Abstract
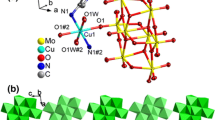
Two new compounds with microporous Co3[MnMo9O32]·15H2O (1) and Cu3[MnMo9O32]·15H2O (2) have been synthesized, and characterized by IR, element analysis, TG and single-crystal X-ray analysis. The structure analyses reveal that compounds 1 and 2 are isostructural. In crystal, the Waugh-type polyoxoanions [MnMo9O32]6− are connected by Co2+ or Cu2+ cations to a 3D open-framework, which possesses channels along the [1 2 2] direction of approximately 8.27 × 11.97 Å. The photocatalytic performances of compounds 1 and 2 for photodegradation of RhB with UV irradiation have been studied, which show a good photocatalytic activity for photodegradation of RhB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheetham AK, Férey G, Loiseau T. Open-framework inorganic materials. Angew Chem Int Ed, 1999, 38: 3268–3292
Cejka J, Beekkum H van, Corma A, Schuth F. Introduction to zeolite science and practice 3 Revised edition, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2007
Themed issue: Metal-organic frameworks, Chem Soc Rev, 2009, 38: 1201–1508
Yaghi OM, O’Keeffe M, Ockwig NW, Chae HK, Eddaoudi M, Kim J. Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature, 2003, 423: 705–714
Férey G, Mellot-Draznieks C, Serre C, Millange F. Crystallized frameworks with giant pores: Are there limits to the possible? Acc Chem Res, 2005, 38: 217–225
Zhang YB, Zhang WX, Feng FY, Zhang JP, Chen XM. A highly connected porous coordination polymer with unusual channel structure and sorption properties. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2009, 48: 5287–5290
Pope MT. Heteropoly and Isopoly Oxometalates, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1983
Long DL, Burkholder E, Cronin L. Polyoxometalate clusters, nanostructures and materials: From self assembly to designer materials and devices. Chem Soc Rev, 2007, 36: 105–121
Kortz U, Müller A, Slageren J van, Schnacke J, Dalal NS, Dressel M. Polyoxometalates: Fascinating structures, unique magnetic properties. Coord Chem Rev, 2009, 253: 2315–2327
Sadakane M, Steckhan E. Electrochemical properties of polyoxometalates as electrocatalysts. Chem Rev, 1998, 98: 219–238
Mizuno N, Misono N. Heterogeneous catalysis. Chem Rev, 1998, 98: 199–218
Sun CY, Liu SX, Liang DD, Shao KZ, Ren YH, Su ZM. Highly stable crystalline catalysts based on a microporous metal-organic framework and polyoxometalates. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 1883–1888
Ma FJ, Liu SX, Sun CY, Liang DD, Ren GJ, Wei F, Chen YG, Su ZM. A sodalite-type porous metal-organic framework with poluoxometalate templates: Adsorption and decomposition of dimethyl methylphosphonate. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 4178–4181
Rodriguez-Albelo LM, Ruiz-Salvador AR, Sampieri A, Lewis D W, Gómez A, Nohra B, Mialane P, Marrot J, Sécheresse F, Mellot-Draznieks C, Biboum RN, Keita B, Nadjo L, Dolbecq A. Zeolitic polyoxometalate-based metal-organic frameworks (Z-POMOFs): Computational evaluation of hypothetical polymorphs and the successful targeted synthesis of the redox-active Z-POMOF1. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 16078–16087
Albelo LMR, Rui-Salvador AR, Lewis DW, Gómez A, Mialane P, Marrot J, Dolbecq A, Sampieri A, Mellot-Draznieks C. Zeolitic polyoxometalates metal organic frameworks (Z-POMOF) with imidazole ligands and ɛ-Keggin ions as building blocks; computational evaluation of hypothetical polymorphs and a synthesis approach. PhysChemChemPhys, 2010, 12: 8632–8639
Weakley TJR, The crystal structure of potassium nonamolybdomanganate( IV) hexahydrate, K6[MnMo9O32]·6H2O. J Less-Common Met, 1977, 54: 289–296
Sheldrick GM. SHELXL97, Program for Crystal Structure Refinement, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 1997; Sheldrick GM, SHELXS97, Program for Crystal Structure Solution, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 1997
Sheldrick GM. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst Sect A, 2008, 64: 112–122
Hall RD. Combinations of the sesquioxides with the acid molybdates. J Am Chem Soc, 1907, 29: 692–714
Waugh JLT, Shoemaker DP, Pauling L. On the structure of the heteropoly anion in ammonium 9-molybdomanganate, (NH4)6MnMo9O32·8H2O. Acta Crystallogr, 1954, 7: 438–441
Weinstock IA. Homogeneous-phase electron-transfer reactions of polyoxometalates. Chem Rev, 1998, 98: 113–170
Hiskia A, Mylonas A, Papaconstantinou E. Comparison of the photoredox properties of polyoxometallates and semiconducting particles. Chem Soc Rev, 2001, 30: 62–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, H., Chen, W., Liu, D. et al. Two new compounds with microporous constructed by Waugh-type polyoxoanion and transition metal ions. Sci. China Chem. 54, 1418–1422 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-011-4340-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-011-4340-9