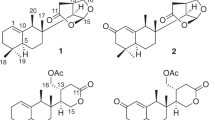
Abstract
A new aaptamine class alkaloid, designated 2-methoxy-3-oxoaaptamine (1), together with seven known aaptamines (2–8) were isolated from a marine sponge of Aaptos sp. as anti-mycobacterial substances against active and dormant bacilli. The chemical structure of 1 was determined on the basis of spectroscopic analysis. Compound 1 was anti-mycobacterial against Mycobacterium smegmatis in both active growing and dormancy-inducing hypoxic conditions with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 6.25 μg/ml, and compounds 2, 5, 6, and 7 showed anti-mycobacterial activities under hypoxic condition selectively, with MIC values of 1.5–6.25 μg/ml.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Idemyor V (2007) HIV and tuberculosis coinfection: inextricably linked liaison. J Natl Med Assoc 99:1414–1419
Global Tuberculosis report 2012 World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed on 10 November 2013
Wayne LG, Sohaskey CD (2001) Nonreplicating persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:139–163
Lim A, Eleuterio M, Hutter B, Murugasu-Oei B, Dick T (1999) Oxygen depletion-induced dormancy in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Bacteriol 181:2252–2256
Dick T, Lee BH, Murugasu-Oei B (1998) Oxygen depletion induced dormancy in Mycobacterium smegmatis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 163:159–164
Arai M, Sobou M, Vilchèze C, Baughn A, Hashizume H, Pruksakorn P, Ishida S, Matsumoto M, Jacobs WR Jr, Kobayashi M (2008) Halicyclamine A, a marine spongean alkaloid as a lead for anti-tuberculosis agent. Bioorg Med Chem 16:6732–6736
Arai M, Ishida S, Setiawan A, Kobayashi M (2009) Haliclonacyclamines, tetracyclic alkylpiperidine alkaloids, as anti-dormant mycobacterial substances from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Chem Pharm Bull 57:1136–1138
Pruksakorn P, Arai M, Kotoku N, Vilchèze C, Baughn AD, Moodley P, Jacobs WR Jr, Kobayashi M (2010) Trichoderins, novel aminolipopeptides from a marine sponge-derived Trichoderma sp., are active against dormant mycobacteria. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:3658–3663
Yamano Y, Arai M, Kobayashi M (2012) Neamphamide B, new cyclic depsipeptide, as an anti-dormant mycobacterial substance from a Japanese marine sponge of Neamphius sp. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:4877–4881
Kobayashi M, Kawazoe K, Kitagawa I (1989) Araguspongines B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and J, new vasodilative bis-1-oxaquinolizidine alkaloids from an Okinawan marine sponge, Xestospongia sp. Chem Pharm Bull 37:1676–1678
Nakamura H, Kobayashi J, Ohizumi Y, Hirata Y (1987) Physiologically active marine natural products from Prolifera. Part 10. Aaptamines. Novel benzo[de][1,6]naphthyridines from the Okinawan marine sponge Aaptos aaptos. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:173–176
Shubina LK, Makarieva TN, Dyshlovoy SA, Fedorov SN, Dmitrenok PS, Stonik VA (2010) Three new aaptamines from the marine sponge Aaptos sp. and their pro apoptotic properties. Nat Prod Commun 5:1881–1884
Calcul L, Longeon A, Mourabit AA, Guyot M, Bourguet-Kondracki ML (2003) Novel alkaloids of the aaptamine class from an Indonesian marine sponge of the genus Xestospongia. Tetrahedron 59:6539–6544
Nakamura H, Kobayashi J, Ohizumi Y, Hirata Y (1982) Isolation and structure of aaptamine, a novel heteroaromatic substance possessing α-blocking activity from the sea sponge Aaptos aaptos. Tetrahedron Lett 23:5555–5558
Pham CD, Hartmann R, Müller WEG, de Voogd N, Lai D, Proksch P (2013) Aaptamine derivatives from the Indonesian sponge Aaptos suberitoides. J Nat Prod 76:103–106
Abate G, Aseffa A, Selassie A, Goshu S, Fekade B, WoldeMeskal D, Miörner H (2004) Direct colorimetric assay for rapid detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol 42:871–873
Rustad TR, Harrell MI, Liao R, Sherman DR (2008) The enduring hypoxic response of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS One 3:e1502
Wedge DE, Nagle DG (2000) A new 2D-TLC bioautography method for the discovery of novel antifungal agents to control plant pathogens. J Nat Prod 63:1050–1054
Runyoro DKB, Matee MIN, Ngassapa OD, Joseph CC, Mbwambo ZH (2006) Screening of Tanzanian medicinal plants for anti-candida activity. BMC Complement Altern Med 6:11–20
Pettit GR, Hoffmann H, McNulty J, Higgs KC, Murphy A, Molloy DJ, Herald DL, Williams MD, Pettit RK, Doubek DL, Hooper JNA, Albright L, Schmidt JM, Chapuis JC, Tackett LP (2004) Antineoplastic agents. 380. Isolation and x-ray crystal structure determination of isoaaptamine from the Republic of Singapore Hymeniacidon sp. and conversion to the phosphate prodrug hystatin 1. J Nat Prod 67:506–509
Larghi EL, Bohn ML, Kaufman TS (2009) Aaptamine and related products. Their isolation, chemical syntheses, and biological activity. Tetrahedron 65:4257–4282
Aoki S, Kong D, Suna H, Sowa Y, Sakai T, Setiawan A, Kobayashi M (2006) Aaptamine, a spongean alkaloid, activates p21 promoter in a p53-independent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:101–106
Fedoreev SA, Prokof’eva NG, Denisenko VA, Rebachuk NM (1988) Cytotoxic activity of aaptamines from suberitid marine sponges. Pharm Chem J 22:615–618
Gul W, Hammond NL, Yousaf M, Bowling JJ, Schinazi RF, Wirtz SS, Andrews GC, Cuevas C, Hamann MT (2006) Modification at the C9 position of the marine natural product isoaaptamine and the impact on HIV-1, mycobacterial, and tumor cell activity. Bioorg Med Chem 14:8495–8505
Pettit GR, Hoffmann H, Herald DL, Blumberg PM, Hamel E, Schmidt JM, Chang Y, Pettit RK, Lewin NE, Pearce LV (2004) Antineoplastic agents. 499. Synthesis of hystatin 2 and related 1H-benzo[de][1,6]-naphthyridinium salts from Aaptamine. J Med Chem 47:1775–1782
Wayne LG, Hayes LG (1996) An in vitro model for sequential study of shift down of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through two stages of nonreplicating persistence. Infect Immun 64:2062–2069
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Hoansha Foundation and Grant-in-Aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, M., Han, C., Yamano, Y. et al. Aaptamines, marine spongean alkaloids, as anti-dormant mycobacterial substances. J Nat Med 68, 372–376 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-013-0811-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-013-0811-y