wang J, Yuan R. Reversemicelle synthesis of electrochemically encoded quantum dot barcodes: application to electronic coding of a cancer marker. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(3): 1138–1141
Wang J, Liu G, Jan M. Ultrasensitive electrical biosensing of proteins and DNA: carbon-nanotube derived amplification of the recognition and transduction events. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(10): 3010–3011
Munge B, Liu G, Collins G, Wang J. Multiple enzyme layers on carbon nanotubes for electrochemical detection down to 80 DNA copies. Anal Chem, 2005, 77(14): 4662–4666
Yu X, Munge B, Patel V, Jensen G, Bhirde A, Sang J, Kim N, Gillespie J, Gutkind J, Papadimitrakopoulos F, Rusling J. Carbon nanotube amplification strategies for highly sensitive immunodetection of cancer biomarkers. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(34): 11199–11205
Tsai T, Heckert G, Neves L, Tan Y, Kao D, Harrison R, Resasco D, Schmidtke D. Adsorption of glucose oxidase onto single-walled carbon nanotubes and its application in layer-by-layer biosensors. Anal Chem, 2009, 81(19): 7917–7925
Lai G, Yan F, Ju H. Dual signal amplification of glucose oxidase-functionalized nanocomposites as a trace label for ultrasensitive simultaneous multiplexed electrochemical detection of tumor markers. Anal Chem, 2009, 81(23): 9730–9736
Malhotra R, Patel V, Vaque J, Gutkind J, Rusling J. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for oral cancer biomarker IL-6 using carbon nanotube forest electrodes and multilabel amplification. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(8): 3118–3123
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for clinical immunoassay using thionine-doped magnetic gold nanospheres as labels and horseradish peroxidase as enhancer. Anal Chem, 2008, 80(5): 1582–1588
Wang J, Liu G, Lin Y. Electroactive silica nanoparticles for biological labeling. Small, 2006, 2(10): 1134–1138
Zhong Z, Li M, Xiang D, Dai N, Qing Y, Wang D, Tang D. Signal amplification of electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of human serum IgG using double-codified nanosilica particles as labels. Biosens Bioelectron, 2009, 24(7): 2246–2249
Wang J, Li J, Baca A, Hu J, Zhou F, Yan W, Pang D. Amplified voltammetric detection of DNA hybridization via oxidation of ferrocene caps on gold nanoparticle/streptavidin conjugates. Anal Chem, 2003, 75(15): 3941–3945
Wang J. Nanomaterial-based amplified transduction of biomolecular interactions. Small, 2005, 1(11): 1036–1043
Qiu F, Jiang D, Ding Y, Zhu J, Huang L. Monolayer-barcoded nanoparticles for on-chip DNA hybridization assay. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47(27): 5009–5012
Yang X, Guo Y, Bi S, Zhang S. Ultrasensitive enhanced chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for the determination of α-fetoprotein amplified by double-codified gold nanoparticles labels. Biosens Bioelectron, 2009, 24(8): 2707–2711
Zhong Z, Wu W, Wang D, Wang D, Shan J, Qing Y, Zhang Z. Nanogold-enwrapped graphene nanocomposites as trace labels for sensitivity enhancement of electrochemical immunosensors in clinical immunoassays: carcinoembryonic antigen as a model. Biosens Bioelectron, 2010, 25(10): 2379–2383
Ho J, Chang H, Shih N, Wu L, Chang Y, Chen C, Chou C. Diagnostic detection of human lung cancer-associated antigen using a gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(14): 5944–5950
Ding C, Ge Y, Lin J. Aptamer based electrochemical assay for the determination of thrombin by using the amplification of the nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron, 2010, 25(6): 1290–1294
Ambrosi A, Castañeda M, Killard A, Alegret M, Merkoçi A. Double-codified gold nanolabels for enhanced immunoanalysis. Anal Chem, 2007, 79(14): 5232–5240
