Abstract
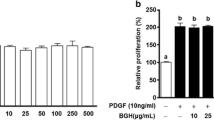
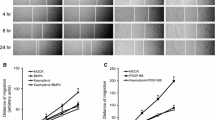
HMC05 is a formulation derived from eight medicinal herbs, and prevents neointima formation by inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway with induction of heat shock protein 27 expression. In this study, we investigated the influence of HMC05 regulation on the MAPK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 signaling cascade in the inhibition of the migration and proliferation of human aortic smooth muscle cells (HASMCs). The inhibitory effects of HMC05 (25, 50, and 100 μg/ml) on tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α; 0 or 100 ng/ml)-induced HASMC migration and proliferation were investigated by wound migration and proliferation assays, Western blotting and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. HMC05 completely inhibited TNF-α-induced HASMC migration and proliferation. HMC05 prevented TNF-α receptor 1-mediated phosphorylation of signal transduction molecules involved in MAPK signaling cascades such as MEK1/2, ERK1/2, Elk-1 transcription factor and p90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase. The expression of matrix metalloproteinase, a modulator of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, was inhibited by HMCO5 treatment, as was TNF-α-induced mRNA expression of intracellular adhesion molecule 1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. HMC05 disruption of the MEK/ERK/Elk-1 and p90RSK pathways prevents HASMC migration and proliferation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz SM (1997) Perspectives series: cell adhesion in vascular biology Smooth muscle migration in atherosclerosis and restenosis. J Clin Invest 99:2814–2816
Raines EW, Ross R (1993) Smooth muscle cells and the pathogenesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis. Br Heart J 69:S30–S37
Jovinge S, Hultgårdh-Nilsson A, Regnström J, Nilsson J (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha activates smooth muscle cell migration in culture and is expressed in the balloon-injured rat aorta. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:490–497
Clausell N, de Lima VC, Molossi S, Liu P, Turley E, Gotlieb AI, Adelman AG, Rabinovitch M (1995) Expression of tumour necrosis factor alpha and accumulation of fibronectin in coronary artery restenotic lesions retrieved by atherectomy. Br Heart J 73:534–539
Zhang H, Park Y, Wu J, Chen X, Lee S, Yang J, Dellsperger KC, Zhang C (2009) Role of TNF-alpha in vascular dysfunction. Clin Sci (Lond) 116:219–230
Goetze S, Xi XP, Kawano Y, Kawano H, Fleck E, Hsueh WA, Law RE (1999) TNF-alpha-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cells is MAPK dependent. Hypertension 33:183–189
Brockhaus M, Schoenfeld HJ, Schlaeger EJ, Hunziker W, Lesslauer W, Loetscher H (1990) Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3127–3131
Barbara JA, Van ostade X, Lopez A (1996) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha): the good, the bad and potentially very effective. Immunol Cell Biol 74:434–443
Nelson PR, Yamamura S, Mureebe L, Itoh H, Kent KC (1998) Smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation are mediated by distinct phases of activation of the intracellular messenger mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Vasc Surg 27:117–125
Blenis J (1993) Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5889–5892
Seger R, Krebs EG (1995) The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J 9:726–735
Frödin M, Gammeltoft S (1999) Role and regulation of 90 kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in signal transduction. Mol Cell Endocrinol 151:65–77
Kawai-Kowase K, Owens GK (2007) Multiple repressor pathways contribute to phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C59–C69
Hsieh HL, Wu CY, Yang CM (2008) Bradykinin induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and cell migration through a PKC-delta-dependent ERK/Elk-1 pathway in astrocytes. Glia 56:619–632
Braun M, Pietsch P, Schrör K, Baumann G, Felix SB (1999) Cellular adhesion molecules on vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 41:395–401
Rauch BH, Müschenborn B, Braun M, Weber AA, Schrör K (2007) ICAM-1 and p38 MAPK mediate fibrinogen-induced migration of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol 577:54–57
Wang CC, Lin WN, Lee CW, Lin CC, Luo SF, Wang JS, Yang CM (2005) Involvement of p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK, JNK, and NF-kappa B in IL-1beta-induced VCAM-1 expression in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L227–L237
Choi KW, Park HJ, Jung DH, Kim TW, Park YM, Kim BO, Sohn EH, Moon EY, Um SH, Rhee DK, Pyo S (2010) Inhibition of TNF-α-induced adhesion molecule expression by diosgenin in mouse vascular smooth muscle cells via downregulation of the MAPK, Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. Vasc Pharmacol 53:273–280
Shin HM, Morgan KG (2003) Vasodilation by banhabackchulchunmatang, a Chinese medicine, is associated with negative modulation of PKCalpha activation and NO production. Life Sci 74:723–732
Kim KM, Choi JY, Yoo SE, Park MY, Lee BS, Ko YH, Sung SH, Shin HM, Park JE (2007) HMCO5, herbal extract, inhibits NF-kappaB expression in lipopolysaccharide treated macrophages and reduces atherosclerotic lesions in cholesterol fed mice. J Ethnopharmacol 114:316–324
Lee JW, Lee BS, Lee JY, Ku HJ, Jeon SR, Kim JY, Ban JM, Sung SH, Shin HM, Park JE (2011) The herbal extract HMC05 inhibits neointima formation in balloon-injured rat carotid arteries: possible therapeutic implications of HMC05. J Ethnopharmacol 133:168–176
Kim SH, Choi EJ, Lee KY, Sung SH, Shin HM (2008) Simultaneous determination of alkaloids and flavonoids in HMC05 preparation by HPLC-DAD. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 31:2917–2926
Moon SK, Cha BY, Kim CH (2004) ERK1/2 mediates TNF-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells via the regulation of NF-kappaB and AP-1: involvement of the ras dependent pathway. J Cell Physiol 198:417–427
Suh SJ, Kim JR, Jin UH, Choi HS, Chang YC, Lee YC, Kim SH, Lee IS, Moon TC, Chang HW, Kim CH (2009) Deoxypodophyllotoxin, flavolignan, from Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. inhibits migration and MMP-9 via MAPK pathways in TNF-alpha-induced HASMC. Vasc Pharmacol 51:13–20
Galis ZS, Khatri JJ (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Circ Res 90:251–262
Sprague AH, Khalil RA (2009) Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol 78:539–552
Lee B, Lee EJ, Kim DI, Park SK, Kim WJ, Moon SK (2009) Inhibition of proliferation and migration by piceatannol in vascular smooth muscle cells. Toxicol In Vitro 23:1284–1291
Yu YM, Lin HC (2010) Curcumin prevents human aortic smooth muscle cells migration by inhibiting of MMP-9 expression. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 20:125–132
George SJ, Dwivedi A (2004) MMPs, cadherins, and cell proliferation. Trends Cardiovasc Med 14:100–105
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (B080031) and the Dongguk University Research Fund of 2011.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Y.H., Yang, I.J. & Shin, H.M. Herbal formula HMC05 prevents human aortic smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation by inhibiting the ERK1/2 MAPK signaling cascade. J Nat Med 66, 177–184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0573-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0573-3