Abstract
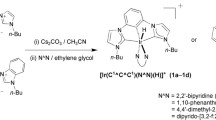
Four luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) dipyridoquinoxaline complexes appended with an indole moiety [Ir(N∧C)2(N∧N)] (PF6) (HN∧C = 2-phenylpyridine, Hppy; N∧N = 2-(N-(2-(indole-3-acetamido)ethyl)aminocarbonyl)dipyrido[3,2-f:2′,3′-h]quinoxaline, dpqC2indole (1a), N∧N = 2-(N-(6-(indole-3-acetamido)hexyl)aminocarbonyl)dipyrido[3,2-f:2′,3′-h]quinoxaline, dpqC6indole (1b); HN∧C = 7,8-benzoquinoline, Hbzq, N∧N = dpqC2indole (2a), N∧N = dpqC6indole (2b)) have been synthesized and characterized. Upon irradiation, all the complexes displayed moderately intense and long-lived luminescence under ambient conditions and in 77 K glass. On the basis of the photophysical data, the emission of the complexes has been assigned to an excited state of triplet metal-to-ligand charge-transfer (3MLCT) ((dπ(Ir) → π*(N∧N)) character. Cyclic voltammetric studies revealed indole-based and iridium-based oxidations at ca. +1.10 V and +1.24 V vs. SCE, respectively, and ligand-based reductions at ca. −1.07 to −2.29 V vs. SCE. The interactions of the complexes with an indole-binding protein, bovine serum albumin (BSA), have been examined by emission titrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishida T, Hamada M, Inoue M, Wakahara A. Crystal and molecular- structure of 6-hydroxymelatonin, a final metabolite of tryptophan. Chem Pharm Bull, 1990, 38: 851–855
Hirata F, Hayaishi O. New degradative routes of 5-hydroxytryptophan and serotonin by intestinal tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1972, 47: 1112–1129
Hirata F, Hayaishi O, Tokuyama T, Senoh S. In-vitro and in-vivo formation of 2 new metabolites of melatonin. J Biol Chem, 1974, 249: 1311–1313
Ljung K, Hull AK, Kowalczyk M, Marchant A, Celenza J, Cohen JD, Sandberg G. Biosynthesis, conjugation, catabolism and homeostasis of indole-3-acetic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol, 2002, 50: 309–332
Niwa T, Ise M, Mitazaki T. Progression of glomerular sclerosis in experimental uremic rats by administration of indole, a precursor of indoxyl sulfate. Am J Nephrol, 1994, 14: 207–212
Bartel B. Auxin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol, 1997, 48: 49–64
Dolušić E, Kowalczyk M, Magnus V, Sandberg G, Normanly J. Biotinylated indoles as probes for indole-binding proteins. Bioconjugate Chem, 2001, 12: 152–162
Lo KKW, Tsang KHK, Hui WK, Zhu N. Luminescent rhenium(I) diimine indole conjugates — photophysical, electrochemical and protein- binding properties. Chem Commun, 2003: 2704-2705
Lo KKW, Tsang KHK, Hui WK, Zhu N. Synthesis, characterization, crystal structure, and electrochemical, photophysical, and protein-binding properties of luminescent rhenium(I) diimine indole complexes. Inorg Chem, 2005, 44: 6100–6110
Lo KKW, Sze KS, Tsang KHK, Zhu N. Luminescent tricarbonylrhenium(I) dipyridoquinoxaline indole complexes as sensitive probes for indole-binding proteins. Organometallics, 2007, 26: 3440–3447
Lo KKW, Lee TKM, Zhang KY. Luminescent probes for indole-binding proteins derived from ruthenium(II) polypyridine complexes. Inorg Chim Acta, 2006, 359: 1845–1854
Lau JSY, Lee PK, Tsang KHK, Ng CHC, Lam YW, Cheng SH, Lo KKW. Luminescent cyclometallated iridium(III) polypyridine indole complexes — synthesis, photophysics, electrochemistry, protein-binding properties, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake. Inorg Chem, 2009, 48: 708–719
Sprouse S, King KA, Spellane PJ, Watts RJ. Photophysical effects of metal-carbon sigma-bonds in ortho-metalated complexes of Ir(III) and Rh(III). J Am Chem Soc, 1984, 106: 6647–6653
King KA, Spellane PJ, Watts RJ. Excited-state properties of a triply ortho-metalated iridium(III) complex. J Am Chem Soc, 1985, 107: 1431–1432
Didier P, Ortmans I, Kirsch-De Mesmaeker A, Watts RJ. Electrochemistry and absorption and emission-spectroscopy of new ortho-metalated complexes of Rh(III) and Ir(III) with the ligands 1,4,5,8-tetraazaphenanthrene and 1,4,5,8,9,12-hexaazatriphenylene. Inorg Chem, 1993, 32: 5239–5245
Tamayo AB, Alleyne BD, Djurovich PI, Lamansky S, Tsyba I, Ho NN, Bau R, Thompson ME. Synthesis and characterization of facial and meridional tris-cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125: 7377–7387
Neve F, Crispini A, Campagna S, Serroni S. Synthesis, structure, photophysical properties, and redox behavior of cyclometalated complexes of iridium(III) with functionalized 2,2′-bipyridines. Inorg Chem, 1999, 338: 2250–2258
Neve F, La Deda M, Crispini A, Bellusci A, Puntoriero F, Campagna S. Cationic cyclometalated iridium luminophores: photophysical, redox, and structural characterization. Organometallics, 2004, 23: 5856–5863
Collin JP, Dixon IM, Sauvage JP, Williams JAG, Barigelletti F, Flamigni L. Synthesis and photophysical properties of iridium(III) bisterpyridine and its homologues: a family of complexes with a long-lived excited state. J Am Chem Soc, 1999, 121: 5009–5016
Wilkinson AJ, Puschmann H, Howard JAK, Foster CE, Williams JAG. Luminescent complexes of iridium(III) containing N∧C∧N-coordinating terdentate ligands. Inorg Chem, 2006, 45: 8685–8699
