Abstract
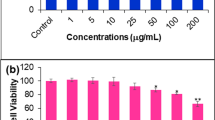
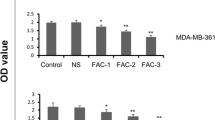
Alpha-eleostearic acid (α-ESA) is a natural and biologically active compound which possesses potent antioxidant and anti-tumor activity. The purpose of this study was to confirm the anticancer activity of α-ESA against human breast cancer cells and to further elucidate its mechanism of activity. Human breast cancer cells and normal liver cells were used for in-vitro tests of the anticancer activity of α-ESA, including cytotoxicity, colony formation inhibition, EdU incorporation, AO/EB staining of apoptotic cells, cell cycle distribution through flow cytometry, and PPARγ, p21, Bax, p53, and caspase-3 mRNA expressions through RT-PCR. After α-ESA treatment, the proliferation, colony formation, and EdU labeling indices of cancer cells decreased (p < 0.05), while the AO/EB-stained apoptotic cells increased (p < 0.05). By FCM analysis, the apoptotic indices increased (p < 0.01), and the cell population decreased in S phase (p < 0.01) and increased in G2/M phase (p < 0.05) in α-ESA treated cancer cells. RT-RCR showed that α-ESA significantly increased the expression levels of PPARγ, p21, Bax, p53, and caspase-3 mRNA. The findings in these studies suggested that α-ESA exhibited a potential cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction effect on human breast cancer cells, with little effect on normal cells at certain concentrations. The mechanism for such effects might be associated with the inhibition of DNA synthesis, induction of apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest of cancer cells through up-regulation of PPARγ, p21, Bax, p53, and caspase-3 expressions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitra AK, Faruque FS (2004) Cancer incidence and exposure to environmental chemicals in 82 counties in Mississippi. South Med J 97:259–263
Mukherjee AK, Basu S, Sarkar N, Ghosh AC (2001) Advances in cancer therapy with plant based natural products. Curr Med Chem 8:1467–1486
Porter PL (2009) Global trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality. Salud Pública Méx 51(Suppl 2):s141–s146
Bhattacharya A, Banu J, Rahman M, Causey J, Fernandes G (2006) Biological effects of conjugated linoleic acids in health and disease. J Nutr Biochem 17:789–810
Wang LS, Huang YW, Liu S, Yan P, Lin YC (2008) Conjugated linoleic acid induces apoptosis through estrogen receptor alpha in human breast tissue. BMC Cancer 8:208
Islam MA, Kim YS, Jang WJ, Lee SM, Kim HG, Kim SY, Kim JO, Ha YL (2008) A mixture of trans, trans conjugated linoleic acid induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells with reciprocal expression of Bax and Bcl-2. J Agric Food Chem 56:5970–5976
Bocca C, Bozzo F, Francica S, Colombatto S, Miglietta A (2007) Involvement of PPAR gamma and E-cadherin/beta-catenin pathway in the antiproliferative effect of conjugated linoleic acid in MCF-7 cells. Int J Cancer 121:248–256
Miglietta A, Bozzo F, Bocca C, Gabriel L, Trombetta A, Belotti S, Canuto RA (2006) Conjugated linoleic acid induces apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through ERK/MAPK signalling and mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Lett 234:149–157
Ma DW, Field CJ, Clandinin MT (2002) An enriched mixture of trans-10, cis-12-CLA inhibits linoleic acid metabolism and PGE2 synthesis in MDA-MB-231 cells. Nutr Cancer 44:203–212
Kelley NS, Hubbard NE, Erickson KL (2007) Conjugated linoleic acid isomers and cancer. J Nutr 137:2599–2607
Martinasso G, Saracino S, Maggiora M, Oraldi M, Canuto RA, Muzio G (2010) Conjugated linoleic acid prevents cell growth and cytokine production induced by TPA in human keratinocytes NCTC 2544. Cancer Lett 287:62–66
Amarù DL, Field CJ (2009) Conjugated linoleic acid decreases mcf-7 human breast cancer cell growth and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor levels. Lipids 44:449–458
Ip MM, McGee SO, Masso-Welch PA (2007) The t10,c12 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid stimulates mammary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice over-expressing erbB2 in the mammary epithelium. Carcinogenesis 28:1269–1276
Badami RC, Patil KB (1980) Structure and occurrence of unusual fatty acids in minor seed oils. Prog Lipid Res 19:119–153
Saha SS, Ghosh M (2009) Comparative study of antioxidant activity of alpha-eleostearic acid and punicic acid against oxidative stress generated by sodium arsenite. Food Chem Toxicol 47:2551–2556
Dhar P, Chattopadhyay K, Bhattacharyya D, Roychoudhury A, Biswas A, Ghosh S (2006) Antioxidative effect of conjugated linolenic acid in diabetic and non-diabetic blood: an in vitro study. J Oleo Sci 56:19–24
Igarashi M, Miyazawa T (2000) Newly recognized cytotoxic effect of conjugated trienoic fatty acids on cultured human tumor cells. Cancer Lett 148:173–179
Grossmann ME, Mizuno NK, Dammen ML, Schuster T, Ray A, Cleary MP (2009) Eleostearic acid inhibits breast cancer proliferation by means of an oxidation-dependent mechanism. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2:879–886
Kobori M, Ohnishi-Kameyama M, Akimoto Y, Yukizaki C, Yoshida M (2008) Alpha-eleostearic acid and its dihydroxy derivative are major apoptosis-inducing components of bitter gourd. J Agric Food Chem 56:10515–10520
