Abstract
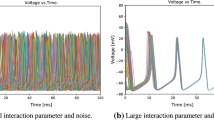
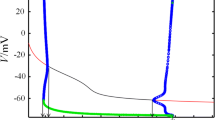
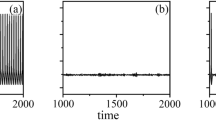
Based on the coupled stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley neurons, we numerically studied the effect of gating currents of ion channels, as well as coupling and the number of neurons, on the collective spiking rate and regularity in the coupled system. It was found, for a given coupling strength and with a relatively large number of neurons, when gating currents are applied, the collective spiking regularity decreases; meanwhile, the collective spiking rate increases, indicating that gating currents can aggravate the desynchronization of the spikings of all neurons. However, gating currents caused hardly any effect in the spiking of any individual neuron of the coupled system. This result, different from the reduction of the spiking rate by gating currents in a single neuron, provides a new insight into the effect of gating currents on the global information processing and signal transduction in real neural systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol, 1952, 117: 500–544
White J A, Rubinstein J T, Kay A R. Channel noise in neurons. Trends Neurosci, 2000, 23: 131–137
Koch K. Biophysics of Computation: Informational Processing in Single Neurons. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999
van Rossum M C W, O’Brien B J, Smith R G. Effects of noise on the spike timing precision of retinal ganglion cells. J Neurophys, 2003, 89: 2406–2419
Skaugen E, Walløe L. Firing behavior in a stochastic nerve membrane model based upon the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Acta Physiol Scand, 1979, 107: 343–363
Clay J R, DeFelice L J. Relationship between membrane excitability and single channel open-close kinetics. Biophys J 1983, 42: 151–157
Strassberg A F, DeFelice L J. Limitations of the Hodgkin-Huxley formalism — effects of single-channel kinetics on trans-membrane voltage dynamics. Neural Comput, 1993, 5: 843–855
DeFelice L J, Isaac A. Chaotic states in a random world — relationship between the nonlinear differential equations of excitability and the stochastic properties of ion channels. J Stat Phys, 1993, 70: 339–354
Fox R F, Lu Y. Emergent collective behavior in large numbers of globally coupled independently stochastic ion channels. Phys Rev E, 1994, 49: 3421–3431
Chow C C, White J A. Spontaneous action potentials due to channel fluctuations. Biophys J, 1996, 71: 3013–3021
Schneidman E, Freedman B, Segev I. Ion channel stochasticity may be critical in determining the reliability and precision of spike timing. Neuronal Comput, 1998, 10: 1679–1694
Bezrukov S M, Vodyanoy I. Noise-induced enhancement of signal- transduction across voltage-dependent ion channels. Nature, 1995, 378: 362–364
Bezrukov S M, Vodyanoy I. Signal transduction across alamethicin ion channels in the presence of noise. Biophys J, 1997, 73: 2456–2464
Schmid G, Goychuk I, Hänggi P. Stochastic resonance as a collective property of ion channel assemblies. Europhys Lett, 2001, 56: 22–28
Jung P, Shuai J W. Optimal sizes of ion channel clusters. Europhys Lett, 2001, 56: 29–35
Gammaitoni L, Hänggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F. Stochastic resonance. Rev Mod Phys, 1998, 70: 223–287
Hänggi P. Stochastic resonance in biology— how noise can enhance detection of weak signals and help improve biological information processing. Chem Phys Chem, 2002, 3: 285–290
Shuai J W, Jung P. Optimal ion channel clustering for intracellular calcium signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2003, 100: 506–510
Ginzburg S L, Pustovoit M A. Bursting dynamics of a model neuron induced by intrinsic channel noise. Fluct Noise Lett, 2003, 3: L265–L274
Schmid G, Goychuk I, Hänggi P, Zeng S, Jung P. Stochastic resonance and optimal clustering for assemblies of ion channels. Fluct Noise Lett, 2004, 4: L33–L42
Gong Y B, Wang M S, Hou Z H, Xin H W. Optimal spike coherence and synchronization on complex Hodgkin-Huxley neuron networks. ChemPhysChem, 2005, 6: 1042–1047
Shuai J W, Jung P. The dynamics of small excitable ion channel clusters. Chaos, 2006, 16: 026104
Li Y P, Li Q S. Implicit and explicit internal signal stochastic resonance in calcium ion oscillations. Chem Phys Lett, 2006, 417: 498–502
Schmid G, Goychuk I, Hänggi P. Channel noise and synchronization in excitable membranes. Physica A, 2003, 325: 165–175.
Wang M S, Hou Z H, Xin H W. Double-system-size resonance for spiking activity of coupled Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. ChemPhys Chem, 2004, 5: 1602–1605
Schmid G, Goychuk I, Hänggi P. Capacitance fluctuations causing channel noise reduction in stochastic Hodgkin-Huxley systems. Phys Bio, 2006, 3: 248–254
Pouget A, Zemel R S, Dayan P. Information processing with population codes. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2000, 1: 125–132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Science Foundation of Ludong University (Grant Nos. 23140301, L20072805)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Y., Xie, Y., Xu, B. et al. Effect of gating currents of ion channels on the collective spiking activity of coupled Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 52, 20–25 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0160-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0160-y