Abstract
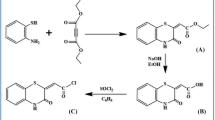
A novel calix[4]arene derivative with pyrene fluorophores at the upper rim and tetraester ionophores at the lower rim was synthesized in six steps, and its structure was proved by NMR and ESI-MS spectroscopies. Furthermore, the chemosensing behavior of the host compound for alkali and alkaline earth metal ions was investigated by fluorescence spectroscopy. The obtained results show that the calixarene host can selectively bind sodium ion with the complexation stability constant of 2190 mol−1·L. The complexation with sodium ion can pronouncedly induce the excimer emission to decrease and the monomer emission to increase, whereas the addition of the other alkali and alkaline earth metal ions does not cause appreciable changes in the fluorescence spectrum of the host compound. The present calix[4]arene derivative displays potential application as fluorescent chemosensor for sodium ion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valeur B, Leray I. Design principles of fluorescent molecular sensors for cation recognition. Coord Chem Rev, 2000, 205: 3–40
He H R, Mortellaro M A, Leiner M J P, Young S T, Fraatz R J, Tusa J K. A fluorescent chemosensor for sodium based on photoinduced electron transfer. Anal Chem, 2003, 75(3): 549–555
Bruno A E, Barnard S, Rouilly M, Waldner A, Berger J, Ehrat M. All-solid-state miniaturized fluorescence sensor array for the determination of critical gases and electrolytes in blood. Anal Chem, 1997, 69(3): 507–513
Witulski B, Weber M, Bergstrasser U, Desvergne J P, Bassani D M, Bouas-Laurent H. Novel alkali cation chemosensors based on N-9-anthrylaza-crown ethers. Org Lett, 2001, 3(10): 1467–1470
Gunnlaugsson T, Nieuwenhuyzen M, Richard L, Thoss V. Novel sodium-selective fluorescent PET and optically based chemosensors: Towards Na+ determination in serum. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 2, 2002: 141–150
Ji Y, Zhang R, Li Y J, Li Y Z, Zuo J L, You X Z. Syntheses, structures, and electrochemical properties of platinum(II) complexes containing di-tert-butylbipyridine and crown ether annlated dithiolate ligands. Inorg Chem, 2006, 46(3), 866–876
Dubach J M, Harjes D I, Clark H A. Fluorescent ion-selective nanosensors for intracellular analysis with improved lifetime and size. Nano Lett, 2007, 7(6), 1827–1831
Xu C, Wygladacz K, Retter R, Bell M, Bakker E. Multiplexed flow cytometric sensing of blood electrolytes in physiological samples using fluorescent bulk optode microspheres. Anal Chem, 2007, 79(24), 9505–9512
Böhmer V. Calixarenes, macrocycles with (almost) unlimited possibilities. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 1995, 34(7): 713–745
Aoki I, Kawabata H, Nakashima K, Shinka S. Fluorescence calix[4]arene which responds to solvent polarity and metal ions. Chem Commun, 1991: 1771–1773
Aoki I, Sakaki T, Shinka S. A new metal sensory system based on intramolecular fluorescence quenching on the ionphoric calix[4] arene ring. Chem Commun, 1992: 730–732
Jin T, Lchikawa K, Koyama T. A fluorescent calix[4]arene as an intramolecular excimer-forming Na+ sensor in nonaqueous solution. Chem Commun, 1992: 499–501
Jin T. A new Na+ sensor based on intramolecular fluorescence energy transfer derived from calix[4]arene. Chem Commun, 1999: 2491–2492
Leray I, O’Reilly F, Habib Jiwan J L, Soumillion J P, Valeur B. A new calix[4]arene-based fluorescent sensor for sodium ion. Chem Commun, 1999: 795–796
Leray I, Lefevre J P, Delouis J F, Delaire J, Valeur B. Synthesis and photophysical and cation-binding properties of mono- and tetranaphthylcalix[4]arenes as highly sensitive and selective fluorecent sensors for sodium. Chem Eur J, 2001, 7(21): 4590–4598
van der Veen N J, Flink S, Deij M A, Egberink R J M, van Veggel F C J M, Reinhoudt D N. Monolayer of a Na+-selective fluoroionophore on glass: Connecting the fields of monolayers and optical detection of metal ions. J Am Chem Soc, 2000, 122(25): 6112–6113
Kim J S, Quan D T. Calixarene-derived fluorescent probes. Chem Rev, 2007, 107(9): 3780–3799
Schazmann B, Alhashimy N, Diamond D. Chloride selective calix[4]arene optical sensor combining urea functionality with pyrene excimer transduction. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(26): 8607–8614
Diamond D, Mckervey M A. Calix[4]arene-based sensing agents. Chem Soc Rev, 1996, 25(1), 15–24
Gutsche C D, Lin L G. Calixarene 12: The synthesis of functionalized calixarene. Tetrahedron, 1986, 42(6): 1633–1640
Rudkevich D M, Verboom W, Reinhoudt D N. Calix[4]arene salenes: A bifunctional receptor for NaH2PO3. J Org Chem, 1994, 59(13): 3683–3686
Arduini A, Fabbi M, Mantovani M, Mirone L, Pochini A, Secchi A, Ungaro R. Calix[4]arenes blocked in a rigid cone conformation by selective functionalization at the lower rim. J Org Chem, 1995, 60(5): 1454–1457
Segura M, Bricoli B, Casnati A, Munoz E M, Sansone F, Ungaro R, Vicent C. A prototype calix[4]arene-based receptor for carbohydrate recognition containing peptide and phosphate binding groups. J Org Chem, 2003, 68(16): 6296–6303
Inoue Y, Yamamoto K, Wada T, Everitt S, Gao X M, Hou Z J, Tong L H, Jiang S K, Wu H M. Inclusion complexation of (cyclo)alkanes and (cyclo)alkanols with 6-O-modified cyclodextrins. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 2, 1998: 1807–181
Ikeda A, Shinkai S. Novel cavity design using calix[n]arene skeleTons: Toward molecular recognition and metal binding. Chem Rev, 1997, 97(5): 1713–1734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 20421202, 20673061 & 20703025) and the 111 Project (Grant No. B06005)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Guo, D., Jiang, B. et al. Highly selective fluorescent chemosensor for Na+ based on pyrene-modified calix[4]arene derivative. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 52, 513–517 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0011-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0011-5