Abstract
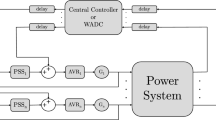
This paper proposes a multi-layer multi-agent model for the performance evaluation of power systems, which is different from the existing multi-agent ones. To describe the impact of the structure of the networked power system, the proposed model consists of three kinds of agents that form three layers: control agents such as the generators and associated controllers, information agents to exchange the information based on the wide area measurement system (WAMS) or transmit control signals to the power system stabilizers (PSSs), and network-node agents such as the generation nodes and load nodes connected with transmission lines. An optimal index is presented to evaluate the performance of damping controllers to the system's inter-area oscillation with respect to the information-layer topology. Then, the authors show that the inter-area information exchange is more powerful than the exchange within a given area to control the inter-area low frequency oscillation based on simulation analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. P. Lekkas, N. M. Avouris, and G. K. Papakonstantinou, Development of distributed problem solving systems for dynamic environments, IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man, and Cybemetics, 1995, 25(3): 400–414.
S. D. J. McArthur, E. M. Davidson, V. M. Catterson, A. L. Dimeas, N. D. Hatziargyriou, F. Ponci, and T. Funabashi, Multi-agent systems for power engineering applications part I: Concepts, approaches, and technical challenges, IEEE Trans. on Power Systems, 2007, 22(4): 1743–1752.
S. D. J. McArthur, E. M. Davidson, V. M. Catterson, A. L. Dimeas, N. D. Hatziargyriou, F. Ponci, and T. Funabashi, Multi-agent systems for power engineering applications part II: Technologies, standards, and tools for building multi-agent systems, IEEE Trans. on Power Systems, 2007, 22(4): 1753–1758.
G. P. Azevedo, B. Feijo, and M. Costa, Control centers evolve with agent technology, IEEE Computer Applications in Power, 2000, 13: 48–53.
C. S. K. Yeung, A. S. Y. Poon, and F. F. Wu, Game theoretical multi-agent modelling of coalition formation for multilateral trades, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 1999, 14(3): 929–934.
A. C. Xue and Y. G. Hong, Non-smooth agent-based dynamics of strategic bidding with linear supply function, in Proceedings of the Chinese Control conference, June 25–29, Zhangjiajie, Hunan, China, 2007, 6: 742–746.
Y. Tomita, C. Fukui, H. Kudo, J. Koda, and K. Yabe, A cooperative protection system with an agent model, IEEE Trans. Power Del., 1998, 13(4): 1060–1066.
R. Giovanini, K. Hopkinson, D. V. Coury, and J. S. Thorp, A primary and backup cooperative protection system based on wide area agents, IEEE Trans. Power Del., 2006, 21(3): 1222–1230.
J. A. Hossack, J. Menal, S. D. J. McArthur, and J. R. McDonald, A multi-agent architecture for protection engineering diagnostic assistance, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2003, 18(2): 639–647.
S. D. J. McArthur, S. M. Strachan, and G. Jahn, The design of a multi-agent transformer condition monitoring system, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2004, 19(4): 1845–1852.
S. D. J. McArthur, C. D. Booth, J. R. McDonald, and I. T. McFadyen, An agent-based anomaly detection architecture for condition monitoring, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2005, 20(4): 1675–1682.
H. F. Wang, H. Li, and H. Chen, Coordinated secondary voltage control to eliminate voltage violations in power system contingencies, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2003, 18(2): 588–595.
M. E. Baran and I. M. El-Markabi, A multi-agent-based dispatching scheme for distributed generators for voltage support on distribution feeders, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2007, 22(1): 52–59.
T. Nagata and H. Sasaki, A multi-agent approach to power system restoration, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2002, 17(2): 457–462.
E. E. Mangina, S. D. J. McArthur, J. R. McDonald, and A. Moyes, A multi-agent system for monitoring industrial gas turbine start-up sequences, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2001, 16(3): 396–401.
M. M. Nordman and M. Lehtonen, Distributed agent-based state estimation for electrical distribution networks, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2005, 2(2): 652–658.
D. P. Buse, P. Sun, Q. H. Wu, and J. Fitch, Agent-based substation automation, IEEE Power Energy Mag., 2003, 1(2): 50–55.
C. C. Liu, J. Jung, G. T. Heydt, V. Vittal, and A. G. Phadke, The strategic power infrastructure defense (SPID) system, a conceptual design, IEEE Control Syst. Mag., 2000, 20(4): 40–52.
H. Ni, G. T. Heydt, and L. Mili. Power system stability agents using robust wide area control, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., 2002, 17(4): 1123–1131.
M. E. Aboul-Ela, A. A. Sallam, J. D. McCalley, and A. A. Fouad, Damping controller design for power system oscillations using global signals, IEEE Trans. Power Systems, 1996, 11(2): 767–773.
T. Hiyama, M. Kawakita, and H. Ono, Multi-agent based wide area stabilization control of power systems using power system stabilizer, Int. Conf. on Power System Technology, 2004, 1239-1244
P. Kundur, Power System Stability and Control, Mc-Graw-Hill, New York, 1992.
A. G. Phadke, Synchronised phasor measurements–a historical overview, in Proc.IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conf. Exhib., Asia Pacific, 2000, 476–479.
IEEE Std. C37.118-2005, (Revision of IEEE Std 1344–1955) IEEE Standard for Synchrophasors for Power Systems, 2005.
J. H. Chow, J. J. Sanchez-Gasca, H. Ren, and S. Wang, Power system damping controller design using multiple input signals, IEEE Contr. Syst. Mag., 2000, 20(4): 82–90.
X. Xie, J. Xiao, C. Lu, and Y. Han, Wide-area stability control for damping interarea oscillations of interconnected power systems, IEEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib., 2006, 153(5): 507–514.
C. R. Houck, J. A. Jones, and M. G. Kay, A genetic algorithm for function optimization: A Matlab implementation, NCSU-IE TR 95-09, 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants Nos. 50707035, 50595411, 60425307, 60221301, and 50607005, in part by the 111 project (B08013) and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT0515) and in part by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-05-0216).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, A., Hong, Y. Performance evaluation for damping controllers of power systems based on multi-agent models. J Syst Sci Complex 22, 77–87 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-009-9148-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-009-9148-8