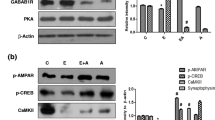
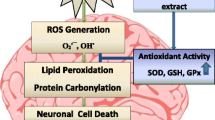
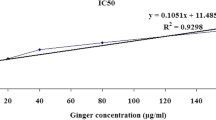
Abstract
As a direct neurotoxin, ethanol exposure is associated with nerve damage and dysfunction of central nervous system (CNS) and induced obvious neurotoxicity by increasing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, activation of endogenous apoptotic as well as necrotic signals, and other molecular mechanisms. The previous studies had demonstrated that natural herbal medicine offers protective effectiveness on ethanol-induced nerve cell damage. Danshen and its extracts have been known to have an antioxidant property and neuroprotective effects. However, the protective effects of Danshen formula granule and salvianic acid A on ethanol-induced neurotoxicity remain unknown. In this study, we found that the Danshen formula granule and salvianic acid A significantly inhibited the ethanol-induced cell death, blocked LDH release, and reduced dendritic spine loss. Furthermore, the intracellular ROS, MDA production, and ethanol-induced apoptosis were significantly ameliorated with Danshen formula granule and salvianic acid A pretreatment by increasing the antioxidant enzymatic activity of CAT, SOD and GSH-Px, and inhibiting apoptotic pathways. In addition, Danshen formula granule and salvianic acid A pretreatment obviously inhibit the apoptotic pathways by regulating the protein expression of Bcl-2, Bax, and Caspase-3. In conclusion, our data demonstrated that the Danshen formula granule and salvianic acid A provide a significantly protective effectiveness against ethanol-induced neurotoxicity, which might be a potential therapeutic drug for ethanol-induced neurological disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casswell S, Thamarangsi T (2009) Reducing harm from alcohol: call to action. Lancet 373:2247–2257
Fang SQ, Wang YT, Wei JX, Shu YH, Xiao L, Lu XM (2016) Beneficial effects of chlorogenic acid on alcohol-induced damage in PC12 cells. Biomed Pharmacother 79:254–262
Zahr NM, Kaufman KL, Harper CG (2011) Clinical and pathological features of alcohol-related brain damage. Nature reviews. Neurology 7:284–294
Acosta D, Stege TE, Erickson CK (1986) Cytotoxicity of ethanol in primary cultures of rat midbrain neurons. Toxicol Lett 30:231–235
Huang J, Xiao L, Wei JX, Shu YH, Fang SQ, Wang YT et al (2017) Protective effect of arctigenin on ethanol-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Mol Med Rep 15:2235–2240
Liu L, Cao JX, Sun B, Li HL, Xia Y, Wu Z et al (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells inhibition of chronic ethanol-induced oxidative damage via upregulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt and modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation in PC12 cells and neurons. Neuroscience 167:1115–1124
Tian H, Ye X, Hou X, Yang X, Yang J, Wu C (2016) SVCT2, a potential therapeutic target, protects against oxidative stress during ethanol-induced neurotoxicity via JNK/p38 MAPKs, NF-kappaB and miRNA125a-5p. Free Radical Biol Med 96:362–373
Shah SA, Yoon GH, Kim MO (2015) Protection of the developing brain with anthocyanins against ethanol-induced oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol 51:1278–1291
Young C, Klocke BJ, Tenkova T, Choi J, Labruyere J, Qin YQ et al (2003) Ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis in vivo requires BAX in the developing mouse brain. Cell Death Differ 10:1148–1155
Zhou L, Zuo Z, Chow MS (2005) Danshen: an overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol 45:1345–1359
Ouyang X, Takahashi K, Komatsu K, Nakamura N, Hattori M, Baba A et al (2001) Protective effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza on angiotensin II-induced hypertrophic responses in neonatal rat cardiac cells. Jpn J Pharmacol 87:289–296
Wang D, Fan G, Wang Y, Liu H, Wang B, Dong J et al (2013) Vascular reactivity screen of Chinese medicine danhong injection identifies Danshensu as a NO-independent but PGI2-mediated relaxation factor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 62:457–465
Zhang XP, Jiang J, Yu YP, Cheng QH, Chen B (2010) Effect of Danshen on apoptosis and NF-kappaB protein expression of the intestinal mucosa of rats with severe acute pancreatitis or obstructive jaundice. Hepatobil Pancreat Dis Int 9:537–546
Gao LN, Yan K, Cui YL, Fan GW, Wang YF (2015) Protective effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Carthamus tinctorius extract against lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 21:9079–9092
Bao D, Wang J, Liu J, Qin T, Liu H (2019) The attenuation of HIV-1 Tat-induced neurotoxicity by Salvianic acid A and Danshen granule. Int J Biol Macromol 124:863–870
Chang CC, Chang YC, Hu WL, Hung YC (2016) Oxidative STRESS and Salvia miltiorrhiza in aging-associated cardiovascular diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:4797102
Su CY, Ming QL, Rahman K, Han T, Qin LP (2015) Salvia miltiorrhiza: traditional medicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacology. Chin J Nat Med 13:163–182
Liu T, Jin H, Sun QR, Xu JH, Hu HT (2010) The neuroprotective effects of tanshinone IIA on beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in rat cortical neurons. Neuropharmacology 59:595–604
