Abstract
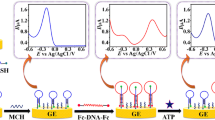
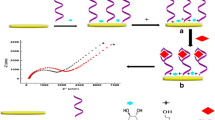
A convenient aptamer-based competitive electrochemical biosensor for a small biomolecule, adenosine, was described. The sensing surface was fabricated by self-assembly of an aptamer/mercaptohexanol monolayer on a gold disk electrode. The principle of this aptasensor is based on the competition between an adenosine target molecule and a ferrocene-conjugated signaling DNA strand for the aptamer binding site on the sensing surface. Due to the competitive nature of this assay, the electrochemical responses of the surface captured ferrocene are inversely proportional to log[adenosine] in the range from 0.05 to 3.2 μM, with a detection limit of 25 nM. Moreover, the aptasensor also shows high selectivity for adenosine. The proposed aptasensor thus holds great potential for the detection of other small biomolecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerman K, Nagatani N, Chikae M, Yuhi T, Takamura Y, Tamiya E. Label-free electrochemical immunoassay for the detection of human chorionic gonadotropin hormone. Anal Chem, 2006, 78(15): 5612–5616
Shankaran D, Gobi K, Miura N. Recent advancements in surface plasmon resonance immunosensors for detection of small molecules of biomedical, food and environmental interest. Sens Actuators B, 2007, 121(1): 158–177
Zayats M, Huang Y, Gill R, Ma C, Willner I. Label-free and reagentless aptamer-based sensors for small molecules. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(42): 13666–13667
Baker B, Lai R, Wood M, Doctor E, Heeger A, Plaxco K. An electronic, aptamer-based small-molecule sensor for the rapid, label-free detection of cocaine in adulterated samples and biological fluids. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(10): 3138–3139
Nutiu R, Li Y. In vitro selection of structure-switching signaling aptamers. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2005, 44(7): 1061–1065
Liu J, Lu Y. Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protocols, 2006, 1(1): 246–252
Liu J, Mazumdar D, Lu Y. A simple and sensitive dipstick test in serum based on lateral flow separation of aptamer-linked nanostructures. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 45(47): 7955–7959
Wu Z, Guo M, Zhang S, Chen C, Jiang J, Shen G, Yu R. Reusable electrochemical sensing platform for highly sensitive detection of small molecules based on structure-switching signaling aptamers. Anal Chem, 2007, 79(7): 2933–2939
Nutiu R, Li Y. Structure-switching signaling aptamers: Transducing molecular recognition into fluorescence signaling. Chem Eur J, 2004, 10(8): 1868–1876
Rupcich N, Chiuman W, Nutiu R, Mei S, Flora K, Li Y, Brennan J. Quenching of fluorophore-labeled DNA oligonucleotides by divalent metal ions: Implications for selection, design, and applications of signaling aptamers and signaling deoxyribozymes. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(3): 780–790
Shen L, Chen Z, Li Y, Jing P, Xie S, He S, He P, Shao Y. A chronocoulometric aptamer sensor for adenosine monophosphate. Chem Commun, 2007, 21: 2169–2171
Chen Z, Li G, Zhang L, Jiang J, Li Z, Peng Z, Deng L. A new method for the detection of ATP using a quantum-dot-tagged aptamer. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2008, 392(6): 1185–1188
Yao W, Wang L, Wang H, Zhang X, Li L. An aptamer-based electrochemiluminescent biosensor for ATP detection. Bisens Bioelectron, 2009, 24(11): 3269–3274
Feng K, Sun C, Kang Y, Chen J, Jiang J, Shen G, Yu R. Label-free electrochemical detection of nanomolar adenosine based on target-induced aptamer displacement. Electrochem Commun, 2008, 10(4): 531–535
Han K, Chen L, Lin Z, Li G. Target induced dissociation (TID) strategy for the development of electrochemical aptamer-based biosensor. Electrochem Commun, 2009, 11(1): 157–160
Zhou X, Song S, Zhang J, Pan D, Wang L, Fan C. A targetresponsive electrochemical aptamer switch (TREAS) for reagentless detection of nanomolar ATP. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129(5): 1042–1043
Lai R, Plaxco K, Heeger A. Aptamer-based electrochemical detection of picomolar platelet-derived growth factor directly in blood serum. Anal Chem, 2007, 79(1): 229–233
Xiao Y, Piorek B, Plaxco K, Heeger A. A reagentless signal-on architecture for electronic, aptamer-based sensors via target-induced strand displacement. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127(51): 17990–17991
Levicky R, Herne T, Tarlov M, Satija S. Using self-assembly to control the structure of DNA monolayers on gold: a neutron reflectivity study. J Am Chem Soc, 1998, 120(38): 9787–9792
Herne T, Tarlov M. Characterization of DNA probes immobilized on gold surfaces. J Am Chem Soc, 1997, 119(38): 8916–8920
Southern E, Mir K, Shchepinov M. Molecular interactions on microarrays. Nat Genet, 1999, 21: 5–9
Steel A, Herne T, Tarlov M. Electrochemical quantitation of DNA immobilized on gold. Anal Chem, 1998, 70(22): 4670–4677
Liu Z, Yuan R, Chai Y, Zhuo Y, Hong C, Yang X, Su H, Qian X. Highly sensitive, reusable electrochemical aptasensor for adenosine. Electrochim Acta, 2009, 54(26): 6207–6211
Wang J, Wang F, Dong S. Methylene blue as an indicator for sensitive electrochemical detection of adenosine based on aptamer switch. J Electroanal Chem, 2009, 626(1): 1–5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xiang, Y., Chai, Y. et al. Aptamer-based competitive electrochemical assay of small biomolecules. Sci. China Chem. 54, 822–826 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4129-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4129-2