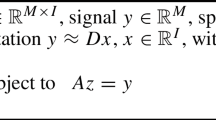Abstract
We consider the block orthogonal multi-matching pursuit (BOMMP) algorithm for the recovery of block sparse signals. A sharp condition is obtained for the exact reconstruction of block K-sparse signals via the BOMMP algorithm in the noiseless case, based on the block restricted isometry constant (block-RIC). Moreover, we show that the sharp condition combining with an extra condition on the minimum ℓ2 norm of nonzero blocks of block K-sparse signals is sufficient to ensure the BOMMP algorithm selects at least one true block index at each iteration until all true block indices are selected in the noisy case. The significance of the results we obtain in this paper lies in the fact that making explicit use of block sparsity of block sparse signals can achieve better recovery performance than ignoring the additional structure in the problem as being in the conventional sense.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai Y, Li S. Convergence analysis of projected gradient descent for schatten-p nonconvex matrix recovery. Sci China Math, 2015, 58: 845–858
Candès E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing. C R Math Acad Sci Paris, 2008, 346: 589–592
Candès E J, Romberg J K, Tao T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2006, 52: 489–509
Candès E J, Tao T T. Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2005, 51: 4203–4215
Chen J, Huo X. Theoretical results on sparse representations of multiple-measurement vectors. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2006, 54: 4634–4643
Chen S, Billings S A, Luo W. Orthogonal least squarses methods and their application to non-linear system identification. Internat J Control, 1989, 50: 1873–1896
Chen W G, Ge H M. A sharp bound on RIC in generalized orthogonal matching pursuit. ArXiv:1604.03306, 2016
Chen W G, Li Y L. Stable recovery of low-rank matrix via nonconvex schatten p-minimization. Sci China Math, 2015, 58: 2643–2654
Chen W G, Wu G Q. Harmonic analysis and research on the channel coding and decoding (in Chinese). Sci Sin Math, 2014, 44: 447–456
Cotter S F, Rao B D. Sparse channel estimation via matching pursuit with application to equalization. IEEE Trans Commun, 2002, 50: 374–377
Cotter S F, Rao B D, Engan K, et al. Sparse solutions to linear inverse problems with multiple measurement vectors. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2005, 53: 2477–2488
Dai W, Milenkovic O. Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2009, 55: 2230–2249
Dan W, Wang R H. Robustness of orthogonal matching pursuit under restricted isometry property. Sci China Math, 2014, 57: 627–634
Dan W. Analysis of orthogonal multi-matching pursuit under restricted isometry property. Sci China Math, 2014, 57: 2179–2188
Donoho D L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2006, 52: 1289–1306
Donoho D L, Drori I, Tsaig Y, et al. Sparse solution of underdetermined linear equations by stagewise orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2012, 58: 1094–1121
Eldar Y C, Kuppinger P, Bölcskei H. Block-sparse signals: Uncertainty relations and efficient recovery. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2010, 58: 3042–3054
Eldar Y C, Mishali M. Robust recovery of signals from a structured union of subspaces. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2009, 55: 5302–5316
Eldar Y C, Mishali M. Block-sparsity and sampling over a union of subspaces. In: DSP’09 Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009, 1–8
Fu Y, Li H, Zhang Q, et al. Block-sparse recovery via redundant block OMP. Signal Process, 2014, 97: 162–171
Huang B X, Zhou T. Recovery of block sparse signals by a block version of StOMP. Signal Process, 2015, 109: 231–244
Huang J, Zhang T. The benefit of group sparsity. Ann Stat, 2010, 38: 1978–2004
Lin J H, Li S. Block Sparse Recovery via mixed ℓ2/ℓ1 minimization. Acta Math Sinica, 2013, 46: 364–375
Lin J H, Li S. Nonuniform support recovery from noisy random measurements by orthogonal matching pursuit. J Approx Theory, 2013, 165: 20–40
Majumdar A, Ward R K. Compressed sensing of color images. Signal Process, 2010, 90: 3122–3127
