Abstract
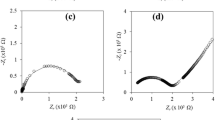
Dielectric monitoring of the adsorption or release process of salicylic acid (SA) by chitosan membrane shows that the dielectric spectra of the chitosan membrane/ SA solution systems change regularly in the adsorption or release process. By analyzing the regularity, a new mechanism for the relaxations is proposed. The concentration polarization layer (CPL) caused by SA adsorption or release is confirmed to be essential for the dielectric relaxations. The changes of the spectra with time are explained by account of the relationship between CPL properties and dielectric strength. Based on this relaxation mechanism, a theoretical method can be established to calculate dynamical parameters of inner structure of the adsorption or release systems from their dielectric spectra. Therefore, dielectric spectroscopy is demonstrated to be a promising method for estimating interfacial distribution of ionic substances and their binding to membrane in a non-invasive way.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernkop-Schnürch A. Chitosan and its derivatives: Potential excipients for peroral peptide delivery systems. Int J Pharm 2000, 194: 1–13
Bhattarai N, Ramay H R, Gunn J, Matsen F A, Zhang M. PEG-grafted chitosan as an injectable thermosensitive hydrogel for sustained protein release. J Contr Rel, 2005, 103: 609–624
Chen X G, Zheng L, Wang Z, Lee C Y, Park H J. Molecular affinity and permeability of different molecular weight chitosan membranes. J Agr Food, 2002, 50(21): 5915–5918
Mi F L, Sung H W, Shyu S S. Release of indomethacin from a novel chitosan microsphere prepared by a naturally occurring crosslinker: Examination of crosslinking and polycation-anionic drug interaction. J Appl Poly, 2001, 81: 1700–1711
Calvo P, Remuñan-López C, Vila-Jato J L, Alonso M J. Chitosan and chitosan/ethylene oxide block copolymer nanoparticles as novel carriers for proteins and vaccines. Pharm Res, 1997, 14: 1431–1436
Gupta K C, Kumar M N V. pH dependent hydrolysis and drug release behavior of chitosan/poly(ethylene glycol) polymer network microspheres. J Mat S M M, 2001, 12: 753–759
Zhao K S, Li Y H. Dielectric characterization of a nanofiltration membrane in electrolyte solutions: Its double-layer structure and ion permeation. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 110(6): 2755–2763
Li Y H, Zhao K S. Dielectric analysis of nanofiltration membrane in electrolyte solutions: Influences of electrolyte concentration and species on membrane permeation. J Col I Sc, 2004, 276: 68–76
Li Y H, Zhao K S, Song C. Salicylic acid adsorption and release on chitosan membrane: Real-time dielectric spectroscopy study. Acta Chim S (in Chinese), 2004, 62(16): 1495–1502
Benavente J, Vázquez M I. Effect of age and chemical treatments on characteristic parameters for active and porous sublayers of polymeric composite membranes. J Coll I Sc, 2004, 273: 547–555
Srikhirin T, Schuele D E, Mann J A, Lando J B. Application of dielectric relaxation spectroscopy to ultrathin Langmuir-Blodgett films. Macromol, 2000, 33(7): 2584–2594
Hianik T, Fajkus M, Tarus B, Frangopol P T, Markin V S, Landers D F. The electrostriction, surface potential and capacitance relaxation of bilayer lipid membranes induced by tetracaine. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg, 1998, 46: 1–5
Asami K, Takahashi K, Shirahige K. Progression of cell cycle monitored by dielectric spectroscopy and flow-cytometric analysis of DNA content. Yeast, 2000, 16: 1359–1363
Fournier J, Williams G, Duch C, Aldridge G A. Changes in molecular dynamics during bulk polymerization of an epoxide-amine system as studied by dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Macromol, 1996, 29: 7097–7107
Fitz B D, Mijovic J. In Situ monitoring of chemical reactions in and molecular dynamics of model compounds by dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B, 2000, 104: 12215–12223
Pethrick R A, Hayward D. Real time dielectric relaxation studies of dynamic polymeric systems. Prog Polym Sci, 2002, 27: 1983–2017
Zhao K S, Asaka K, Sekine K, Hanai T. Dielectric relaxations due to the interfacial polarization in bilamellar structure. Theory derivation in terms of electrostatic laws and the consideration by experiments. Bull Inst Chem Res, Kyoto Univ, 1989, 66: 540–553
Asami K. Dielectric analysis of mitochondria isolated from rat liver II. Intact mitochondria as simulated by a double-shell model. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1984, 778: 570–578
Bordi F, Cametti C, Gili T. Dielectric spectroscopy of erythrocyte cell suspensions. A comparison between Looyenga and Maxwell-Wagner-Hanai efective medium theory formulations. J Non-Cryst, 2002, 305: 278–284
Maxwell J C. Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1891
Wagner K W. Erklärung der dielektrishen Nachwirkungsvorgänge auf Grund Maxerllsher Vorstellungen. Arch Electrotechnik (Berl), 1914, 2: 371–387
Li Y H, Zhao K S, Hikida T. Dielectric spectroscopy and its analysis for the system of reverse osmosis membrane UTC-10 in aqueous solution. Acta Phys Chim Sin (in Chinese), 2003, 19(6): 523–527
Zhao K S, Asaka K, Asami K, Hanai T. Dielectric analysis of concentration polarization structure at anion-exchange membrane/solution interface under dc bias voltage application. J Coll I S, 1992, 153: 562–571
Hanai T, Zhao K S, Asaka K, Asami K. Dielectric theory of concentration polarization. Relaxation of capacitance and conductance for electrolyte solutions with locally varying conductivity. J Memb Sci, 1991, 64: 153–161
Zhao K S, Hanai T. D c bias effect on the dielectric behaviour of some disperse systems. Bull Inst Chem Res, Kyoto Univ, 1991, 69(4): 358–374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20673014) and Open Topic Research Foundation of Jiangsu Laboratory of Advanced Functional Materials (No. 06KFJJ009)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhao, K. & Han, Y. Dielectric study on membrane adsorption and release: Relaxation mechanism and diffusion dynamics. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 51, 813–822 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0037-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-008-0037-0