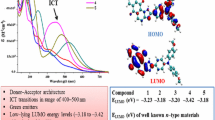
Abstract
Triarylboron compounds are significant optoelectronic materials due to their excellent emissive and electron-transport properties, and could be applied in organic light-emitting diodes as emissive and/or electron-transport layers. Triarylboron compounds have vacant pπ orbital and have received increasing interest as fluoride ion and cyanide ion sensors utilizing specific Lewis acid-base interaction. This review summarizes their structural characteristics, optical properties and applications in chemosensors for anions and optoelectronic devices developed in recent years and discusses the problems and prospects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Entwistle CD, Marder TB. Applications of three-coordinate organoboron compounds and polymers in optoelectronics. Chem Mater, 2004, 16(23): 4574–4585
Zhao Q, Zhang H Y, Wakamiya A, Yamaguchi S. Coordination-induced intramolecular double cyclization: synthesis of boron-bridged dipyridylvinylenes and dithiazolylvinylenes. Synthesis, 2009, 1: 127–132
Elbing M, Bazan GC. A new design strategy for organic optoelectronic materials by lateral boryl substitution. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47(5): 834–838
Matsumi N, Chujo Y. π-Conjugated organoboron polymers via the vacant p-orbital of the boron atom. Polymer J, 2008, 40(2): 77–89
Hudson ZM, Wang S. Impact of donor-acceptor geometry and metal chelation on photophysical properties and applications of triarylboranes. Acc Chem Res, 2009, 42(10): 1584–1596
Cui Y, Li FH, Lu ZH, Wang S. Three-coordinate organoboron with a B=N bond: substituent effects, luminescence/electroluminescence and reactions with fluoride. Dalton Trans, 2007, 25: 2634–264
Lee MH, Agou T, Kobayashi J, Kawashima T, Gabbai FP. Fluoride ion complexation by a cationic borane in aqueous solution. Chem Commun, 2007, 11: 1133–1135
Sun Y, Ross N, Zhao SB, Huszarik K, Jia WL, Wang RY, Macartney D, Wang S. Enhancing electron accepting ability of triarylboron via pi-conjugation with 2,2′-bipy and metal chelation: 5,5′-bis(BMes(2))-2,2′-bipy and its metal complexes. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129(24): 7510–7512
Martinez-Manez R, Sancenon F. Fluorogenic and chromogenic chemosensors and reagents for anions. Chem Rev, 2003, 103(11): 4419–4476
Gale PA. Structural and molecular recognition studies with acyclic anion receptors. Acc Chem Res, 2006, 39(7): 465–475
Jia W L, Feng X D, Bai D R, Lu Z H, Wang S, Vamvounis G. MeS2B(p-4,4′-biphenyl-NPh(1-naphthyl)): A multifunctional molecule for electroluminescent devices. Chem Mater, 2005, 17(1): 164–170
Mazzeo M, Vitale V, Della SF, Anni M, Barbarella G, Favaretto L, Sotgiu G, Cingolani R, Gigli G. Bright white organic light-emitting devices from a single active molecular material. Adv Mater, 2005, 17(1): 34–39
Lin S L, Chan LH, Lee RH, Yen MY, Kuo WJ, Chen CT, Jeng RJ. Highly efficient carbazole-π-dimesitylborane bipolar fluorophores for nondoped blue organic light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater, 2008, 20(20): 3947–3952
Jia WL, Bai DR, Mccormick T, Liu QD, Motala M, Wang RY, Seward C, Tao Y, Wang SM. Three-coordinate organoboron compounds BAr2R (Ar = mesityl, R = 7-azaindolyl- or 2,2′-dipyridylaminofunctionalized aryl or thienyl) for electroluminescent devices and supramolecular assembly. Chem Eur J, 2004, 10(4): 994–1006
Noda T, Shirota Y. 5,5′-Bis(dimesitylboryl)-2,2′-bithiophene and 5,5″-bis(dimesitylboryl)-2,2′:5′,2″-terthiophene as a novel family of electron-transporting amorphous molecular materials. J Am Chem Soc, 1998, 120(37): 9714–9715
Liu ZQ, Fang Q, Wang D, Cao DX, Xue G, Yu WT, Lei H. Trivalent boron as an acceptor in donor-acceptor-type compounds for single- and two-photon excited fluorescence. Chem Eur J, 2003, 9(20): 5074–5084
