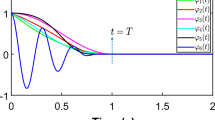
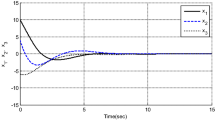
Abstract
This paper studies global robust tracking of uncertain Euler-Lagrange systems with input disturbances. The authors develop a robust regulation-based approach for the problem. Specifically, by introducing a novel nonlinear internal model, the authors solve global asymptotic trajectory tracking with disturbance rejection of multiple step/sinusoidal signals with unknown amplitudes, frequencies, and phases. Moreover, the authors show that a robustness property to actuator noises can be guaranteed in a sense of strong integral input-to-state stability (iISS). That is, the closed-loop system is not only iISS but also input-to-state stable (ISS) to small magnitude actuator noises. Furthermore, the authors explore a by-product overparametrized linear regression estimation, coming up with robust estimation of the unknown parameters. Finally, the authors present several numerical examples to illustrate the theoretical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ortega R, Loría A, Nicklasson P J, et al., Passivity-Based Control of Euler-Lagrange Systems: Mechanical, Electrical and Electromechanical Applications, Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, 1998.
Slotine J J E and Li W, Applied Nonlinear Control, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1991.
Spong M W, Hutchinson S, and Vidyasagar M, Robot Modeling and Control, Wiley, New York, 2006.
Craig J J, Hsu P, and Sastry S S, Adaptive control of mechanical manipulators, The International Journal of Robotics Research, 1987, 6(2): 16–28.
Middleton R H and Goodwin G C, Adaptive computed torque control for rigid link manipulations, Systems & Control Letters, 1988, 10(1): 9–16.
Spong M W and Ortega R, On adaptive inverse dynamics control of rigid robots, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1990, 35(1): 92–95.
Dawson D M and Lewis F L, Comments on “On adaptive inverse dynamics control of rigid robots”, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1991, 36(10): 1215–1216.
Slotine J J E and Li W, On the adaptive control of robot manipulators, The International Journal of Robotics Research, 1987, 6(3): 49–59.
Slotine J J E, Putting physics in control — The example of robotics, IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 1988, 8(6): 12–18.
Leal R L and Dewit C C, Passivity based adaptive control for mechanical manipulators using LS-type estimation, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1990, 35(12): 1363–1365.
Tang Y and Arteaga M A, Adaptive control of robot manipulators based on passivity, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1994, 39(9): 1871–1875.
Scherpen J M A and Ortega R, On nonlinear control of Euler-Lagrange systems: Disturbance attenuation properties, Systems & Control Letters, 1997, 30(1): 49–56.
Tomei P, Tracking control of flexible joint robots with uncertain parameters and disturbances, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1994, 39(5): 1067–1072.
Luo G L and Saridis G N, Robust compensation for a robotic manipulator, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1983, 29(6): 564–567.
Chen B S, Lee T S, and Feng J H, A nonlinear H ∞ control design in robotic systems under parameter perturbation and external disturbance, International Journal of Control, 1994, 59(2): 439–461.
Battilotti S and Lanari L, Adaptive disturbance attenuation with global stability for rigid and elastic joint robots, Automatica, 1997, 33(2): 239–243.
Tomei P, Robust adaptive control of robots with arbitrary transient performance and disturbance attenuation, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1999, 44(3): 654–658.
Mei K, Ding S, Yang X, et al., Second-order sliding mode controller design with a larger domain of attraction, Journal of Systems Science & Complexity, 2020, 33(1): 61–73.
Patre P M, MacKunis W, Dupree K, et al., Modular adaptive control of uncertain Euler-Lagrange systems with additive disturbances, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(1): 155–160.
Chen B S, Chang Y C, and Lee T C, Adaptive control in robotic systems with H ∞ tracking performance, Automatica, 1997, 33(2): 227–234.
Jayawardhana B and Weiss G, Tracking and disturbance rejection for fully actuated mechanical systems, Automatica, 2008, 44(11): 2863–2868.
Lu M, Liu L, and Feng G, Adaptive tracking control of uncertain Euler-Lagrange systems subject to external disturbances, Automatica, 2019, 104: 207–219.