Bi S, Yan Y, Yang X, Zhang S. Gold nanolabels for new enhanced chemiluminescence immunoassay of alpha-fetoprotein based on magnetic beads. Chem Eur J, 2009, 15(18): 4704–4709
Xiang Y, Xie M, Bash R, Chen J, Wang J. Ultrasensitive label-free aptamer-based electronic detection. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2007, 46(47): 9054–9056
Cissell K, Rahimi Y, Shrestha S, Hunt E, Deo S. Bioluminescence-based detection of microRNA, miR21 in breast cancer cells. Anal Chem, 2008, 80(7): 2319–2325
Zhao W, Ali M, Brook M, Li Y. Rolling circle amplification: applications in nanotechnology and biodetection with functional nucleic acids. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47(34): 6330–6337
Ali M, Li Y. Colorimetric sensing by using allosteric-DNAzyme-coupled rolling circle amplification and a peptide nucleic acid-organic dye probe. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2009, 48(19): 3512–3515
Cheng W, Yan F, Ding L, Ju H, Yin Y. Cascade signal amplification strategy for subattomolar protein detection by rolling circle amplification and quantum dots tagging. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(8): 3337–3342
Ou L, Liu S, Chu X, Shen G, Yu R. DNA encapsulating liposome based rolling circle amplification immunoassay as a versatile platform for ultrasensitive detection of protein. Anal Chem, 2009, 81(23): 9664–9673
Kwon S, Yang H, Jo K, Kwak J. An electrochemical immunosensor using p-aminophenol redox cycling by NADH on a self-assembled monolayer and ferrocene-modified Au electrodes. Analyst, 2008, 133(11): 1599–1604
Campàs M, Iglesia P, Berre M, Kane M, Diogène J, Marty J. Enzymatic recycling-based amperometric immunosensor for the ultrasensitive detection of okadaic acid in shellfish. Biosens Bioelectron, 2008, 24(4): 716–722
Murielle R, Naïma D, Benoît L, Pierre B. Bienzymatic-based electrochemical DNA biosensors: a way to lower the detection limit of hybridization assays. Analyst, 2009, 134(2): 349–353
Xiang Y, Zhang Y, Qian X, Chai Y, Wang J, Yuan R. Ultrasensitive aptamer-based protein detection via a dual amplified biocatalytic strategy. Biosens Bioelectron, 2010, 25(11): 2539–2542
Li Q, Tang D, Tang J, Su B, Huang J, Chen G. Carbon nanotube-based symbiotic coaxial nanocables with nanosilica and nanogold particles as labels for electrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen in biological fluids. Talanta, 2011, 84(2): 538–546
Wu W, Yi P, He P, Jing T, Liao K, Yang K, Wang H. Nanosilverdoped DNA polyion complex membrane for electrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen using nanogold-labeled secondary antibodies. Anal Chim Acta, 2010, 673(2): 126–132
Song Z, Yuan R, Chai Y, Jiang W, Su H, Che X, Ran X. Simultaneous immobilization of glucose oxidase on the surface and cavity of hollow gold nanospheres as labels for highly sensitive electrochemical immunoassay of tumor marker. Biosens Bioelectron, 2011, 26(5): 2776–2780
Grabar K, Freeman R, Hommer M, Natan M. Preparation and characterization of Au colloid monolayers. Anal Chem, 1995, 67(4): 735–743
Ambrosi A, Castaňeda M, Killard A, Smyth M, Alegret S, Merkoci A. Double-codified gold nanolabels for enhanced immunoanalysis. Anal Chem, 2007, 79(14): 5232–5240
Qian J, Zhang C, Cao X, Liu S. Versatile immunosensor using a quantum dot coated silica nanosphere as a label for signal amplification. Anal Chem, 2010, 82(15): 6422–6429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xiang, Y., Chai, Y. et al. Gold nanolabels and enzymatic recycling dual amplification-based electrochemical immunosensor for the highly sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Sci. China Chem. 54, 1770–1776 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-011-4373-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-011-4373-0