Abstract
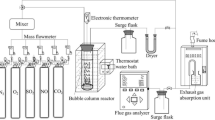
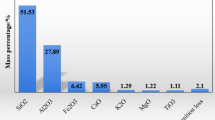
The oxidizing highly reactive absorbent was prepared from fly ash, industry lime, and an oxidizing additive M. Experiments of simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification were carried out in a flue gas circulating fluidized bed (CFB). The effects of influencing factors and calcium availability were also investigated on the removal efficiencies of desulfurization and denitrification. Removal efficiencies of 95.5% for SO2 and 64.8% for NO were obtained respectively under the optimal experimental conditions. The component of the spent absorbent was analyzed with chemical analysis methods. The results indicated that more nitrogen species appeared in the spent absorbent except sulfur species. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) and an accessory X-ray energy spectrometer were used to observe micro-properties of the samples, including fly ash, oxidizing highly reactive absorbent and spent absorbent. The simultaneous removal mechanism of SO2 and NO based on this absorbent was proposed according to the experimental results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhong Q. Techniques of Flue Gas Desulfuriztion and Denitrification for Coal-fired and Examples (in Chinese). Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002. 182–203
Chu H, Chien T W, Li S Y. Simultaneous absorption of SO2 and NO from flue gas with KMnO4/NaOH solutions. Sci Total Environ, 2001, 275(3): 127–135
Hori M, Matsunga N, Malte P C, et al. The effect of low concentration-fuels on the conversion of nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide. In: Twenty-Four Symposium (International) on Combustion. The Combustion Institute, Sydney, Australia, 1992. 909–916
Zhao Y, Ma S C, Li Y Z, et al. Experimental investigation of desulfurization and denitrification from flue gas by absorbents based on fly ash. Zhongguo Dianji Gongcheng Xuebao/Proceedings of the Chinese Society of Electrical Engineering (in Chinese), 2002, 22(3): 108–112
Zhao Y, Ma S C, Huang J J, et al. Experimental study on SO2 and NOx removal and mechanism by highly reactive sorbent. Proc Chin Soc Electr Eng (in Chinese), 2003, 23(10): 236–240
Fan B G, Qi H Y, Yu C F, et al. Mass balance and chemical change of bed materials in circulating fluidized bed during desulfuriztion. Therm Energy Power Eng(in Chinese), 2001, 23(10): 236–240
Gao X, Luo Z Y, Chen Y F, et al. Study on effect of moisture on desulfurization characteristic of calcium-based sorbent. Combust Sci Technol (in Chinese), 1999, 5(1): 39–45
Gao X, Luo Z Y, Liu N. Desulfurization characteristic of calcium-based sorbent during activation process. J Chem Eng JPN, 2001, 34(9): 1114–1119
Yoon H, Stouffer M R, Rosenhoover W A, et al. Pilot process variable study of coolside desulfurization. Environ Prog, 1988, 7(2): 101–111
Stouffer M R, Yoon H F, Burker P. An investigation of the mechanisms of flue gas desulfurization on by in-duct dry sorbent injection. Ind Eng Chem Res, 1989, 28: 20–27
Cook J L, Khang S J, Lee S K, et al. Attrition and changes in particle size of lime sorbents in a circulating fludizied bed absorber. Power Technol, 1996, 89: 1–8
Christopher H N, Gary T R. Simultaneous sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide removal by calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate solids. J Air Waste Manage, 1998, 48(9): 819–828
Zhao P G. Synthetic Utilization of Fly Ash (in Chinese). Shenyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Publishing House, 1993. 68–99
Sakai M, Su C L, Sasaoka E J. Simultaneous removal of SOx and NOx using slaked lime at low temperature. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2002, 41(20): 5029–5033
Tomohiro I, Hajime K, Tsutomu Y, et al. Initial step of flue gas desulfurization—An IR study of the reaction of SO2 with NOx on CaO. Environ Sci Technol, 2000, 34(13): 2799–2803
Ervin B M J, Thomas J O. Hydrogen peroxide scrubber for the control of nitrogen oxides. Environ Eng Sci, 2002, 19(5): 321–327
Chironna R J, Altshuler B. Chemical aspects of NOx scrubbing. Pollut Eng, 1998, 31: 32–37
Gu J G, Zhou, Q X, Wang X. Reused path of heavy metal polluti on in soils and its research advance. J Basic Sci Eng (in Chinese), 2003, 12(2): 143–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Significant Pre-research Foundation of North China Electric Power University (D03-035)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Xu, P., Sun, X. et al. Experimental and mechanism studies on simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification from flue gas using a flue gas circulating fluidized bed. SCI CHINA SER B 50, 135–144 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-007-0013-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-007-0013-0