Liu ZQ, Fang Q, Wang D, Xue G, Yu WT, Shao ZS, Jiang MH. Trivalent boron as acceptor in D-π-A chromophores: Synthesis, structure and fluorescence following single- and two-photon excitation. Chem Commun, 2002, 23: 2900–2901
Doty JC, Babb B, Grisdale PJ, Glogowski M, Williams JLR. J Organomet Chem 1972, 38: 229–236
Zhao CH, Wakamiya A, Inukai Y, Yamaguchi S. Highly emissive organic solids containing 2,5-diboryl-1,4-phenylene unit. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(50): 15934–15935
Wakamiya A, Mori K, Yamaguchi S. 3-Boryl-2,2′-bithiophene as a versatile core skeleton for full-color highly emissive organic solids. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2007, 46(23): 4273–4276
Zhao CH, Wakamiya A, Yamaguchi S. Highly emissive poly(aryleneethynylene) s containing 2,5-diboryl-1,4-phenylene as a building unit. Macromolecules, 2007, 40(11): 3898–3900
Reitzenstein D, Lambert C. Localized versus backbone fluorescence in N-p-(diarylboryl)phenyl-substituted 2,7-and 3,6-linked polycarbazoles. Macromolecules, 2009, 42(3): 773–782
Liu C, Zhou ZG, Gao Y, Yang H, Li BG, Li FY, Huang CH. Fluorescence turn-on chemosensor for Hg2+ based on a rhodamine derivative and its application in bioimaging. Sci China Ser B-Chem, 2009, 52(6): 760–764
Tang L, Jin JK, Zhang S, Mao Y, Sun JZ, Yuan WZ, Zhao H, Xu HP, Qin AJ, Tang BZ. Detection of the critical micelle concentration of cationic and anionic surfactants based on aggregation-induced emission property of hexaphenylsilole derivatives. Sci China Ser B-Chem, 2009, 52(6): 755–759
Riggs BL. Bone and Mineral Research. The Netherlands: Elsevier, 1984. 366–367
Wiseman A, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1970. 48–52
Kirk KL. Biochemistry of the Halogens and Inorganic Halides. New York: Plenum Press, 1991. 58–59
Zhou G, Baumgarten M, Mullen K. Mesitylboron-substituted ladder-type pentaphenylenes: Charge-transfer, electronic communication, and sensing properties. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130(37): 12477–12484
Liu XY, Bai DR, Wang S. Charge-transfer emission in nonplanar three-coordinate organoboron compounds for fluorescent sensing of fluoride. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 45(33): 5475–5478
Bai DR, Liu XY, Wang S. Charge-transfer emission involving three-coordinate organoboron: V-shape versus U-shape and impact of the spacer on dual emission and fluorescent sensing. Chem Eur J, 2007, 13(20): 5713–5723
Cao DX, Liu ZQ, Zhang GH, Li GZ. The synthesis, photophysical properties and fluoride anion recognition of a novel branched organoboron compound. Dyes Pigments, 2009, 81(3): 193–196
Liu ZQ, Shi M, Li FY, Fang Q, Chen ZH, Yi T, Huang CH. Highly selective two-photon chemosensors for fluoride derived from organic boranes. Org Lett, 2005, 7(24): 5481–5484
Arnendola V, Bonizzoni M, Estebangomez D, Fabbrizzi L, Licchelli M, Sancenon F, Taglietti A. Some guidelines for the design of anion receptors. Coord Chem Rev, 2006, 250(11–12): 1451–1470
Sole S, Gabbai FP. A bidentate borane as colorimetric fluoride ion sensor. Chem Commun, 2004, 11: 1284–1285
Melaimi M, Gabbai FP. A heteronuclear bidentate Lewis acid as a phosphorescent fluoride sensor. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127(27): 9680–9681
Dorsey CL, Jewula P, Hudnall TW, Hoefelmeyer JD, Taylor TJ, Honesty NR, Chiu CW, Schulte M, Gabbai FP. Fluoride ion complexation by a B2/Hg heteronuclear tridentate lewis acid. Dalton Trans, 2008, 4442–4450
Chiu CW, Gabbai FP. Fluoride ion capture from water with a cationic borane. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(44): 14248–14249
Lee MH, Gabbai FP. Synthesis and properties of a cationic bidentate lewis acid. Inorg Chem, 2007, 46(20): 8132–8138
Hudnall TW, Gabbai FP. Ammonium boranes for the selective complexation of cyanide or fluoride ions in water. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129(39): 11978–11986
