Abstract
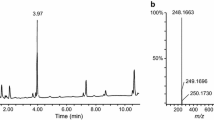
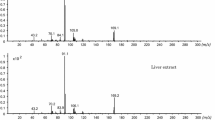
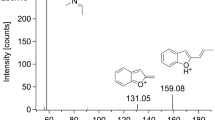
A couple bought “aroma liquid” and “bath salt” type drugs at a dubious drug shop. Both of them orally took the liquid type drug; although the male subject showed no symptoms, the female subject suffered shivering, convulsions, and low levels of consciousness. The woman was taken to an emergency hospital to receive intensive medical treatment, but died about 20 h after admission. The aroma liquid solution, and the antemortem blood and urine collected during medical treatment at the hospital were brought to our laboratory by the police for analysis of the causative drug(s). In addition, a sample of postmortem femoral vein blood was collected from the cadaver. After some screening tests, we finally identified PV9 (α-POP) in all specimens by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS). The concentration of PV9 was 18.3 mg/ml in the aroma liquid solution, 45.7 ng/ml in the antemortem blood, 20.3 ng/ml in the antemortem urine, and 180 ng/ml in the postmortem femoral vein blood. The concentrations in antemortem blood and urine and in postmortem blood were greatly lowered by dilution during the intensive medical treatment, including intravenous drip infusion of a large volume of solution. The probable coexistence of a β-hydroxyl metabolite was also investigated by mass chromatography and analysis of fragment ions of the product ion spectrum obtained by LC–MS–MS. To our knowledge, this is the first reported identification and quantitation of PV9 in human specimens in a fatal PV9 poisoning case.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kikura-Hanajiri R, Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Goda Y (2013) Changes in the prevalence of synthetic cannabinoids and cathinone derivatives in Japan until early 2012. Forensic Toxicol 31:44–53
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) Two new-type cannabimimetic quinolinyl carboxylates, QUPIC and QUCHIC, two new cannabimimetic carboxamide derivatives, ADB-FUBINACA and ADBICA, and five synthetic cannabinoids detected with a thiophene derivative α-PVT and an opioid receptor agonist AH-7921 identified in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 31:223–240
Swortwood MJ, Boland DM, DeCaprio AP (2013) Determination of 32 cathinone derivatives and other designer drugs in serum by comprehensive LC–QQQ–MS/MS analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:1383–1397
Shima N, Katagi M, Kamata H, Matsuta S, Nakanishi K, Zaitsu K, Kamata T, Nishioka H, Miki A, Tatsuno M, Sato T, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K (2013) Urinary excretion and metabolism of the newly encountered designer drug 3,4-dimethylmethcathinone in humans. Forensic Toxicol 31:101–112
Zaitsu K, Katagi M, Tatsuno M, Tsuchihashi H, Ishii A (2014) Recently abused synthetic cathinones, α-pyrrolidinophenone derivatives: a review of their pharmacology, acute toxicity, and metabolism. Forensic Toxicol 32:1–8
Kudo K, Ishida T, Hikiji W, Hayashida M, Uekusa K, Usumoto Y, Tsuji A, Ikeda N (2009) Construction of calibration-locking databases for rapid and reliable drug screening by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol 27:21–31
Cayman Chemical (2014) Cayman spectral library. https://www.caymanchem.com/app/template/SpectralLibrary.vm. Accessed Jan 2014
Usui K, Hayashizaki Y, Hashiyada M, Funayama M (2012) Rapid drug extraction from human whole blood using a modified QuEChERS extraction method. Legal Med 14:286–296
Wurita A, Suzuki O, Hasegawa K, Gonmori K, Minakata K, Yamagishi I, Nozawa H, Watanabe K (2013) Sensitive determination of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol and diethylene glycol in human whole blood by isotope dilution gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, and the presence of appreciable amounts of the glycols in blood of healthy subjects. Forensic Toxicol 31:272–280
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Shimokawa Y, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Aritake K, Urade Y, Goda Y (2014) Characterization of four new designer drugs, 5-chloro-NNEI, NNEI indazole analog, α-PHPP and α-POP, with 11 newly distributed designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Sci Int 243:1–13
Shima N, Katagi M, Kawata H, Matsuta S, Sasaki K, Kamata T, Nishioka H, Miki A, Tatsuno M, Zaitsu K, Ishii A, Sato T, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K (2014) Metabolism of the newly encountered designer drug α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone in humans: identification and quantitation of urinary metabolites. Forensic Toxicol 32:59–67
Marinetti LJ, Antonides HM (2013) Analysis of synthetic cathinones commonly found in bath salts in human performance and postmortem toxicology: method development, drug distribution and interpretation of results. J Anal Toxicol 37:135–146
Wyman JF, Lavins ES, Engelhart D, Armstrong EJ, Snell KD, Boggs PD, Taylor SM, Norris RN, Miller FP (2013) Postmortem tissue distribution of MDPV following lethal intoxication by “bath salts”. J Anal Toxicol 37:182–185
Namera A, Urabe S, Saito T, Torikoshi-Hatano A, Shiraishi H, Arima Y, Nagao M (2013) A fatal case of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone poisoning: coexistence of α-pyrrolidinobutiophenone and α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone in blood and/or hair. Forensic Toxicol 31:338–343
Saito T, Namera A, Osawa M, Aoki H, Inokuchi S (2013) SPME–GC–MS analysis of α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone in blood in a fatal poisoning case. Forensic Toxicol 31:328–332
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasegawa, K., Wurita, A., Minakata, K. et al. Identification and quantitation of a new cathinone designer drug PV9 in an “aroma liquid” product, antemortem whole blood and urine specimens, and a postmortem whole blood specimen in a fatal poisoning case. Forensic Toxicol 32, 243–250 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-014-0230-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-014-0230-0