Abstract
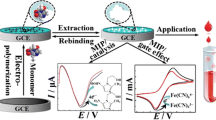
A novel capacitive sensor for pazufloxacin mesilate (pazufloxacin) determination was developed by electropolymerizing p-aminobenzene sulfonic (p-ABSA) and molecularly imprinted polymers (MPs), which was synthesized through thermal radical copolymerization of metharylic acid (MAA) and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) in the presence of pazufloxacin template molecules, on the gold electrode surface. Furthermore, 1-dedecanethiol was used to insulate the modified electrode. Alternating current (ac) impedance experiments were carried out with a Model IM6e to obtain the capacitance responses. Under the optimum conditions, the sensor showed linear capacitance response to pazufloxacin in the range of 5 ng·mL−1 to 5 μg·mL−1 with a relative standard deviation (RSD) 5.3% (n=7) and a detection limit of 1.8 ng·mL−1. The recoveries for different concentration levels of pazufloxacin samples varied from 94.0% to 102.0%. Electrochemical experiments indicated the capacitive sensor exhibited good sensitivity and selectivity and showed excellent parameters of regeneration and stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takei M, Fukuda H, Kishi R, Hosaka M. Target preference of 15 quinolone against Staphylococcus aureus, based on antibacterial activities and target inhibition. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2001, 45: 3544–3547
Yang X Y, You X F. Pazufloxacin mesilate’s pharmacological study and clinical application. Medicine Antibiotics in Overseas (in Chinese), 2003, 24(2): 80–87
Wang X L, Chen S L, Zhao H C, Jin L P, Li X. Europium sensitized chemiluminescence determination of pazufloxacin mesylate in urine and serum. Anal Lett, 2005, 38(6): 971–979
Chen S L, Ma H W, Zhao H C, Feng R, Jin L. Terbium-sensitized fluorescence method for the determination of pazufloxacin mesilate and its application. Anal Sci, 2004, 20(7): 1075–1078
Li Q, Wang R, Pei F. Determination of pazufloxacin mesilate in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Asian J Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 2004, 4(4): 289–293
Merkoci A, Alegret S. New materials for electrochemical sensing IV. Molecular imprinted polymers. Trends Anal Chem, 2002, 21(11): 717–725
Jenkins A L, Manuel O, Murray G M. Polymer-based lanthanide luminescent sensor for detection of the hydrolysis product of the nerve agent soman in water. Anal Chem, 1999, 71: 373–378
Jenkins A L, Yin R, Jensen J L. Molecularly imprinted polymer sensors for pesticide and insecticide detection in water. Analyst, 2001, 126: 798–802
Haupt K, Noworyta K, Kutner W. Imprinted polymer-based enantioselective acoustic sensor using a quartz crystal microbalance. Anal Commun, 1999, 36: 391–394
Dickert F L, Tortschanoff M, Bulst W E. Molecularly imprinted sensor layers for the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water. Anal Chem, 1999, 71: 4559–4563
Sergeyeva T A, Piletsky S A, Panasyuk T L, El’skaya A V, Brovko A A, Slinchenko E A, Sergeeva L M. Conductimetric sensor for atrazine detection based on molecularly imprinted polymer membranes. Analyst, 1999, 124: 331–334
Hedborg E, Winquist F, Lundström I, Andersson I, Mosbach K. Some studies of molecularly-imprinted polymer membranes in combination with field-effect devices. Sensor Actuat A, 1999, 38: 796–799
Panasyuk T L, Mirsky V M, Piletsky S A, Wolfbeis O S. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor layers in capacitive chemical sensors. Anal Chem, 1999, 71(20): 4609–4613
Piletsky S A, Piletskaya E V, Sergeyeva T A, Panasyuk T L, El’skaya A V. Molecularly imprinted self-assembled films with specificity to Cholesterol. Sensor Actuat B, 1999, 60: 216–220
Vlatakis G, Andersson L I, Muller R, Mosbach K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature, 1993, 361(3): 645–647
Jin G Y, Zhang Y Z, Cheng W X. Poly(p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid)-modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of dopamine and ascorbic acid. Sensor Actuat B, 2005, 107: 528–534
Berggren C, Bjarnason B, Johansson G. Capacitive biosensors, electroanalysis, 2001, 13(3): 173–180
Ho W O, Krause S, McNeil C J, Pritchard J A, Armstrong R D, Athey D, Rawson K. Electrochemical sensor for measurement of urea and creatinine in serum based on ac impedance measurement of enzyme-catalyzed polymer transformation. Anal Chem, 1999, 71: 1940–1946
Panasyuk-Delaney T, Mirsky V M, Ulbricht M, Wolfbeis O S. Impedometric herbicide chemosensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chim Acta, 2001, 435(1): 157–162
Panasyuk-Delaney T, Mirsky V M, Wolfbeis O S. Capacitive creatinine sensor based on a photografted molecularly imprinted polymer. Electroanalysis, 2002, 14(3): 221–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20675064), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing City (Grant No. CSTC-2004BB4149 and 2005BB4100) and High Technology Project Foundation of Southwest University (Grant No. XSGX02).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Ye, G., Yuan, R. et al. A capacitive sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers and poly(p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid) film for detection of pazufloxacin mesilate. SCI CHINA SER B 50, 547–553 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-007-0035-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-007-0035-7