Hudnall TW, Kim YM, Bebbington MW, Bourissou D, Gabbai FP. Fluoride ion chelation by a bidentate phosphonium/borane Lewis acid. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130(33): 10890–10891
Kim Y, Gabbai FP. Cationic boranes for the complexation of fluoride ions in water below the 4 ppm maximum contaminant level. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131(9): 3363–3369
Zhao SB, Mccormick T, Wang S. Ambient-temperature metal-to-ligand charge-transfer phosphorescence facilitated by triarylboron: Bnpa and its metal complexes. Inorg Chem, 2007, 46(26): 10965–10967
Sun Y, Wang S. Conjugated Triarylboryl donor-acceptor systems supported by 2,2′-bipyridine: metal chelation impact on intraligand charger transfer emission, electron accepting ability, and “turn-on” fluoride sensing. Inorg Chem, 2009, 48(8): 3755–3767
Hudson ZM, Zhao SB, Wang RY, Wang S. Switchable Ambienttemperature singlet-triplet dual emission in nonconjugated donor-acceptor triarylboron-Pt-II complexes. Chem Eur J, 2009, 15(25): 6131–6137
Chou PT, Chi Y. Phosphorescent dyes for organic light-emitting diodes. Chem Eur J, 2007, 13(2): 380–395
Grushin V V. Mixed phosphine-phosphine oxide ligands. Chem Rev, 2004, 104(3): 1629–1662
Zhao Q, Li L, Li F Y, Yu M X, Liu Z P, Yi T, Huang C H. Aggregation-induced phosphorescent emission (AIPE) of iridium(III) complexes. Chem Commun, 2008, 6: 685–687
Zhao Q, Li FY, Liu SJ, Yu MX, Liu ZQ, Yi T, Huang CH. Highly selective phosphorescent chemosensor for fluoride based on an iridium( III) complex containing arylborane units. Inorg Chem, 2008, 47(20): 9256–9264
Xu WJ, Liu SJ, Zhao XY, Sun S, Cheng S, Ma TC, Sun HB, Zhao Q, Huang W. Novel cationic iridium(III) complex containing both triarylboron and carbazole moieties as ratiometric fluoride probe utilizing the switchable triplet-singlet emission. Chem Eur J, in press
You YM, Park SY. A phosphorescent Ir(III) complex for selective fluoride ion sensing with a high signal-to-noise ratio. Adv Mater, 2008, 20(20): 3820–3826
Lam ST, Zhu NA, Yam VW. Synthesis and characterization of luminescent rhenium(I) tricarbonyl diimine complexes with a triarylboron moiety and the study of their fluoride ion-binding properties. Inorg Chem, 2009, 48(20): 9664–9670
Lou XD, Li Z, Qin JG. DDTC-Na-based colorimetric chemosensor for the sensing of cyanide in water. Sci China Ser B-Chem, 2009, 52(6): 802–808
Huh JO, Do Y, Lee MH. A BODIPY borane dyad for the selective complexation of cyanide ion. Organometallics. 2007, 27(6): 1022–1025
Chiu CW, Kim Y, Gabbai FP. Lewis acidity enhancement of triarylboranes via peripheral decoration with cationic groups. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131(1): 60–61
Kim Y, Zhao H, Gabbai FP. Sulfonium boranes for the selective capture of cyanide ions in water. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2009, 48(27): 4957–4960
Wade CR, Gabbai FP. Cyanide anion binding by a triarylborane at the outer rim of a cyclometalated ruthenium(II) cationic complex. Inorg Chem, 2010, 49(2): 714–720
Yamaguchi S, Akiyama S, Tamao K. Tri-9-anthrylborane and its derivatives: New boron-containing pi-electron systems with divergently extended pi-conjugation through boron. J Am Chem Soc, 2000, 122(26): 6335–6336
Yasuhiko S, Motoi K, Tetsuya N, Kenji O, Takahiro O. A novel class of emitting amorphous molecular materials as bipolar radical formants: 2-“4-[bis(4-methylphenyl)amino]phenyl”-5-(dimesitylboryl) thiophene and 2-(4-[bis(9,9-dimethylfluorenyl)amino]phenyl)-5-(dimesityl-borly)thiophene. J Am Chem Soc, 2000, 122(44): 11021–11022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mou, X., Liu, S., Dai, C. et al. A class of fascinating optoelectronic materials: Triarylboron compounds. Sci. China Chem. 53, 1235–1245 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-3190-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-3190-1