Avilov I, Minoofar P, Cornil J, De Cola L. Influence of substituents on the energy and nature of the lowest excited states of heteroleptic phosphorescent Ir(III) complexes: A joint theoretical and experimen tal study. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129: 8247–8258
Obara S, Itabashi M, Okuda F, Tamaki S, Tanabe Y, Ishii Y, Nozaki K, Haga M. Highly phosphorescent iridium complexes containing both tridentate bis(benzimidazolyl)-benzene or -pyridine and bidentate phenylpyridine: Synthesis, photophysical properties, and theoretical study of Ir-bis(benzimidazolyl) benzene complex. Inorg Chem, 2006, 45: 8907–8921
Polson M, Fracasso S, Bertolasi V, Ravaglia M, Scandola F. Iridium cyclometalated complexes with axial symmetry. Synthesis and photophysical properties of a trans-biscyclometalated complex containing the terdentate ligand 2,6-diphenylpyridine. Inorg Chem, 2004, 43: 1950–1956
Zhao Q, Li L, Li F, Yu M, Liu Z, Yi T, Huang C. Aggregation-induced phosphorescent emission (AIPE) of iridium(III) complexes. Chem Commun, 2008: 685–687
Lo KKW, Ng DCM, Chung CK. First examples of luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes as labeling reagents for biological substrates. Organometallics, 2001, 20: 4999–5001
Lo KKW, Chung CK, Ng DCM, Zhu N. Syntheses, characterisation and photophysical studies of novel biological labelling reagents derived from luminescent iridium(III) terpyridine complexes. New J Chem, 2002, 26: 81–88
Lo KKW, Chung CK, Lee TKM, Lui LH, Tsang KHK, Zhu N. New luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) diimine complexes as biological labeling reagents. Inorg Chem, 2003, 42: 6886–6897
Lo KKW, Chan JSW, Lui LH, Chung CK. Novel luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) diimine complexes that contain a biotin moiety. Organometallics, 2004, 23: 3108–3116
Lo KKW, Li CK, Lau JSY. Luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) arylbenzothiazole biotin complexes. Organometallics, 2005, 24: 4594–4601
Lo KKW, Chung CK, Zhu N. Synthesis, photophysical and electrochemical properties, and biological labeling studies of cyclometalated iridium(III) bis(pyridylbenzaldehyde) complexes: novel luminescent cross-linkers for biomolecules. Chem Eur J, 2003, 9: 475–483
Lo KKW, Chung CK, Zhu N. Nucleic acid intercalators and avidin probes derived from luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III)-dipyridoquinoxaline and -dipyridophenazine complexes. Chem Eur J, 2006, 12: 1500–1512
Lo KKW, Zhang KY, Chung CK, Kwok KY. Synthesis, photophysical and electrochemical properties, and protein-binding studies of luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) bipyridine estradiol conjugates. Chem Eur J, 2007, 13: 7110–7130
Lo KKW, Zhang KY, Leung SK, Tang MC. Exploitation of the dual-emissive properties of cyclometalated iridium(III)-polypyridine complexes in the development of luminescent biological probes. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47: 2213–2216
Lo KKW, Lau JSY. Cyclometalated iridium(III) diimine bis(biotin) complexes as the first luminescent biotin-based cross-linkers for avidin. Inorg Chem, 2007, 46: 700–709
Zhang KY, Lo KKW. Synthesis, properties, and live-cell imaging studies of luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) polypyridine complexes containing two or three biotin pendants. Inorg Chem, 2009, 48: 6011–6025
Lo KKW, Lee PK, Lau JSY. Synthesis, characterization, and properties of luminescent organoiridium(III) polypyridine complexes appended with an alkyl chain and their interactions with lipid bilayers, surfactants, and living cells. Organometallics, 2008, 27: 2998–3006
O’Donoghue KA, Kelly JM, Kruger PE. Unusual photophysical switching in a Ru(II) diimine DNA probe caused by amide functionalisation. Dalton Trans, 2004: 13–15
Pfeiffer MJ, Hanna SB. Aminolysis of activated esters of indole-3-acetic acid in acetonitrile. J Org Chem, 1993, 58: 735–740
Demas JN, Crosby GA. Measurement of photoluminescence quantum yields — review. J Phys Chem, 1971, 75: 991–1024
Nakamaru K. Synthesis, luminescence quantum yields, and lifetimes of trischelated ruthenium(II) mixed-ligand complexes including 3,3′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridyl. Bull Chem Soc Jpn, 1982, 55: 2697–2705
Carter DC, Ho JX. Structure of serum-albumin. Adv Protein Chem, 1994, 45: 153–203
Okabe N, Adachi K. Binding characteristics of tryptophan-metabolites to bovine serum-albumin. Chem Pharm Bull, 1992, 40: 499–500
Lo KKW, Hui WK, Chung CK, Tsang KHK, Lee TKM, Li CK, Lau JS Y, Ng DCM. Luminescent transition metal complex biotin conjugates. Coord Chem Rev, 2006, 250: 1724–1736
Lo KKW. Luminescent transition metal complexes as biological labels and probes. Struc Bonding, 2007, 123: 205–245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, K.KW., Leung, A.HH. Luminescent cyclometalated iridium(III) dipyridoquinoxaline indole complexes as biological probes. Sci. China Chem. 53, 2091–2098 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4120-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4120-y