Shi LL, Yang WN, Chen XL, Zhang JS, Yang PB, Hu XD et al (2012) The protective effects of tanshinone IIA on neurotoxicity induced by beta-amyloid protein through calpain and the p35/Cdk5 pathway in primary cortical neurons. Neurochem Int 61:227–235
Yu H, Yao L, Zhou H, Qu S, Zeng X, Zhou D et al (2014) Neuroprotection against Abeta25-35-induced apoptosis by Salvia miltiorrhiza extract in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Int 75:89–95
Wang XJ, Xu JX (2005) Salvianic acid A protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against MPP+-induced cytotoxicity. Neurosci Res 51:129–138
Bao D, Wang J, Pang X, Liu H (2017) Protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress-induced cytotoxicity in rat pheochromocytoma (PC-12) cells. Molecules 22:11
Frotscher M, Heimrich B (1995) Lamina-specific synaptic connections of hippocampal neurons in vitro. J Neurobiol 26:350–359
Stoppini L, Buchs PA, Muller D (1991) A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods 37:173–182
Li J, Cheng J (2018) Apolipoprotein E4 exacerbates ethanol-induced neurotoxicity through augmentation of oxidative stress and apoptosis in N2a-APP cells. Neurosci Lett 665:1–6
Ikonomidou C, Bittigau P, Ishimaru MJ, Wozniak DF, Koch C, Genz K et al (2000) Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrome. Science 287:1056–1060
Romero AM, Renau-Piqueras J, Pilar Marin M, Timoneda J, Berciano MT, Lafarga M et al (2013) Chronic alcohol alters dendritic spine development in neurons in primary culture. Neurotox Res 24:532–548
Korkotian E, Botalova A, Odegova T, Segal M (2015) Chronic exposure to alcohol alters network activity and morphology of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurotoxicology 47:62–71
Haorah J, Ramirez SH, Floreani N, Gorantla S, Morsey B, Persidsky Y (2008) Mechanism of alcohol-induced oxidative stress and neuronal injury. Free Radical Biol Med 45:1542–1550
Ramachandran V, Watts LT, Maffi SK, Chen J, Schenker S, Henderson G (2003) Ethanol-induced oxidative stress precedes mitochondrially mediated apoptotic death of cultured fetal cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res 74:577–588
Luo J (2014) Autophagy and ethanol neurotoxicity. Autophagy 10:2099–2108
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2:647–656
Vaudry D, Rousselle C, Basille M, Falluel-Morel A, Pamantung TF, Fontaine M et al (2002) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide protects rat cerebellar granule neurons against ethanol-induced apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6398–6403
Takasu T (1997) The action by ethanol and pathogenetic mechanism in chronic alcoholic neurological disorders. Nihon Rinsho Jpn J Clin Med 55(Suppl):71–75
Zhu H, Chen Z, Ma Z, Tan H, Xiao C, Tang X et al (2017) Tanshinone IIA protects endothelial Cells from H(2)O(2)-induced injuries via PXR activation. Biomol Ther 25:599–608
Pohland M, Glumm R, Wiekhorst F, Kiwit J, Glumm J (2017) Biocompatibility of very small superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in murine organotypic hippocampal slice cultures and the role of microglia. Int J Nanomed 12:1577–1591
Tomasini MC, Borelli AC, Beggiato S, Tanganelli S, Loche A, Cacciaglia R et al (2016) GET73 prevents ethanol-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons. Alcohol Alcohol 51:128–135
Moon KH, Tajuddin N, Brown J 3rd, Neafsey EJ, Kim HY, Collins MA (2014) Phospholipase A2, oxidative stress, and neurodegeneration in binge ethanol-treated organotypic slice cultures of developing rat brain. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38:161–169
Harris BR, Gibson DA, Prendergast MA, Blanchard JA, Holley RC, Hart SR et al (2003) The neurotoxicity induced by ethanol withdrawal in mature organotypic hippocampal slices might involve cross-talk between metabotropic glutamate type 5 receptors and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1724–1735
Guo C, Sun L, Chen X, Zhang D (2013) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regener Res 8:2003–2014
Berry MD, Boulton AA (2003) Apoptosis and human neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:197–198
Caroppi P, Sinibaldi F, Fiorucci L, Santucci R (2009) Apoptosis and human diseases: mitochondrion damage and lethal role of released cytochrome C as proapoptotic protein. Curr Med Chem 16:4058–4065
Ekshyyan O, Aw TY (2004) Apoptosis: a key in neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Neurovasc Res 1:355–371
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the Key Science and Technology Fund of Henan Province in China (no. 182102310120), the Medical Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province in China (no. SB201902030), project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (no. 2019M652542).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors of this paper declare no conflicts interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chen, H., Yang, Y. et al. Danshen formula granule and salvianic acid A alleviate ethanol-induced neurotoxicity. J Nat Med 74, 399–408 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-019-01379-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-019-01379-4