Abstract
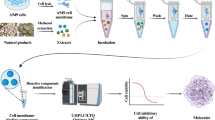
The intracellular kinase domains of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in some tumor cells are significant targets for drug discovery. We have developed a new EGFR cell membrane chromatography (EGFR/CMC)-online-high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (HPLC/MS) method for screening anti-EGFR antagonists from medicinal herbs such as Radix Angelicae Pubescentis. In this study, the HEK293 EGFR cells with high expression of EGFR were used to prepare cell membrane stationary phase (CMSP) in the EGFR/CMC model. The retention fractions on the EGFR/CMC model were directly analyzed by combining a 10 port columns switcher with a HPLC/MS system online. As a result, osthole from Radix Angelicae Pubescentis was found to be the active component acting on EGFR like dasatinib as the control drug. There was a good relationship between their inhibiting effects on EGFR secretion and HEK293 EGFR cell growth in vitro. This new EGFR/CMConline-HPLC/MS method can be applied for screening anti-EGFR antagonists from TCMs, for instance, Radix Angelicae Pubescentis. It will be a useful method for drug discovery with natural medicinal herbs as a leading compound resource.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sugawa N, Ekstrand AJ, James CD, Collins VP. Identical splicing of aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor transcripts from amplified rearranged genes in human glioblastomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1990, 87: 8602–8606
Richard J, Sainsbury C, Needham GK, Farndon JR, Malcolm AJ, Harris AL. Epidermal-growth-factor receptor status as predictor of early recurrence of and death from breast cancer. Lancet, 1987, 329: 1398–1402
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med, 2004, 350: 2129–2139
Radinsky R, Risin S, Fan D, Dong ZY, Bielenberg D, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ. Level and function of epidermal growth factor receptor predict the metastatic potential of human colon carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res, 1995, 1: 19–31
Eales-Reynolds LJ, Laver H, Mojtahedi H. Evidence for the expression of the EGFReceptor on human monocytic cells. Cytokine, 2001, 5: 169–172
Kris MK, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H, Sandler A, Albain KS, Cella D, Wolf MK, Averbuch SD, Ochs JJ, Kay AC. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Am Med Assoc, 2003, 290: 2149–2158
Carmeliet P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nature Medicine, 2000, 6: 389–395
Stamos J, Sliwkowski MX, Eigenbrot C. Structure of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain alone and in complex with a 4-anilinoquinazoline inhibitor. J Biol Chem, 2002, 227: 46265–46272
Ciardiello F, Tortora G. A novel approach in the treatment of cancer: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res, 2001, 7: 2958–2970
Yang XD, Jia XC, Corvalan JRF, Wang P, Davis CG. Development of ABX-EGF, a fully human anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody, for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2001, 38: 17–23
Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, Ashton SE, Curry BJ, Barker AJ, Gibson KH. ZD1839 (Iressa): An orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res, 2002, 62: 5749–5754
Ullrich A, Coussens L, Hayflick JS, Dull TJ, Gray A, Tam AW, Lee J, Yarden Y, Libermann TA, Schlessinger J, Downward J, Mayes ELV, Whittle N, Waterfield MD, Seeburg PH. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Nature, 309: 418–425
Webb SED, Roberts SK, Needham SR, Tynan CJ, Rolfe DJ, Winn MD, Clarke DT, Barraclough R, Martin-Fernandez ML. Single-molecule imaging and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy show different structures for high- and low-affinity epidermal growth factor receptors in A431 cells. Biophysical J, 2008, 94: 803
Schreiber SL. Target-oriented and diversity-oriented organic synthesis in drug discovery. Science, 2000, 287: 1964–1969
Drews J. Drug discovery: a historical perspective. Science, 2000, 287: 1960–1964
Kingsmore SF, Lindquist IE, Mudge J, Gessler DD, Beavis WD. Genome-wide association studies: progress and potential for drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2008, 7: 221–230