Wu H and Xu D, Inverse optimality and adaptive asymptotic tracking control of uncertain Euler-Lagrange systems, 2019 IEEE 15th International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), 2019, 242–247.
Sontag E D, Input to state stability: Basic concepts and results, Eds. by Nistri P and Stefani G, Nonlinear and Optimal Control Theory, Springer, Berlin, 2007, 163–220.
Angeli D, Input-to-state stability of PD-controlled robotic systems, Automatica, 1999, 35(7): 1285–1290.
Angeli D, Sontag E D, and Wang Y, A characterization of integral input-to-state stability, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(6): 1082–1097.
Liberzon D, Sontag E D, and Wang Y, Universal construction of feedback laws achieving ISS and integral-ISS disturbance attenuation, Systems & Control Letters, 2002, 46(2): 111–127.
Jiang Z P and Hill D J, Passivity and disturbance attenuation via output feedback for uncertain nonlinear systems, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1998, 43(7): 992–997.
Liu T, Jiang Z P, and Hill D J, Nonlinear Control of Dynamic Networks, CRC Press, New York, 2014.
Huang J and Chen Z, A general framework for tackling the output regulation problem, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(12): 2203–2218.
Xu D, Constructive nonlinear internal models for global robust output regulation and application, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(5): 1523–1530.
Xu D and Huang J, A generic internal model for robust output regulation problem for plants subject to an uncertain exosystem, 2019 IEEE 15th International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), 2019, 1179–1184.
Chaillet A, Angeli D, and Ito H, Combining iISS and ISS with respect to small inputs: The strong iISS property, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(9): 2518–2524.
Huang J, Nonlinear Output Regulation: Theory and Applications, SIAM, Philadelphia, 2004.
Byrnes C I and Isidori A, Limit sets, zero dynamics, and internal models in the problem of nonlinear output regulation, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(10): 1712–1723.
Bastin G, Bitmead R R, Campion G, et al. Identification of linearly overparametrized nonlinear systems, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1992, 37(7): 1073–1078.
Sun W, Xia J, and Wu Y, Adaptive tracking control for mobile manipulators with stochastic disturbances, Journal of Systems Science & Complexity, 2019, 32(5): 1393–1403.
Byrnes C I and Isidori A, Nonlinear internal models for output regulation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(12): 2244–2247.
Krstić M, Kanellakopoulos I, and Kokotović P V, Nonlinear and Adaptive Control Design, Wiley, New York, 1995.
Astolfi D, Isidori A, Marconi L, et al., Nonlinear output regulation by post-processing internal model for multi-input multi-output systems, IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2013, 46(23): 295–300.
Bin M and Marconi L, Output regulation by postprocessing internal models for a class of multi-variable nonlinear systems, International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2020, 30(3): 1115–1140.
Xu D, Chen Z, and Wang X, Global robust stabilization of nonlinear cascaded systems with integral ISS dynamic uncertainties, Automatica, 2017, 80: 210–217.
Wang H and Xie Y, Flocking of networked mechanical systems on directed topologies: A new perspective, International Journal of Control, 2015, 88(4): 872–884.
Sontag E D and Wang Y, New characterizations of input-to-state stability, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1996, 41(9): 1283–1294.
Xu D, Wang X, and Chen Z, Output regulation of nonlinear output feedback systems with exponential parameter convergence, Systems & Control Letters, 2016, 88: 81–90.
Zhang Y and Guo L, Convergence of self-tuning regulators under conditional heteroscedastic noises with unknown high-frequency gain, Journal of Systems Science & Complexity, 2021, 34(1): 236–250.
Sastry S, Nonlinear Systems: Analysis, Stability and Control, Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, USA, 1999.
Khalil H K, Nonlinear Systems, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This paper was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61673216 and 62073168; The work of Wu was supported by the China Scholarship Council on his study at the University of Groningen, The Netherlands; The work of Xu was partially done when he was with the School of Automation, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor LIU Tengfei.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Xu, D. Trajectory Tracking Control of Euler-Lagrange Systems with ISS-Like Robustness to Actuator Noises. J Syst Sci Complex 35, 1719–1747 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-022-0219-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-022-0219-4