Abstract
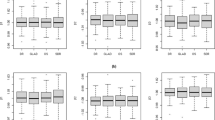
This paper studies the reduced rank regression problem, which assumes a low-rank structure of the coefficient matrix, together with heavy-tailed noises. To address the heavy-tailed noise, we adopt the quantile loss function instead of commonly used squared loss. However, the non-smooth quantile loss brings new challenges to both the computation and development of statistical properties, especially when the data are large in size and distributed across different machines. To this end, we first transform the response variable and reformulate the problem into a trace-norm regularized least-square problem, which greatly facilitates the computation. Based on this formulation, we further develop a distributed algorithm. Theoretically, we establish the convergence rate of the obtained estimator and the theoretical guarantee for rank recovery. The simulation analysis is provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando R K, Zhang T. A framework for learning predictive structures from multiple tasks and unlabeled data. J Mach Learn Res, 2005, 6: 1817–1853
Argyriou A, Evgeniou T, Pontil M. Multi-task feature learning. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 19. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2007, 41–48
Banerjee M, Durot C, Sen B. Divide and conquer in nonstandard problems and the super-efficiency phenomenon. Ann Statist, 2019, 47: 720–757
Battey H, Fan J, Liu H, et al. Distributed testing and estimation under sparse high dimensional models. Ann Statist, 2018, 46: 1352–1382
Bunea F, She Y, Wegkamp M H. Optimal selection of reduced rank estimators of high-dimensional matrices. Ann Statist, 2011, 39: 1282–1309
Cai J-F, Candes E J, Shen Z. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J Optim, 2010, 20: 1956–1982
Cai T T, Liu W. Adaptive thresholding for sparse covariance matrix estimation. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2011, 106: 672–684
Candes E J, Recht B. Exact matrix completion via convex optimization. Found Comput Math, 2009, 9: 717–772
Chao S-K, Hardle W, Yuan M. Factorisable multi-task quantile regression. SFB 649 Discussion Paper 2016-057, https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2892555, 2016
Chen K, Chan K, Stenseth N C. Reduced rank stochastic regression with a sparse singular value decomposition. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol, 2011, 74: 203–221
Chen K, Dong H, Chan K-S. Reduced rank regression via adaptive nuclear norm penalization. Biometrika, 2013, 100: 901–920
Chen X, Liu W, Mao X, et al. Distributed high-dimensional regression under a quantile loss function. J Mach Learn Res, 2020, 21: 182
Chen X, Liu W, Zhang Y. Quantile regression under memory constraint. Ann Statist, 2019, 47: 3244–3273
Fan J, Wang D, Wang K, et al. Distributed estimation of principal eigenspaces. Ann Statist, 2019, 47: 3009–3031
Franklin J N. Matrix Theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 1968
Horn R A, Johnson C R. Matrix Analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012
Izenman A J. Reduced-rank regression for the multivariate linear model. J Multivariate Anal, 1975, 5: 248–264
Izenman A J. Modern Multivariate Statistical Techniques: Regression, Classification, and Manifold Learning, 2nd ed. New York: Springer, 2013
Jordan M I, Lee J D, Yang Y. Communication-efficient distributed statistical inference. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2019, 114: 668–681
Koenker R. Quantile Regression. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005
Lee J D, Liu Q, Sun Y, et al. Communication-efficient sparse regression. J Mach Learn Res, 2017, 18: 5
Li R, Lin D K, Li B. Statistical inference in massive data sets. Appl Stoch Models Bus Ind, 2013, 29: 399–409
Lian H, Fan Z. Divide-and-conquer for debiased li-norm support vector machine in ultra-high dimensions. J Mach Learn Res, 2017, 18: 6691–6716
Lu Z, Monteiro R D, Yuan M. Convex optimization methods for dimension reduction and coefficient estimation in multivariate linear regression. Math Program, 2012, 131: 163–194
Mao X, Chen S X, Wong R K. Matrix completion with covariate information. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2019, 114: 198–210
Mazumder R, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Spectral regularization algorithms for learning large incomplete matrices. J Mach Learn Res, 2010, 11: 2287–2322
Merikoski J K, Kumar R. Inequalities for spreads of matrix sums and products. Appl Math E-Notes, 2004, 4: 150–159
Pong T K, Tseng P, Ji S, et al. Trace norm regularization: Reformulations, algorithms, and multi-task learning. SIAM J Optim, 2010, 20: 3465–3489
Reinsel G C, Velu R P. Multivariate Reduced-Rank Regression: Theory and Applications. New York: Springer, 1998
Shamir O, Srebro N, Zhang T. Communication-efficient distributed optimization using an approximate Newton-type method. J Mach Learn Res, 2014, 32: 1000–1008
She Y, Chen K. Robust reduced-rank regression. Biometrika, 2017, 104: 633–647
Shi C, Lu W, Song R. A massive data framework for M-estimators with cubic-rate. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2018, 113: 1698–1709
Volgushev S, Chao S-K, Cheng G. Distributed inference for quantile regression processes. Ann Statist, 2019, 47: 1634–1662
Yuan M, Ekici A, Lu Z, et al. Dimension reduction and coefficient estimation in multivariate linear regression. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol, 2007, 69: 329–346
Zhang Y, Duchi J, Wainwright M. Divide and conquer kernel ridge regression: A distributed algorithm with minimax optimal rates. J Mach Learn Res, 2015, 16: 3299–3340
Zhang Y, Yang Q. An overview of multi-task learning. Natl Sci Rev, 2017, 5: 30–43
Zhao T, Cheng G, Liu H. A partially linear framework for massive heterogeneous data. Ann Statist, 2016, 44: 1400–1437
Zou H. The adaptive lasso and its oracle properties. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2006, 101: 1418–1429
Acknowledgements
The second author was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant No. 2018AAA0100704), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11825104 and 11690013), Youth Talent Support Program and Australian Research Council. The third author was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12001109), Shanghai Sailing Program (Grant No. 19YF1402800) and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 20dz1200600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Liu, W. & Mao, X. Robust reduced rank regression in a distributed setting. Sci. China Math. 65, 1707–1730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-020-1785-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-020-1785-0