Araujo RP, Liotta LA, Petricoin EF. Proteins, drug targets and the mechanisms they control: the simple truth about complex networks. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2007, 6: 871–880
He LC, Geng XD. Determination of ligustilide in rat blood and tissues by capillary gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. New Prog Biomed Chromatogr, 1996, 3, 8–9
He LC, Yang GD, Geng XD. Enzymatic activity and chromatographic characteristics of the cell membrane immobilized on silica surface. Chin Sci Bull, 1999, 44: 826–831
He LC, Wang SC, Geng XD. Coating and fusing cell membranes onto a silica surface and their chromatographic characteristics. Chromatographia, 2001, 54: 71–76
Hou XF, Zhou MZ, Jiang Q, Wang SC, He LC. A vascular smooth muscle/cell membrane chromatography-offline-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry method for recognition, separation and identification of active components from traditional Chinese medicines. J Chromatogr A, 2009, 1216(42): 7081–7087
Yuan BX, Hou J, Yang GD, Zhao LM, He LC. Comparison of Determination of drug-muscarinic receptor affinity by cell-membrane chromatography and by radioligand-binding assay with the cerebrum membrane of the rat. Chromatographia, 2005, 61: 381–384
Wang Y, Yuan BX, Deng XL, He LC, Zhang YY, Han QD. The preparation of HEK293 α1A or HEK293 α1B cell membrane stationary phase and the chromatographic affinity study of ligands of α1 adrenoceptor. Anal Biochem, 2005, 339: 198–205
Wang Y, Yuan BX, Deng XL, He LC, Wang SC, Zhang YY, Han QD. Comparison of alpha1-adrenergic receptor cell-membrane stationary phases prepared from expressed cell line and from rabbit hepatocytes. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2006, 386: 2003–2011
Zeng AG, Yuan BX, Wang CH, Yang GD, He LC. Frontal analysis of cell-membrane chromatography for determination of drug-alpha(1D) adrenergic receptor affinity. J Chromatogr B, 2009, 877(20–21): 1833–1837
Zeng AG, Yuan BX, Zhu F, Zhao LM, He LC. Cell membrane chromatography correlated with functional assay for ligand-beta-adrenergic receptor affinities. Chromatographia, 2009, 69(11–12): 1373–1377
Wang CH, He LC, Wang N, Yang GD, He LC. Screening anti-inflammatory components from Chinese traditional medicines using a peritoneal macrophage/cell membrane chromatography-offline-GC/MS method. J Chromatogr B, 2009, 877(27): 3019–3024
Wang L, Ren J, Sun M, Wang SC. A combined cell membrane chromatography and online HPLC/MS method for screening compounds from Radix Caulophylli acting on the human α1A-adrenoceptor. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2010, 51: 1302–1306
Wang SC, Wen BY, Wang L, Liu JT, He LC. Fluorenone alkaloid from Caulophyllum robustum Maxim with anti-myocardial ischemia activity. Arch Pharmacal Res, 2009, 32: 521–526
Li CQ, He LC. Establishment of the model of white blood cell membrane chromatography and screening of antagonizing TLR4 receptor component from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. Sci China Ser C-Bio, 2006, 49(2): 182–189
Li YP, He LC. Establishment of the model of vascular endothelial cell membrane chromatography and its preliminary application. Chin Sci Bull, 2007, 52: 922–928
Li CQ, He LC, Dong HY, Jin JQ. Screening for the anti-inflammatory activity of fractions and compounds from Atractylodes macrocephala koidz. J Ethnopharmacol, 2007, 114: 212–217
Liang MJ, He LC, Yang GD. Screening, analysis and in vitro vasodilatation of effective components from Ligusticum Chuanxiong. Life Sci, 2005, 78: 128–133
He LC, Luo WJ, Li X, Xu XM, Wang SC, Ge XW, Li C. A wild-type EGFR expression of recombinant HEK293 cells. Chinese Patent, 200910022565.9
Situ ZQ, Wu JZ. Cell Culture. Xi’an World Publishing Corporation. Xi’an, 2004, 241–250
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods, 1983, 65: 55–63
Shimamura M, Hazato T, Ashino H, Yamamoto Y, Iwasaki E, Tobe H, Yamamoto K, Yamamoto S. Inhibition of angiogenesis by humulone, a bitter acid from beer hop. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2001, 289: 220–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Sun, M., Zhang, Y. et al. EGFR/cell membrane chromatography-online-high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry method for screening EGFR antagonists from Radix Angelicae Pubescentis . Sci. China Chem. 53, 2357–2362 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4010-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-4010-3