Abstract
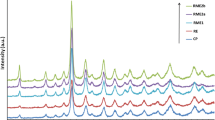
The aim of this study is to synthesize the catalysts of Fe- and Mn-substituted hexaaluminate by reverse microemulsion medium for methane catalytic combustion application. Pseudo-ternary phase diagrams in quaternary microemulsion systems of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), n-butanol, n-octane, and water [or Al(NO3)3 solution] were presented. The effects of the alcohol chain length, ratio of sur-factant to cosurfactant, and salt concentration on the formation and stability of microemulsion systems were studied. The phase behavior of microemulsion systems was confirmed through the varying of the conductivity with the water content. The performance and structure of the catalysts, La(Mn x /Fe x )Al12−x − O19-δ synthesized with the optimal parameter in the phase diagrams of microemulsions systems were characterized by BET, TG-DTA, and XRD. The micro fix-bed reactor was used to measure the catalytic activities of catalysts to methane combustion. The results showed that this synthesis method could yield non-agglomerated and highly dispersed precursors that would undergo crystallization at the lower temperature of 950°C. When temperature was raised up to 1050°C, the complete crystalline La-hexaaluminate was shaped. The hexaaluminate substituted with Fe had high-catalytic activity and stability at high temperature, while the Mn-substituted had higher catalytic activity at lower temperature. When the cooperation of Fe and Mn occurred, i.e., LaFeMnAl10O19−δ exhibited a high surface area and catalytic activity to CH4 combustion, the CH4 light-off temperature was only 475°C and the complete combustion temperature was 660°C. This was attributed to the synergistic effect between Fe and Mn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johansson E M, Danielsson K M J, Pocoroba E, Haralson E D, Jaras S G. Catalytic combustion of gasified biomass over hexaaluminate catalysts: Influence of palladium loading and ageing. Appl Catal A, 1999, 182: 199–208
Thevenin P O, Ersson A G, Kusar H M J, Menon P G, Jaras S G. Deactivation of high temperature combustion catalysts. Appl Catal A, 2001, 212(1/2): 189–197
Groppi G, Cristiani C, Forzatti P. Preparation, characterisation and catalytic activity of pure and substituted La-hexaaluminate systems for high temperature catalytic combustion. Appl Catal B, 2001, 35(2): 137–148
Wang L L, Jia G W, Xu Y S. Preparation of nanosized SiO2 particles in a reverse microemulsion system (in Chinese). Chin J Inorg Chem, 2005, 21(10): 1055–1059
Ye F M, He W D, Wang Y M, Li L F, Liu Q F, Zhang X J. Preparation of P(BMA-co-NVP) nanoparticles by interfacial-initiating microe-mulsion polymerization (in Chinese). J Func Polym, 2004, 17(3): 87–91
Vishal C, Pushan A, Chattopadhyay S, Maitra A N. Preparation of acicular λ-Fe2O3 particles from a microemulsion-mediated reaction. Mater Lett, 1996, 26(1): 21–26
Zarur A J, Ying J Y. Reverse microemulsion synthesis of nanostruc-tured complex oxides for catalytic combustion. Nature, 2000, 403: 65–67
Zarur A J, Hwu H H, Ying J Y. Reverse microemulsion-mediated synthesis and structural evolution of barium hexaaluminate nanoparticles. Langmuir, 2000, (16): 3042–3049
Watt S L, Tunaley D, Biggs S. The formation of water-in-oil microemulsions using a concentrated saline aqueous phase. Coll Surf A, 1998, 137(1–3): 25–33
Cui Z G, Yin F S. Microemulsion Technique and Application (in Chinese). Beijing: Publishing Company of Chinese Light Industry, 2001. 191–198
Cui Z G, Yin F S. Microemulsion Technique and Application (in Chinese). Beijing: Publishing Company of Chinese Light Industry, 2001. 179–182
Lam A C, Schechter R S. A study of diffusion and electrical conduction in microemulsions. Coll Interf Sci, 1987, 120(1): 42–45
Lam A C, Schechter R S. The theory of diffusion in microemulsion. Coll Interf Sci, 1987, 120(1): 56–63
Borkovec M, Eicke H F. Surfactant monolayer rigidities from Kerr effect measurements on microemulsions. Chem Phys Lett, 1989, 157(5): 457–461
Fletcher P D I, Robinson B H. Dynamic processes in water in oil microemulsion. Phys Chem J, 1981, 85: 863
Lada A, Lang L, Zana R. Relation between electric percolation and rate constant for exchange of material between droplets in water in oil microemulsions. Phys Chem J, 1989, 93: 10
Quintela M A L, Rivas J. Chemical reactions in microemulsions: A powerful method to obtain ultrafine particles. Coll Interf Sci, 1993, 158: 446–451
Naoufal D, Millet J M, Garbowski E, Brulle Y, Primet M. Synthesis, structure and catalytic properties of Fe-substituted barium hexaalu-mintes. Catal Lett, 1998, (54): 141–148
Bellotto M, Artioli G, Cristiani G C, Forzatti P, Groppi G. On the crystal structure and cation valence of Mn in Mn-substituted Ba-β-Al2O3. J Catal, 1998(179): 597–605
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20706004) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 2062017 and 8072018)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, S., Wang, L., Shi, B. et al. Synthesis of hexaaluminate catalysts for methane combustion by reverse microemulsion medium. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 52, 31–38 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0039-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0039-y