Abstract
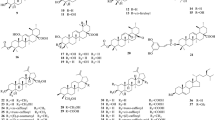
Oplopanax horridus (OH), or Devil’s club, is an ethnobotanical used by the indigenous people native to the Pacific Northwest of North America. There are three species in the genus Oplopanax, and OH is the only species that is distributed in North America. Compared with the extensive research on OH’s “cousin,” American ginseng, there is comparatively little reported about the chemical makeup and pharmacological effects of OH. Nevertheless, there has been some research over the past few years that shows promise for the future usage perspectives of OH. To date, 17 compounds were isolated and elucidated, including polyynes, glycosides, lignans, and polyenes, with most of the attention being paid to the polyynes. Gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) were used to determine the contents of volatile compounds and polyynes in the essential oil and extracts of OH. For the pharmacological studies, antibacterial and antidiabetes effects of polyynes were reported. Our recent study has focused more on the anticancer effects of OH and the involved mechanisms of action. In this review, we will summarize the research status in the botany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of OH.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lantz TC, Antos JA (2002) Clonal expansion in the deciduous understory shrub, devil’s club (Oplopanax horridus; Araliaceae). Can J Bot 80:1052–1062
Lantz TC, Swerhun K, Turner NJ (2004) Devil’s club (Oplopanax horridus): an ethnobotanical review. HerbalGram 62:33–48
Lin WN, Lu HY, Lee MS, Yang SY, Chen HJ, Chang YS, Chang WT (2010) Evaluation of the cultivation age of dried ginseng radix and its commercial products by using (1)H-NMR fingerprint analysis. Am J Chin Med 38:205–218
Chan PC, Peckham JC, Malarkey DE, Kissling GE, Travlos GS, Fu PP (2011) Two-year toxicity and carcinogenicity studies of Panax ginseng in Fischer 344 rats and B6C3F1 mice. Am J Chin Med 39:779–788
Wang CZ, Aung HH, Mehendale SR, Shoyama Y, Yuan CS (2010) High performance liquid chromatographic analysis and anticancer potential of Oplopanax horridus: comparison of stem and berry extracts. Fitoterapia 81:132–139
Taira S, Ikeda R, Yokota N, Osaka I, Sakamoto M, Kato M, Sahashi Y (2010) Mass spectrometric imaging of ginsenosides localization in Panax ginseng root. Am J Chin Med 38:485–493
Qi LW, Wang CZ, Yuan CS (2011) Isolation and analysis of ginseng: advances and challenges. Nat Prod Rep 28:467–495
Jang HI, Shin HM (2010) Wild Panax ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) protects against methotrexate-induced cell regression by enhancing the immune response in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Am J Chin Med 38:949–960
Reunova GD, Kats IL, Zhuravlev YN (2010) Genetic variation of Oplopanax elatus (Araliaceae) populations estimated using DNA molecular markers. Dokl Biol Sci 433:252–256
Luna T (2001) Propagation protocol for devil’s club (Oplopanax horridus). Native Plants J 2:106–108
Artiukova EV, Goncharov AA, Kozyrenko MM, Reunova GD, Zhuravlev IN (2005) Phylogenetic relationships of the Far Eastern Araliaceae inferred from ITS sequences of nuclear rDNA. Genetika 41:800–810
Wang GS, Yang XH, Xu JD (2004) Structures of four new triterpenoid saponins from the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. Yao Xue Xue Bao 39:354–358
Liu P-P, Li M, Kang T-G, Dou D-Q, Smith DC (2010) New lupane-type triterpenoid saponins from leaves of Oplopanax horridus (Devil’s Club). Nat Prod Commun 5:1019–1022
Zhao Y, Kang T, Dou D, Zhang F, Wang S (2008) Study on the HPLC fingerprints of Oplopanax horridus and the comparison of constituents between O. horridus and O. elatus Nakai. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao 19:546–548
Rodriguez M, Du GJ, Wang CZ, Yuan CS (2010) Letter to the editor: Panaxadiol’s anticancer activity is enhanced by epicatechin. Am J Chin Med 38:1233–1235
Si YC, Zhang JP, Xie CE, Zhang LJ, Jiang XN (2011) Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on proliferation and differentiation of rat hippocampal neural stem cells. Am J Chin Med 39:999–1013
