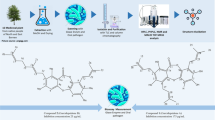
Abstract
Four new galloyl-oxygen-diphenyl (GOD)-type ellagitannins, brambliins A–D (1–4), were isolated from the leaves of Rubus suavissimus. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analyses and the absolute configurations of 1–4 were determined by chemical and phytochemical evidence. These GOD-type ellagitannins inhibited the formation of dental plaque, which is beneficial for oral hygiene.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Z, Schwimer J, Liu D, Lewis J, Greenway FL, York DA, Woltering EA (2006) Gallic acid is partially responsible for the antiangiogenic activities of Rubus leaf extract. Phytother Reserch 20:806–813
Takasugi M, Kitagawa T, Kato M, Maeda N, Nagata N, Niwa J, Shimada K (2008) Correlation among suppression of leukotriene B4 release, radical scavenging activity and polyphenol contents of commercial tea extract. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 55:87–94
Li H, Tanaka T, Zhang Y-J, Yang C-R, Kouno I (2007) Rubusuaviins A-F; monomeric and oligomeric ellagitannins from chinese sweet tea and their α-amylase inhibitory activity. Chem Pharm Bull 55:1325–1331
Venkata SPC, Rafael ISM, Indra P (2012) Chemical constituents from the polar fraction of Rubus suavissimus. Org Chem 1:1–6
Shimizu K, Maeda Y, Osawa K, Shimura S (2004) Deodorizing effect of Rubus suavissimus extract against allyl methyl sulfide. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 51:205–209
Scully C, Porter S, Greenman J (1994) What to do about halitosis. BMJ 308:217–218
Cortelli JR, Barbosa MDS, Westphal MA (2008) Halitosis: a review of associated factors and therapeutic approach. Braz Oral Res 22:44–54
Shibata H, Nakahara K, Ono H, Miyagawa K (2000) Japan Patent JP3084128B2
Sawamura S, Tonosaki Y, Hamada S (1992) Inhibitory effects of ellagic ecid on glucosyl-transferases from mutans streptococci. Biosci Biotech Biochem 56:766–768
Matsunaga T, Nakahara A, Minnatul K, Noiri Y, Ebisu S, Kato A, Azakami H (2010) The inhibitory effects of catechins on biofilm formation by the periodontopathogenic bacterium, Eikenella corrodens. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:2445–2450
Yoshida T, Maruyama Y, Okuda T, Memon U, Shingu T (1982) Gemin B and C dimeric ellagitannins from Geum japonicum. Chem Pharm Bull 30:4245–4248
Okuda T, Yoshida T, Hatano T, Yazaki K, Ashida M (1982) Ellagitannins of the casuarinaceae; Stachyuraceae and Myrtaceae. Phytochemistry 21:2871–2874
Hussein SAM, Ayoub NA, Nawwar MAM (2003) Caffeoyl sugar esters and an ellagitannin from Rubus sanctus. Phytochemistry 63:905–911
Nasser ALM, Carli CBA, Rodrigues CM, Maia DCG, Carlos IZ, Eberlin MN, Hiruma-Lima CA, Vilegas W (2008) Identification of ellagic acid derivatives in methanolic extracts from Qualea species. Z Naturforsch 63:794–800
Saijo R, Nonoka G, Nishioka I (1989) Tannins and related compounds. LXXXVII. isolation and characterization of four new hydrolyzable tannins from the leaves of Mallotus repandus. Chem Pharm Bull 37:2624–2630
Yoshida T, Feng W-S, Okuda T (1992) Tannins and related polyphenols of rosaceous medicinal plants. XII. Roshenins A-E; dimeric hydrolyzable tannins from Rosa henryi BOUL. Chem Pharm Bull 40:1997–2001
Murakami T, Hirano K, Yoshikawa M (2001) Medicinal foodstuffs. XXIII. structures of new oleanane-type triterpene oligoglycosides; basellasaponins A; B; C; and D; from the fresh aerial parts of Basella rubra L. Chem Pharm Bull 49:776–779
Gupta RK, Al-Shafi SMK, Layden K, Haslam E (1982) The metabolism of gallic acid and hexahydroxydiphenic acid in plants. Part 2. Esters of (S)-hexahydroxydiphenic acid with d-glucopyranose (4 C 1). J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1:2525–2534
Okuda T, Yoshida T, Hatano T, Koga T, Toh N, Kuriyama K (1982) Circular dichroism of hydrolysable tannins-I ellagitannins and gallotannins. Tetrahedron Lett 23:3937–3940
Tanaka T, Nonaka G, Nishioka I (1985) Tannins and related compounds. Part 28. Revision of the structures of sanguiins H-6, H-2, and H-3, and isolation and characterization of sanguiin H-11, a novel tetrameric hydrolyzable tannin, and seven related tannins, from Sanguisorba officinalis. J Chem Res Synop 6:176–177
Nonaka G, Tanaka T, Nishioka J (1982) Tannins and related compounds. Part 3. A new phenolic acid; sanguisorbic acid dilactone, and three new ellagitannins; sanguiins H-1, H-2, and H-3, from Sanguisorba officinalis. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:1067–1073
Nakahara K, Kawabata S, Ono H, Ogura K, Tanaka T, Ooshima T, Hamada S (1993) Inhibitory effect of oolong tea polyphenols on glucosyltransferases of mutans streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:968–973
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Yoshiki Kashiwada and Mr. Kanji Niwa of Tokushima University for the measurement of CD spectra for structure determination. We also thank Prof. Xia Nianhe of South China Botanical Garden for plant determination.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakano, F., Miyoshi, S. & Murakami, T. New ellagitannins from Tiencha and their inhibitory activity against dental plaque. J Nat Med 71, 545–552 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1090-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1090-9