Mishali M, Eldar Y C. Reduce and boost: Recovering arbitrary sets of jointly sparse vectors. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2008, 56: 4692–4702
Mishali M, Eldar Y C. Blind multi-band signal reconstruction: Compressed sensing for analog signals. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2009, 57: 993–1009
Mishali M, Eldar Y C, Dounaevsky O, et al. Xampling: Analog to digital at sub-Nyquist rates. Circuits Devices Syst IET, 2011, 5: 8–20
Mo Q. A sharp restricted isometry constant bound of orthogonal matching pursuit. ArXiv:1501.01708, 2015
Mo Q, Shen Y. A Remark on the restricted isometry property in orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2012, 58: 3654–3656
Needell D, Troop J A. CoSaMP: Itertive signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl Comput Harmon Anal, 2009, 26: 301–321
Needell D, Vershynin R. Signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process, 2010, 4: 310–316
Parvaresh F, Vikalo H, Misra S, et al. Recovering sparse signals using sparse measurement matrices incompressed DNA microarrays. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process, 2008, 2: 275–285
Shen Y, Li S. Sparse signals recovery from noisy measurements by orthogonal matching pursuit. Inverse Probl Imaging, 2015, 9: 231–238
Stojnic M, Parvaresh F, Hassibi B. On the reconstruction of block-sparse signals with an optimal number of measurements. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2010, 57: 3075–3085
Sun Q Y. Recovery of sparsest signals via l q-minimization. Appl Comput Harmon Anal, 2012, 32: 329–341
Swirszcz G, Abe N, Lozano A C. Grouped orthogonal matching pursuit for variable selection and prediction. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, 2009, 22: 1150–1158
Tropp J A. Algorithms for simultaneous sparse approximation. Part I: Greedy pursuit. Signal Process, 2006, 86: 572–588
Tropp J A, Gilbert A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2007, 53: 4655–4666
Wang J, Kwon S, Shim B. Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2012, 60: 6202–6216
Wang J, Shim B. On the recovery limit of sparse signals using orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2012, 60: 4973–4976
Wang Y, Wang J J, Xu Z B. On recovery of block-sparse signals via mixed ℓ2/ℓp (0 < p ≤ 1) norm minimization. Eurasip J Adv Signal Process, 2013, 76: 1–17
Wang Y, Wang J J, Xu Z B. Restricted p-isometry properties of nonconvex block-sparse compressed sensing. Signal Process, 2014, 104: 188–196
Wen J M, Zhou Z C, Li D F, et al. Improved sufficient conditions for sparse recovery with generalized orthogonal matching pursuit. ArXiv:1603.01507, 2016
Wen J M, Zhou Z C, Liu Z, et al. Sharp sufficient conditions for stable recovery of block sparse signals by block orthogonal matching pursuit. ArXiv:1605.02894, 2016
Wu R, Huang W, Chen D R. The exact support recovery of sparse signals with noise via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Signal Proc Lett, 2013, 20: 403–406
Xu Y, Qiu X H. Block-sparse signals recovery using orthogonal multimatching. J Signal Process, 2014, 30: 706–711
Xu Z Q. Compressed sensing: A survey (in Chinese). Sci Sin Math, 2012, 42: 865–877
Xu Z Q. The performance of orthogonal multi-matching pursuit under RIP. J Comput Math, 2015, 33: 495–516
Zhao Q, Wang J, Han Y, et al. Compressive sensing of block-sparse signals recovery based on sparsity adaptive regularized orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. In: IEEE Fifth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence. New York: IEEE, 2012, 1141–1144
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11271050 and 11371183). The authors thank the referees for their valuable comments that improve the presentation of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Ge, H. A sharp recovery condition for block sparse signals by block orthogonal multi-matching pursuit. Sci. China Math. 60, 1325–1340 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-016-0448-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-016-0448-7
Keywords
- compressed sensing
- block sparse signal
- block restricted isometry property
- block orthogonal multimatching pursuit