Abstract
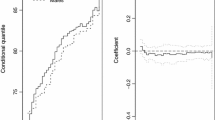
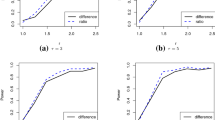
Prevalent cohort studies frequently involve length-biased and right-censored data, a fact that has drawn considerable attention in survival analysis. In this article, we consider survival data arising from lengthbiased sampling, and propose a new semiparametric-model-based approach to estimate quantile differences of failure time. We establish the asymptotic properties of our new estimators theoretically under mild technical conditions, and propose a resampling method for estimating their asymptotic variance. We then conduct simulations to evaluate the empirical performance and efficiency of the proposed estimators, and demonstrate their application by a real data analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addona V, Wolfson D B. A formal test for the stationarity of the incidence rate using data from a prevalent cohort study with follow-up. Lifetime Data Anal, 2006, 12: 267–284
Andersen P K, Gill R D. Cox’s regression model for counting processes: A large sample study. Ann Statist, 1982, 10: 1100–1120
Arnold B C, Strauss D. Bivariate distributions with exponential conditionals. J Amer Statist Assoc, 1988, 83: 522–527
Asgharian M. On the singularities of the information matrix and multipath change-point problems. Theory Probab Appl, 2014, 58: 546–561
Asgharian M, Wolfson D B. Asymptotic behavior of the unconditional NPMLE of the length-biased survivor function from right censored prevalent cohort data. Ann Statist, 2005, 33: 2109–2131
Asgharian M, Wolfson D B, Zhang X. Checking stationarity of the incidence rate using prevalent cohort survival data. Stat Med, 2006, 25: 1751–1767
Chen X R, Zhou Y. Quantile regression for right-censored and length-biased data. Acta Math Appl Sin Engl Ser, 2012, 28: 443–462
Gijbels I, Wang J L. Strong representations of the survival function estimator for truncated and censored data with applications. J Multivariate Anal, 1993, 47: 210–229
Huang C Y, Qin J. Composite partial likelihood estimation under length-biased sampling with application to a prevalent cohort study of dementia. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2012, 107: 946–957
Kosorok M R. Introduction to Empirical Processes and Semiparametric Inference. New York: Springer, 2008
Lin C, Zhou Y. Analyzing right-censored and length-biased data with varying-coefficient transformation model. J Multivariate Anal, 2014, 130: 45–63
Lin C, Zhou Y. Semiparametric varying-coefficient model with right-censored and length-biased data. J Multivariate Anal, 2016, 152: 119–144
Qin J, Shen Y. Statistical methods for analyzing right-censored length-biased data under Cox model. Biometrics, 2010, 66: 382–392
Reiss R D. Approximate Distributions of Order Statistics. New York: Springer, 1989
Shen Y, Ning J, Qin J. Analyzing length-biased data with semiparametric transformation and accelerated failure time models. J Amer Statist Assoc, 2009, 104: 1192–1202
Tsai W Y. Pseudo-partial likelihood for proportional hazards models with biased-sampling data. Biometrika, 2009, 96: 601–615
Tsai W Y, Jewell N P, Wang M C. A note on the product-limit estimator under right censoring and left truncation. Biometrika, 1987, 74: 883–886
Van der Vaart A W. Asymptotic Statistics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000
Wang H J, Wang L. Quantile regression analysis of length-biased survival data. Stat, 2014, 3: 31–47
Wang M C. Nonparametric estimation from cross-sectional survival data. J Amer Statist Assoc, 1991, 86: 130–143
Wang M C, Brookmeyer R, Jewell N. Statistical models for prevalent cohort data. Biometrics, 1993, 49: 1–11
Wang Y, Liu P, Zhou Y. Quantile residual lifetime for left-truncated and right-censored data. Sci China Math, 2015, 58: 1217–1234
Winter B B, Foldes A. A product-limit estimator for use with length-biased data. Canad J Statist, 1988, 16: 337–355
Xun L, Shao L, Zhou Y. Efficiency of estimators for quantile differences with left truncated and right censored data. Statist Probab Lett, 2017, 121: 29–36
Yang H, Zhao Y. Smoothed jackknife empirical likelihood for the one-sample difference of quantiles. Comput Statist Data Anal, 2018, 120: 58–69
Zelen M. Forward and backward recurrence times and length biased sampling: Age specific models. Lifetime Data Anal, 2004, 10: 325–334
Zelen M, Feinleib M. On the theory of screening for chronic diseases. Biometrika, 1969, 56: 601–614
Zeng D, Lin D Y. Efficient resampling methods for nonsmooth estimating function. Biostatistics, 2008, 9: 355–363
Zhang F, Chen X, Zhou Y. Proportional hazards model with varying coefficients for length-biased data. Lifetime Data Anal, 2014, 20: 132–157
Zhou W, Jing B. Smoothed empirical likelihood confidence intervals for the difference of quantiles. Statist Sinica, 2003, 13: 83–95
Zhou Y, Yip P. A strong representation of the product-limit estimator for left truncated and right censored data. J Multivariate Anal, 1999, 69: 261–280
Acknowledgements
Liu's work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11401603), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. QL 18009) and Discipline Foundation of Central University of Finance and Economics (Grant No. CUFESAM201811). Zhou's work was supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71331006) and the State Key Program in the Major Research Plan of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 91546202). The authors thank two anonymous referees for many helpful comments and suggestions, which have greatly improved the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhang, S. & Zhou, Y. Semiparametric quantile-difference estimation for length-biased and right-censored data. Sci. China Math. 62, 1823–1838 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-017-9250-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-017-9250-0