Kobaisy M, Abramowski Z, Lermer L, Saxena G, Hancock RE, Towers GH, Doxsee D, Stokes RW (1997) Antimycobacterial polyynes of Devil’s Club (Oplopanax horridus), a North American native medicinal plant. J Nat Prod 60:1210–1213
Inui T, Wang Y, Nikolic D, Smith DC, Franzblau SG, Pauli GF (2010) Sesquiterpenes from Oplopanax horridus. J Nat Prod 73:563–567
Huang W, Yang J, Zhao J, Wang CZ, Yuan CS, Li SP (2010) Quantitative analysis of six polyynes and one polyene in Oplopanax horridus and Oplopanax elatus by pressurized liquid extraction and on-line SPE-HPLC. J Pharm Biomed Anal 53:906–910
Huang WH, Zhang QW, Wang CZ, Yuan CS, Li SP (2010) Isolation and identification of two new polyynes from a North American ethnic medicinal plant—Oplopanax horridus (Smith) Miq. Molecules 15:1089–1096
Xu LA, Wu XH, Zheng GR, Cai JC (2000) First total synthesis of optically active oplopandiol acetate, a potent antimycobacterial polyyne isolated from Oplopanax horridus. Chinese Chem Lett 11:213–216
Huang WH, Zhang QW, Meng LZ, Yuan CS, Wang CZ, Li SP (2011) Oplopanphesides A–C, three new phenolic glycosides from the root barks of Oplopanax horridus. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 59:676–679
Gruber JW, Kittipongpatana N, Bloxton JD, Der Marderosian A, Schaefer FT, Gibbs R (2004) High-performance liquid chromatography and thin-layer chromatography assays for Devil’s Club (Oplopanax horridus). J Chromatogr Sci 42:196–199
Garneau FX, Collin G, Gagnon H, Jean FI, Strobl H, Pichette A (2006) The essential oil composition of devil’s club, Oplopanax horridus J. E. Smith Miq. Flavour Fragr J 21:792–794
Li M, Dou D, Smith DC (2009) Studies on chemical constituents of volatile oil from the leaves of Oplopanax horridus by GC-MS. Zhongguo Xiandai Zhongyao 11:24–26
Hirai Y, Murayama T, Miyakoshi M, Hirono S, Isoda S, Ideura N, Ida Y, Shoji J, Wang G-S, Xu J-D (1995) Three new lupane type glycosyl esters from Oplopanax japonicus leaves. Nat Med 49:462–467
Wang GS, Zhao CF, Xu JD, Murayama T, Miyakoshi M, Junzo S (1994) Isolation and structure elucidation of new glycosides from the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai 2. Chem Res Chin Univ 10:285–290
Wang GS, Xu JD, Murayama T, Shoji J (1994) Isolation and structure elucidation of new glycosides from the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai 3. Chin Sci Bull 39:1969–1972
Wang GS, Xu JD, Ma XL, Sun YX, Liu JZ, Murayama T, Shoji J (1997) Chemical studies on glycosides in the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. (4). Chem Res Chin Univ 13:34–38
Wang GS, Chen YP, Xu JD, Murayama T, Shoji J (1996) Isolation and structure elucidation of cirensenosides O and P from the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. Yao Xue Xue Bao 31:940–944
Wang G, Xu J, Murayama T, Shoji J (1997) Isolation and structure elucidation of cirensenosides Q and R. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 22:101–103, 128
Wang G, Xu J (1999) Structures of four new triterpenoids saponins from the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai VII. Stud Plan Sci 6:52–57
Wang G, Xu J (1993) Chemical studies on the glycosides of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi 28:593–594
Wang GS, Zhao CF, Xu JD, Murayama T, Miyakoshi M, Junzo S (1994) Studies on the glycosides in the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. Chem Res Chin Univ 10:185–192
Wang GS, Meng Q, Xu JD, Chuenshan Z, Zhuanshi S (1996) Glycosides in the leaves of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi 31:522–524
Liu JP, Wu GX (1993) Chemical constituents of the roots of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. J Chin Pharm Sci 2:168
Zhang H, Wu G (1996) Chemical constituents from the stems of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. J Chin Pharm Sci 5:112
Yang MC, Kwon HC, Kim YJ, Lee KR, Yang HO (2010) Oploxynes A and B, polyacetylenes from the stems of Oplopanax elatus. J Nat Prod 73:801–805
