Abstract
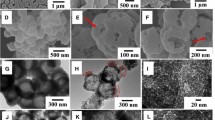
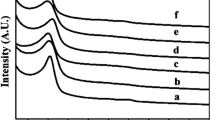
MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanospheres (MSN) have been prepared using n-cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as a soft template. The pseudo-moire’ rotational pattern inside the MSN results in many interior defects. Hollow mesoporous silica (HMS) spheres were synthesized by solvent extraction of the template from MSN. The morphology and structure of MSN and HMS were studied by TEM, XRD and nitrogen sorption techniques. A model drug, bromocresol green dye, was packed inside different regions of HMS through impregnation at different pressures and temperatures, and the drug release performance of the resulting materials was compared. The results showed that vacuum evaporation of solvents may enhance the controlled release properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kresge CT, Leonowicz ME, Roth WJ. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature, 1992, 359: 710–712
Clemens Z, Liang YC, Willy N, Anwander R. A general strategy for the rational design of size-selective mesoporous catalysts. Chem Eur J, 2007, 13: 3169–3176
Kanatzidis MG. Beyond silica: nonoxidic mesostructured materials. Adv Mater, 2007, 19: 1165–1181
Rivera-Jiménez SM, Hernández-Maldonado AJ. Nickel(II) grafted MCM-41: A novel sorbent for the removal of naproxen from water. Micropor Mesopor Mater, 2008, 116: 246–252
Zhu YF, Shi JL, Shen WH, Dong XP, Feng JW, Ruan ML, Li YS. Stimuli-responsive controlled drug release from a hollow mesoporous silica sphere/polyelectrolyte multilayer core-shell structure. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2005, 44: 5083–5087
Balas F, Manzano M, Horcajada P, Vallet-RegĽ M. Confinement and controlled release of bisphosphonates on ordered mesoporous silica-based materials. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 8116–8117.
Slowing I, Trewyn BG, Lin SY. Effect of surface functionalization of MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the endocytosis by human cancer cells. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 14792–14793
Qu FY, Zhu GS, Huang SY, Li SG, Qiu SL. Effective controlled release of captopril by silylation of mesoporous MCM-41. ChemPhys Chem, 2006, 7: 400–406
Trewyn BG, Whitman CM, Lin SY. Morphological control of roomtemperature ionic liquid templated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled release of antibacterial agents. Nano Lett, 2004, 4: 2139–2143
Möller K, Kobler J, Bein T. Colloidal suspensions of nanometersized mesoporous silica. Adv Funct Mater, 2007, 17: 605–612
Che SA, Garcia BEA, Toshiyuki Y. A novel anionic surfactant templating route for synthesizing mesoporous silica with unique structure. Nat Mater, 2003, 2: 801–805
Juan FD, Hitzky R. Selective functionalization of mesoporous silica. Adv Mater, 2000, 12: 430–432
Dai S, Burleigh MC, Shin YS, Morrow CC, Barnes CE, Xue Z. Imprint coating: A novel synthesis of selective functionalized ordered mesoporous sorbents. Angew Chem Int Ed, 1999, 38: 1235–1239
Feng X, Fryxell GE, Wang LQ, Kim AY, Liu J, Kimner KM. Functionalized monolayers on ordered mesoporous supports. Science, 1997, 276: 923–926
Hijn WMV, Vos DED, Sels BF, Bossaert WD. Sulfonic acid functionalised ordered mesoporous materials as catalysts for condensation and esterification reactions. Chem Commun, 1998, 317–318
Hoffmann F, Cornelius M, Morell J, Fröba M. Silica-based mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2006, 45: 3216–3251
Yang Q, Wang S, Fan P, Wang LF, Di Y, Lin KF, Xiao FS. pH-Responsive carrier system based on carboxylic acid modified mesoporous silica and polyelectrolyte for drug delivery. Chem Mater, 2005, 7: 5999–6003
Qu FY, Zhu GS, Lin HM, Sun JY, Zhang DL, Li SG, Qiu SL. Drug self-templated synthesis of ibuprofen/mesoporous silica for sustained release. Eur J Inorg Chem, 2006, 19: 3943–3947
Lai CY, Trewyn BG, Jeftinija DM, Jeftinija K, Xu S, Jeftinija S, Lin SY. A mesoporous silica nanosphere-based carrier system with chemically removable CdS nanoparticle caps for stimuli-responsive controlled release of neurotransmitters and drug molecules. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 25: 4451–4459
Giri S, Trewyn BG, Stellmaker MP, Lin SY. Stimuli-responsive controlled-release delivery system based on mesoporous silica nanorods capped with magnetic nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2005, 44: 5038–5044
Horcajada P, Rámila A, Pérez-Pariente J, Vallet-Regí M. Influence of pore size of MCM-41 matrices on drug delivery rate. Micropor Mesopor Mater, 2004, 68: 105–109
Zhu YF, Shi JL, Chen HR, Shen WH, Dong XP. A facile method to synthesize novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and advanced storage property. Micropor Mesopor Mater, 2005, 84: 218–222
Du L, Song HY, Yang X, Liao SJ, Petrik L. A novel hollow sphere mesoporous material synthesized by using DADD template and embedding Nd into framework simultaneously. Micropor Mesopor Mater, 2008, 113: 261–267
Zhang FQ, Yan Y, Meng Y, Xia YL, Tu B, Zhao DY. Ordered bimodal mesoporous silica with tunable pore structure and morphology. Micropor Mesopor Mater, 2007, 98: 6–15
Zhang Q, Zhang TR, Ge JP, Yin YD. Permeable silica shell through surface-protected etching. Nano Lett, 2008, 8: 2867–2871
Zhang TR, Ge JP, Hu YX. Zhang Q, Aloni S, Yin Y D. Formation of hollow silica colloids through a spontaneous dissolution-regrowth process. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2008, 47: 5806–5811
Park SJ, Kim YJ, Park SJ. Size-dependent shape evolution of silica nanoparticles into hollow structures. Langmuir, 2008, 24: 12134–12137
Glarneau A, Iapichella J, Bonhomme K, Renzo FD, Kooyman P, Terasaki O, Fajula F. Controlling the morphology of mesostructured silicas by pseudomorphic transformation: a route towards applications. Adv Funct Mater, 2006, 16: 1657–1667
Wu S, Ju HX, Liu Y. Conductive mesocellular silica-carbon nanocomposite foams for immobilization, direct electrochemistry, and biosensing of proteins. Adv Funct Mater, 2007, 17: 585–592
State Pharmacopoeia Commission. People’s Republic of China Pharmacopoeia. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000. Appendix 203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Wang, X., Tao, L. et al. Fabrication and sustained release properties of porous hollow silica nanoparticles. Sci. China Chem. 53, 556–561 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0192-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0192-y