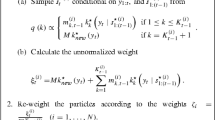Abstract
In this paper, we propose a new estimation method for a nonparametric hidden Markov model (HMM), in which both the emission model and the transition matrix are nonparametric, and a semiparametric HMM, in which the transition matrix is parametric while emission models are nonparametric. The estimation is based on a novel composite likelihood method, where the pairs of consecutive observations are treated as independent bivariate random variables. Therefore, the model is transformed into a mixture model, and a modified expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm is developed to compute the maximum composite likelihood. We systematically study asymptotic properties for both the nonparametric HMM and the semiparametric HMM. We also propose a generalized likelihood ratio test to choose between the nonparametric HMM and the semiparametric HMM. We derive the asymptotic distribution and prove the Wilk’s phenomenon of the proposed test statistics. Simulation studies and an application in volatility clustering analysis of the volatility index in the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam T, Mayr A, Kneib T. Gradient boosting in Markov-switching generalized additive models for location, scale, and shape. Econom Stat, 2022, 22: 3–16
Alexandrovich G, Holzmann H, Leister A. Nonparametric identification and maximum likelihood estimation for hidden Markov models. Biometrika, 2016, 103: 423–434
Bartolucci F, Farcomeni A. A multivariate extension of the dynamic logit model for longitudinal data based on a latent Markov heterogeneity structure. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2009, 104: 816–831
Bartolucci F, Farcomeni A, Pennoni F. Latent Markov Models for Longitudinal Data. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2012
Baum L E, Petrie T. Statistical inference for probabilistic functions of finite state Markov chains. Ann Math Statist, 1996, 37: 1554–1563
Bickel P J, Ritov Y, Ryden T. Asymptotic normality of the maximum-likelihood estimator for general hidden Markov models. Ann Statist, 1998, 26: 1614–1635
Chen J H, Huang Y, Wang P M. Composite likelihood under hidden Markov model. Statist Sinica, 2016, 26: 1569–1586
Dannemann J. Semiparametric hidden Markov models. J Comput Graph Statist, 2012, 21: 677–692
De Castro Y, Gassiat Á, Lacour C. Minimax adaptive estimation of nonparametric hidden Markov models. J Mach Learn Res, 2016, 17: 3842–3884
Fan J, Heckman N E, Wand M P. Local polynomial kernel regression for generalized linear models and quasi-likelihood functions. J Amer Statist Assoc, 1995, 90: 141–150
Fan J, Zhang C, Zhang J. Generalized likelihood ratio statistics and Wilk’s phenomenon. Ann Statist, 2001, 29: 153–193
Frühwirth-Schnatter S. Finite Mixture and Markov Switching Models. New York: Springer, 2006
Gassiat E, Rousseau J. Nonparametric finite translation hidden Markov models and extensions. Bernoulli, 2016, 22: 193–212
Hamilton J D. A new approach to the economic analysis of nonstationary time series and the business cycle. Econometrica, 1989, 57: 357–384
Huang M, Ji Q, Yao W. Semiparametric hidden Markov model with non-parametric regression. Comm Statist Theory Methods, 2018, 47: 5196–5204
Huang M, Li R, Wang S. Nonparametric mixture of regression models. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2013, 108: 929–941
Huang M, Yao W. Mixture of regression models with varying mixing proportions: A semiparametric approach. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2012, 107: 711–724
Huang X D, Baker J, Reddy R. A historical perspective of speech recognition. Commun ACM, 2014, 57: 94–103
Huang Y. Estimation and testing of nonparametric hidden Markov model with application in stock market. Comm Statist Theory Methods, 2020, 49: 5917–5929
Hughes J P, Guttorp P, Charles S P. A non-homogeneous hidden Markov model for precipitation occurrence. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat, 1999, 48: 15–30
Khalili A, Chen J H. Variable selection in finite mixture of regression models. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2007, 102: 1025–1038
Krogh A, Brown M, Mian I S, et al. Hidden Markov models in computational biology: Applications to protein modeling. J Mol Biol, 1994, 235: 1501–1531
Langrock R, Kneib T, Sohn A, et al. Nonparametric inference in hidden Markov models using P-splines. Biometrics, 2015, 71: 520–528
Lindsay B G. Composite likelihood methods. Contemp Math, 1988, 80: 221–239
Lindsay B G. Mixture Models: Theory, Geometry and Applications. NSF-CBMS Regional Conference Series in Probability and Statistics, vol. 5. Bethesda: Inst Math Statist, 1995
Mandelbrot B. The variation of some other speculative prices. J Business, 1967, 40: 393–413
McLachlan G, Peel D. Mixtures of factor analyzers. In: Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Conference on Machine Learning. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2000, 599–606
Mehrotra R, Sharma A. A nonparametric nonhomogeneous hidden Markov model for downscaling of multisite daily rainfall occurrences. J Geophys Res Atmos, 2005, 110: D16
Meligkotsidou L, Dellaportas P. Forecasting with non-homogeneous hidden Markov models. Stat Comput, 2011, 21: 439–449
Piyathilaka L, Kodagoda S. Gaussian mixture based HMM for human daily activity recognition using 3D skeleton features. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 8th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. New York: IEEE, 2013, 567–572
Rabiner L R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 77. New York: IEEE, 1989, 257–286
Ruppert D, Wand M P. Multivariate locally weighted least squares regression. Ann Statist, 1994, 22: 1346–1370
Titman A C. Flexible nonhomogeneous Markov models for panel observed data. Biometrics, 2011, 67: 780–787
Titterington D M, Smith A, Makov U. Statistical Analysis of Finite Mixture Distributions. New York: Wiley, 1985
Vermunt J K, Langeheine R, Bockenholt U. Discrete-time discrete-state latent Markov models with time-constant and time-varying covariates. J Educ Behav Stat, 1999, 24: 179–207
Wang S L, Yao W X, Huang M. A note on the identifiability of nonparametric and semiparametric mixtures of GLMs. Statist Probab Lett, 2014, 93: 41–45
Wong K-C, Chan T-M, Peng C, et al. DNA motif elucidation using belief propagation. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41: e153
Yakowitz S J, Spragins J D. On the identifiability of finite mixtures. Ann Math Statist, 1968, 39: 209–214
Yang L J, Tschernig R. Multivariate bandwidth selection for local linear regression. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol, 1999, 61: 793–815
Yau C, Papaspiliopoulos O, Roberts G O, et al. Bayesian non-parametric hidden Markov models with applications in genomics. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol, 2011, 73: 37–57
Zucchini W, MacDonald I L, Langrock R. Hidden Markov Models for Time Series: An Introduction Using R. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC, 2016
Acknowledgements
Mian Huang was supported by Shanghai Young Talent Development Program and Innovative Research Team of Shanghai University of Finance and Economics (Grant No. 2020110930). Weixin Yao was supported by the Department of Energy of USA (Grant No. DE-EE0008574).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., Huang, Y. & Yao, W. Statistical inference for the nonparametric and semiparametric hidden Markov model via the composite likelihood approach. Sci. China Math. 66, 601–626 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-020-1913-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-020-1913-7
Keywords
- nonparametric HMM
- nonhomogeneous HMM
- semiparametric estimate
- composite likelihood
- generalized likelihood ratio test