Abstract
Background
Locking plates have been used increasingly for the management of distal humerus fractures. Studies that compare patient-centered outcomes between locking and non-locking fixation for distal humerus fractures are lacking.
Questions/Purposes
The purposes of this study were to (1) determine whether locking plates offered superior fixation compared with non-locking plates for distal humerus fractures, (2) determine whether the use of locking plates was associated with fewer complications, and (3) determine whether locking plate use resulted in superior radiographic outcome compared with non-locking plates. Lastly, another aim was to determine the average cost difference associated with locking plate use versus non-locking plate use for distal humerus fracture fixation.
Patients and Method
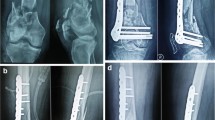
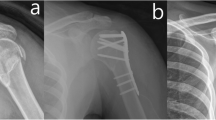
Demographic, clinical, and radiographic data including loss of fixation, range of motion, rate of infection, nonunion and reoperation, as well as measures of fixation were collected retrospectively and compared on 96 patients with surgically treated AO type 13C distal humerus fractures (65 locking, 31 non-locking) at 6-week and 6-month follow-up. Average costs of locking and non-locking constructs were calculated and compared.
Results
Three in 96 (3.1%) of all cases experienced loss of fixation, with no difference between the two groups. There was no difference between locking and non-locking groups with regard to the rate of nonunion, infection, and reoperation at 6 weeks and 6 months. On average, locking plate constructs were 348% more expensive than non-locking constructs.
Conclusion
While there are some significant differences in radiographic parameters and cost between locking and non-locking constructs for internal fixation of intra-articular distal humerus fractures, there were no statistically significant differences in clinical outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnander MW, Reeves A, MacLeod IA, Pinto TM, Khaleel A.A biomechanical comparison of plate configuration in distal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(5):332–6.
Brown RF, Morgan RG. Intercondylar T-shaped fractures of the humerus. Results in ten cases treated by early mobilization. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1971;53(3):425–8
Hahnloser D, Platz A, Amgwerd M, Trentz O: Internal fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal dislocation: Pi-plate or two 1/4 tube plates? A prospective randomized study. J Trauma 1999;47:760–765.
Haidukewych GJ, Ricci W. Locked plating in orthopaedic trauma: a clinical update. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2008;16(6):347–55 (review).
Handschin AE, Cardell M, Contaldo C, Trentz O, Wanner GA: Functional results of angular-stable plate fixation in displaced proximal humeral fractures. Injury 2008;39:306–313.
Helfet DL, Hotchkiss RN. Internal fixation of the distal humerus: a biomechanical comparison of methods. J Orthop Trauma 1990;4:224–260.
Helfet DL, Schmeling GJ. Bicondylar intraarticular fracture of the distal humerus in adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;292:26–36.
Jacobson SR, Glisson RR, Urbaniak JR. Comparison of distal humerus fracture fixation: a biomechanical study. J South Orthop Assoc. 1997;6(4):241–249 (Winter).
Jiang R, Luo CF, Wang MC, Yang TY, Zeng BF: A comparative study of Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) fixation and two-incision double plating for the treatment of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Knee 2008;15:139–143.
Korner J, Diederichs G, Arzdorf M et al. A biomechanical evaluation of methods of distal humerus fracture fixation using locking compression plates versus conventional reconstruction plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(5):286–93.
Koshimune M, Kamano M, Takamatsu K, Ohashi H: A randomized comparison of locking and non-locking palmar plating for unstable Colles’ fractures in the elderly. J Hand Surg [Br] 2005;30:499–503.
Sanchez-Sotelo J, Torchia ME, O’Driscoll SW. Complex distal humerus fractures:internal fixation with a principle-based parallel-plating technique. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 2 Pt 1:31–46.
Sanchez-Sotelo J, Torchia ME, O’Driscoll SW. Complex distal humerus fractures:internal fixation with a principle-based parallel-plating technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:961–969.
Schemitsch EH, Tencer AF, Henley MB. Biomechanical evaluation of methods of internal fixation of the distal humerus. J Orthop Trauma 1994;8:468–475.
Schuster I, Korner J, Arzdorf M, Schwieger K, Diederichs G, Linke B. Mechanical comparison in cadaver specimens of three different 90-degree double-plate osteosyntheses for simulated C2-type distal humerus fractures with varying bone densities. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(2):113–20.
Wong AS, Baratz ME.Elbow fractures: distal humerus. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2009;34(1):176–90.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Yanna Song for statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (WTO) has received funding from The Southeast Fracture Consortium.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the reporting of these cases, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participating in the study was obtained.
Level of Evidence: Level III, therapeutic study. See the guidelines for authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berkes, M., Garrigues, G., Solic, J. et al. Locking and Non-locking Constructs Achieve Similar Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes for Internal Fixation of Intra-articular Distal Humerus Fractures. HSS Jrnl 7, 244–250 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-011-9219-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-011-9219-y