Abstract
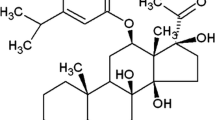
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common and aggressive type of primary brain tumor. Uncontrolled activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway resulting from genetic alterations in phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) correlates with poor prognosis and resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy of glioblastomas. In this study, we found that gambogenic acid (GNA), a polyprenylated xanthone isolated from the traditional medicine gamboge, efficiently arrested the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase by specifically repressing the expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E, suppressed cell proliferation, colony formation and cell migration, and induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in U251 glioblastoma cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. The pro-apoptotic effect of GNA on U251 cells was shown to be mediated through inactivation of the Akt pathway, because GNA efficiently suppressed the expression level of EGFR and reduced the phosphorylation of Akt (T308) and GSK3β (S9). Furthermore, the combined treatment with LY294002, a specific inhibitor of the PI3K/Akt kinase pathway, and GNA showed a synergistic or additive effect on the growth of U251 cells. Our results showed that GNA is a promising therapeutic agent for glioblastomas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panthong A, Norkaew P, Kanjanapothi D, Taesotikul T, Anantachoke N, Reutrakul V (2008) Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities of the extract of gamboge from Garcinia hanburyi Hook f. J Ethnopharmacol 111:335–340
Zhang HZ, Kasibhatla S, Wang Y, Herich J, Guastella J, Tseng B, Drewe J, Cai SX (2004) Discovery, characterization and SAR of gambogic acid as a potent apoptosis inducer by a HTS assay. Bioorg Med Chem 12:309–317
Yu J, Guo QL, You QD, Zhao L, Gu HY, Yang Y, Zhang HW, Tan Z, Wang X (2007) Gambogic acid-induced G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest via disturbing CDK7-mediated phosphorylation of CDC2/p34 in human gastric carcinoma BGC-823 cells. Carcinogenesis 28:632–638
Lu GB, Yang XX, Huang QS (1984) Isolation and structure of neo-gambogic acid from Gamboge. Acta Pharmacol Sin 19:636–639
Qu BX, Hao XG, Li DH (1991) The experimental study on antineoplastic action of Gambogic-II. Chin J Clin Oncol 18:50–52
Li QL, Cheng H, Zhu GQ, Yang L, Zhou A, Wang XS, Fang NB, Xia LZ, Su JJ, Wang M, Peng DY, Xu Q (2010) Gambogenic acid inhibits proliferation of A549 cells through apoptosis-inducing and cell cycle arresting. Biol Pharm Bull 33:415–420
Surawicz TS, Davis F, Freels S, Laws ER Jr, Menck HR (1998) Brain tumor survival: results from the National Cancer Data Base. J Neurooncol 40:151–160
Postma TJ, van Groeningen CJ, Witjes RJ, Weerts JG, Kralendonk JH, Heimans JJ (1998) Neurotoxicity of combination chemotherapy with procarbazine, CCNU and vincristine (PCV) for recurrent glioma. J Neurooncol 38:69–75
Neyns B, Sadones J, Chaskis C, De Ridder M, Keyaerts M, Veld PI, Michotte A (2005) The role of chemotherapy in the treatment of low-grade glioma. A review of the literature. Acta Neurol Belg 105:137–143
Perilongo G (2005) Considerations on the role of chemotherapy and modern radiotherapy in the treatment of childhood low-grade glioma. J Neurooncol 75:301–307
Minniti G, Muni R, Lanzetta G, Marchetti P, Enrici RM (2009) Chemotherapy for glioblastoma: current treatment and future perspectives for cytotoxic and targeted agents. Anticancer Res 29:5171–5184
Koul D (2008) PTEN signaling pathways in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1321–1325
West KA, Castillo SS, Dennis PA (2002) Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist Updat 5:234–248
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, Chin L, DePinho RA, Cavenee WK (2007) Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21:2683–2710
Cheng CK, Fan QW, Weiss WA (2009) PI3K signaling in glioma—animal models and therapeutic challenges. Brain Pathol 19:112–120
Denizot F, Lang R (1986) Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods 89:271–277
Zheng X, Rao XM, Gomez-Gutierrez JG, Hao H, McMasters KM, Zhou HS (2008) Adenovirus E1B55K region is required to enhance cyclin E expression for efficient viral DNA replication. J Virol 82:3415–3427
Chintala SK, Tonn JC, Rao JS (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases and their biological function in human gliomas. Int J Dev Neurosci 17:495–502
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG (1998) Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273:9357–9360
Teng DH, Hu R, Lin H, Davis T, lliev D, Frye C, Swedlund B, Hansen KL, Vinson VL, Gumpper KL, Ellis L, El-Naggar A, Frazier M, Jasser S, Langford LA, Lee J, Mills GB, Pershouse MA, Pollack RE, Tornos C, Troncoso P, Yung WK, Fujii G, Berson A, Bookstein R, Bolen JB, Tavtigian SV, Steck PA (1997) MMAC1/PTEN mutations in primary tumor specimens and tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 57:5221–5225
Etienne MC, Formento JL, Lebrun-Frenay C, Gioanni J, Chatel M, Paquis P, Bernard C, Courdi A, Bensadoun RJ, Pignol JP, Francoual M, Grellier P, Frenay M, Milano G (1998) Epidermal growth factor receptor and labeling index are independent prognostic factors in glial tumor outcome. Clin Cancer Res 4:2383–2390
Sano T, Lin H, Chen X, Langford LA, Koul D, Bondy ML, Hess KR, Myers JN, Hong YK, Yung WK, Steck PA (1999) Differential expression of MMAC/PTEN in glioblastoma multiforme: relationship to localization and prognosis. Cancer Res 59:1820–1824
Smith JS, Tachibana I, Passe SM, Huntley BK, Borell TJ, Iturria N, O’Fallon JR, Schaefer PL, Scheithauer BW, James CD, Buckner JC, Jenkins RB (2001) PTEN mutation, EGFR amplification, and outcome in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1246–1256
Simmons ML, Lamborn KR, Takahashi M, Chen P, Israel MA, Berger MS, Godfrey T, Nigro J, Prados M, Chang S, Barker FG, Aldape K (2001) Analysis of complex relationships between age, p53, epidermal growth factor receptor, and survival in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Res 61:1122–1128
Shinojima N, Tada K, Shiraishi S, Kamiryo T, Kochi M, Nakamura H, Makino K, Saya H, Hirano H, Kuratsu J, Oka K, Ishimaru Y, Ushio Y (2003) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 63:6962–6970
Heimberger AB, Suki D, Yang D, Shi W, Aldape K (2005) The natural history of EGFR and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma patients. J Transl Med 3:38
Lucibello FC, Sewing A, Brüsselbach S, Bürger C, Müller R (1993) Deregulation of cyclins D1 and E and suppression of cdk2 and cdk4 in senescent human fibroblasts. J Cell Sci 105:123–133
Ohtsubo M, Theodoras AM, Schumacher J, Roberts JM, Pagano M (1995) Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 15:2612–2624
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the funding (to L.H.) from the Shenzhen Municipal Government and the Bureau of Science Technology and Information through the programs of the Shenzhen National Key Laboratory of Health Science and Technology and the Key Laboratory of Gene and Antibody Therapy; and partly from key projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the 11th 5-year plan period 2009ZX09103-399 (Q. Li, co-PI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
H.-B. Chen and L.-Z. Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HB., Zhou, LZ., Mei, L. et al. Gambogenic acid-induced time- and dose-dependent growth inhibition and apoptosis involving Akt pathway inactivation in U251 glioblastoma cells. J Nat Med 66, 62–69 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0553-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-011-0553-7