Abstract
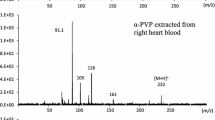
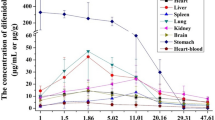
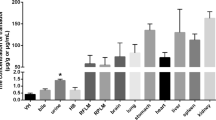
We investigated the distribution of zolpidem throughout femoral vein blood, urine, stomach contents, the brain, lung, liver, and kidney in five autopsy cases using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Four out of the five cases showed toxic levels of zolpidem. Only one case showed a lethal blood level. The zolpidem concentrations in solid organ tissues were generally several times higher than that in blood. Among four solid organ tissues, the differences in concentration were not drastic; they were similar or within the same order of magnitude except for one case. These results suggested that measurements of zolpidem concentrations in multiple solid organ tissues are useful for estimating whether zolpidem poisoning is related to the cause of death, especially when blood cannot be collected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baselt RC (2004) Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man, 7th edn. Biomedical Publications, Foster City, pp 1212-1214
Garnier R, Guerault E, Muzard D, Azoyan P, Chaumet-Riffaud A, Efthymiou M (1994) Acute zolpidem poisoning—analysis of 344 cases. Clin Toxicol 32:391–404
Arbilla S, Depoortere H, George P, Langer Z (1985) Pharmacological profile of the imidazopyridine zolpidem at benzodiazepine receptors and electrocorticogram in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 330:248–251
Depoortere H, Zivkovic B, Lloyd KG, Sanger DJ, Perrault G, Langer SZ, Bartholini G (1986) Zolpidem, a novel nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic. I. Neuropharmacological and behavioral effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:649–658
Nicholson AN, Pascoe PA (1986) Hypnotic activity of an imidazo-pyridine (zolpidem). Br J Clin Pharmacol 21:205–211
Ascalone V, Flaminio L, Guinebault P, Thenot JP, Morselli PL (1992) Determination of zolpidem, a new sleep-inducing agent, and its metabolites in biological fluids: pharmacokinetics, drug metabolism and overdosing investigations in humans. J Chromatogr B 581:237–250
Pichard L, Gillet G, Bonfils C, Domergue J, Thenot J, Maurel P (1995) Oxidative metabolism of zolpidem by human liver cytochrome P450s. Drug Metab Dispos 23:1253–1262
von Moltke LL, Greenblatt DJ, Granada BW, Duan S, Grassi JM, Venkatakrishnan K, Harmatz JS, Shader RI (1999) Zolpidem metabolism in vitro: responsible cytochromes, chemical inhibitors, and in vivo correlations. Br J Clin Pharmacol 48:89–97
Lheureux P, Debailleul G, De Witte O, Askenasi R (1990) Zolpidem intoxication mimicking narcotic overdose: response to flumazenil. Hum Exp Toxicol 9:105–107
Lichtenwalner M, Tully R (1997) A fatality involving zolpidem. J Anal Toxicol 21:567–569
Levine B, Eu SC, Smialek JE (1999) Zolpidem distribution in postmortem cases. J Forensic Sci 44:369–371
Gock SB, Wong SHY, Nuwayhid N, Venuti SE, Kelley PD, Teggatz JR, Jentzen JM (1999) Acute zolpidem overdose—report of two cases. J Anal Toxicol 23:559–562
Takayasu T, Kondo T (2005) Assessment of a drug screening kit Instracheck for human samples. Jpn J Forensic Toxicol 23:209–213
Ohshima T, Takayasu T, Ohtsuji M, Sato Y, Kondo T (1998) Suicide due to multiple-drug overdose caused mainly by amitriptyline, nortriptyline and amobarbital. Jpn J Forensic Toxicol 16:75–84
Takayasu T, Kondo T, Sato Y, Ohshima T (2001) A fatal intoxication case due to haloperidol, biperidin and levomepromazine: their distribution in body fluids and organs. Jpn J Forensic Toxicol 19:58–64
Takayasu T, Hayashi T, Ishida Y, Nosaka M, Mizunuma S, Miyashita T, Kawaguchi M, Kimura A, Kondo T (2008) A fatal intoxication from ingestion of 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (MCPA). J Anal Toxicol 32:187–191
Tracqui A, Kintz P, Mangin P (1993) A fatality involving two unusual compounds—zolpidem and acepromazine. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 14:309–312
Meeker JE, Som CW, Macapagal EC, Benson PA (1995) Zolpidem tissue concentrations in a multiple-drug related death involving Ambien. J Anal Toxicol 19:531–534
Winek CL, Wahba WW, Janssen JK, Rozin L, Rafizadeh V (1996) Acute overdose of zolpidem. Forensic Sci Int 78:165–168
Keller T, Schneider A, Tutsuch-Bauer E (1999) GC/MS determination of zolpidem in postmortem specimens in a voluntary intoxication. Forensic Sci Int 106:103–108
Winek CL, Wahba WW, Winek CLJr, Balzer TW (2001) Drug and chemical blood-level data 2001. Forensic Sci Int 122:107–123
Pelissier-Alicot AL, Gaulier JM, Champsaur P, Marquet P (2003) Mechanisms underlying postmortem redistribution of drugs: a review. J Anal Toxicol 27:533–544
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takayasu, T., Ishida, Y., Kimura, A. et al. Distribution of zolpidem in body fluids and organ tissues in five autopsy cases. Forensic Toxicol 26, 80–84 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-008-0055-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-008-0055-9