Zhang S, Wang K (1980) The effect of Echinopanax elatum Nakai on experimental arthritis and the neuro-hypophyseal-adrenal system. Yao Xue Xue Bao 15:81–85
Mi HM, Li CG, Su ZW, Wang NP, Zhao JX, Jiang YG (1987) Studies on the chemical constituents and antifungal activities of essential oil from Oplopanax elatus Nakai. Yao Xue Xue Bao 22:549–552
Dou DQ, Hu XY, Zhao YR, Kang TG, Liu FY, Kuang HX, Smith DC (2009) Studies on the anti-psoriasis constituents of Oplopanax elatus Nakai. Nat Prod Res 23:334–342
Qu S, Wu Y, Wang Y, Pan D (1984) Inhibitory effect of tall oplopanax (Oplopanax elatus) oil on the central nervous system. Zhongcaoyao 15:259–261
Chan E, Wong CY, Wan CW, Kwok CY, Wu JH, Ng KM, So CH, Au AL, Poon CC, Seto SW, Kwan YW, Yu PH, Chan SW (2010) Evaluation of anti-oxidant capacity of root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, in comparison with roots of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb and Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Am J Chin Med 38:815–827
Lee JS, Choi HS, Kang SW, Chung JH, Park HK, Ban JY, Kwon OY, Hong HP, Ko YG (2011) Therapeutic effect of Korean red ginseng on inflammatory cytokines in rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Am J Chin Med 39:83–94
Jung HL, Kwak HE, Kim SS, Kim YC, Lee CD, Byurn HK, Kang HY (2011) Effects of Panax ginseng supplementation on muscle damage and inflammation after uphill treadmill running in humans. Am J Chin Med 39:441–450
Inui T, Wang YH, Deng SX, Smith DC, Franzblau SG, Pauli GF (2007) Counter-current chromatography based analysis of synergy in an anti-tuberculosis ethnobotanical. J Chromatogr A 1151:211–215
Inui T, Case R, Chou E, Soejarto DD, Fong HHS, Franzblau SG, Smith DC, Pauli GF (2005) CCC in the phytochemical analysis of anti-tuberculosis ethnobotanicals. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 28:2017–2028
McCutcheon AR, Roberts TE, Gibbons E, Ellis SM, Babiuk LA, Hancock REW, Towers GHN (1995) Antiviral screening of British Columbian medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol 49:101–110
Thommasen HV, Wilson RA, McIlwain RG (1990) Effect of devil’s club tea on blood glucose levels in diabetes mellitus. Can Fam Physician 36:62–65
Large RG, Brocklesby HN (1938) A hypoglycaemic substance from the roots of the devil’s club (Fatsia horrida). Can Med Assoc J 39:32–35
Wattenberg LW (1991) Inhibition of azoxymethane-induced neoplasia of the large bowel by 3-hydroxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-1,6,10-dodecatriene (nerolidol). Carcinogenesis 12:151–152
Tai J, Cheung S, Chan E, Hasman D (2010) Inhibition of human ovarian cancer cell lines by devil’s club Oplopanax horridus. J Ethnopharmacol 127:478–485
Tai J, Cheung S, Cheah S, Chan E, Hasman D (2006) In vitro anti-proliferative and antioxidant studies on Devil’s Club Oplopanax horridus. J Ethnopharmacol 108:228–235
Sun S, Li XL, Wang CZ, Williams S, Yuan CS (2010) Improving anticancer activities of Oplopanax horridus root bark extract by removing water-soluble components. Phytother Res 24:1166–1174
Sun S, Du GJ, Qi LW, Williams S, Wang CZ, Yuan CS (2010) Hydrophobic constituents and their potential anticancer activities from Devil’s Club (Oplopanax horridus Miq.). J Ethnopharmacol 132:280–285
Li XL, Sun S, Du GJ, Qi LW, Williams S, Wang CZ, Yuan CS (2010) Effects of Oplopanax horridus on human colorectal cancer cells. Anticancer Res 30:295–302
Russell PN (1991) English Bay and Port Graham Alutiiq plantlore. Homer, Kenai Peninsula, Alaska
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NIH/NCCAM grants (AT004418, AT005362), the University of Chicago Digestive Disease Research Core Center (5P30DK042086), and a University of Macau grant (UL015/09-Y1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calway, T., Du, GJ., Wang, CZ. et al. Chemical and pharmacological studies of Oplopanax horridus, a North American botanical. J Nat Med 66, 249–256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0602-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0602-2