Tsuzuki T, Tokuyama Y, Igarashi M, Miyazawa T (2004) Tumor growth suppression by alpha-eleostearic acid, a linolenic acid isomer with a conjugated triene system, via lipid peroxidation. Carcinogenesis 25:1417–1425
Tsuzuki T, Kawakami Y (2008) Tumor angiogenesis suppression by alpha-eleostearic acid, a linolenic acid isomer with a conjugated triene system, via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Carcinogenesis 29:797–806
Kitamura Y, Yamagishi M, Okazaki K, Umemura T, Imazawa T, Nishikawa A, Matsumoto W, Hirose M (2006) Lack of chemopreventive effects of alpha-eleostearic acid on 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) and 1,2-dimethylhydrazine (DMH)-induced mammary and colon carcinogenesis in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol 44:271–277
Choi EJ, Ahn WS, Bae SM (2009) Equol induces apoptosis through cytochrome c-mediated caspases cascade in human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells. Chem Biol Interact 177:7–11
Kim MJ, Kim YJ, Park HJ, Chung JH, Leem KH, Kim HK (2006) Apoptotic effect of red wine polyphenols on human colon cancer SNU-C4 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 44:898–902
Diermeier-Daucher S, Clarke ST, Hill D, Vollmann-Zwerenz A, Bradford JA, Brockhoff G (2009) Cell type specific applicability of 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) for dynamic proliferation assessment in flow cytometry. Cytometry A 75:535–546
Salic A, Mitchison TJ (2008) A chemical method for fast and sensitive detection of DNA synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2415–2420
Wang J, Wang X, Jiang S, Lin P, Zhang J, Lu Y, Wang Q, Xiong Z, Wu Y, Ren J, Yang H (2008) Cytotoxicity of fig fruit latex against human cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol 46:1025–1033
Bougnoux P, Hajjaji N, Maheo K, Couet C, Chevalier S (2010) Fatty acids and breast cancer: sensitization to treatments and prevention of metastatic re-growth. Prog Lipid Res 49:76–86
Ribble D, Goldstein NB, Norris DA, Shellman YG (2005) A simple technique for quantifying apoptosis in 96-well plates. BMC Biotechnol 5:1–7
Kuniyasu H (2008) The roles of dietary PPARgamma ligands for metastasis in colorectal cancer. PPAR Res 2008:529720
Liu JJ, Guo YW, Fang ZG, Si XN, Wu XY, Liu PQ, Lin DJ, Xiao RZ, Xu Y, Wang CZ, Li XD, He Y, Huang RW (2009) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma induces apoptosis on acute promyelocytic leukemia cells via downregulation of XIAP. Int J Mol Med 24:623–632
Ochoa JJ, Farquharson AJ, Grant I, Moffat LE, Heys SD, Wahle KW (2004) Conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs) decrease prostate cancer cell proliferation: different molecular mechanisms for cis-9, trans-11 and trans-10, cis-12 isomers. Carcinogenesis 25:1185–1191
Cho HJ, Kwon GT, Park JH (2009) Trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid induces depolarization of mitochondrial membranes in HT-29 human colon cancer cells: a possible mechanism for induction of apoptosis. J Med Food 12:952–958
Beppu F, Hosokawa M, Tanaka L, Kohno H, Tanaka T, Miyashita K (2006) Potent inhibitory effect of trans9, trans11 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid on the growth of human colon cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem 17:830–836
Majumder B, Wahle KW, Moir S, Schofield A, Choe SN, Farquharson A, Grant I, Heys SD (2002) Conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs) regulate the expression of key apoptotic genes in human breast cancer cells. FASEB J 16:1447–1449
Ou L, Ip C, Lisafeld B, Ip MM (2007) Conjugated linoleic acid induces apoptosis of murine mammary tumor cells via Bcl-2 loss. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356:1044–1049
Bocca C, Bozzo F, Cannito S, Colombatto S, Miglietta A (2010) CLA reduces breast cancer cell growth and invasion through ERα and PI3K/Akt pathways. Chem Biol Interact 183:187–193
Eom JM, Seo MJ, Baek JY, Chu H, Han SH, Min TS, Cho CS, Yun CH (2010) Alpha-eleostearic acid induces autophagy-dependent cell death through targeting AKT/mTOR and ERK1/2 signal together with the generation of reactive oxygen species. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 391:903–908
Moon HS, Guo DD, Lee HG, Choi YJ, Kang JS, Jo K, Eom JM, Yun CH, Cho CS (2010) Alpha-eleostearic acid suppresses proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells via activation of PPARgamma and inhibition of ERK 1/2. Cancer Sci 101:396–402
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Foundation of Science and Technology Bureau of Sichuan Province, China (grant no. 2008SG0016) and the Research Foundation of Health Bureau of Sichuan Province, China (grant no. 090316).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Zhang and Y. Gao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Gao, Y., Mao, Y. et al. Growth inhibition and apoptotic effect of alpha-eleostearic acid on human breast cancer cells. J Nat Med 66, 77–84 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0556-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0556-4