Abstract
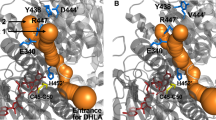
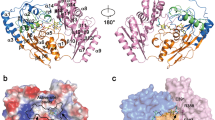
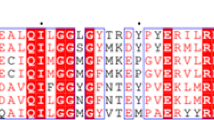
Human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (hE3) is a common component of α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Mutations of this homodimeric protein cause E3 deficiency and are always fatal. To investigate its reaction mechanism, we first performed multiple sequence alignment with other 17 eukaryotic E3s. According to hE3 structure and the result of multiple sequence alignment, two amino acids, T148 and R281, were subjected to mutagenesis and four hE3 mutants, T148G, T148S, R281N, and R281K, were expressed and assayed. The specific activities of T148G, T148S, R281N, and R281K are 76.34%, 88.62%, 12.50%, and 11.93% to that of wild-type E3, respectively. The FAD content analysis indicated that the FAD content of these mutant E3s were about 71.0%, 92%, 96%, and 93% that of wild-type E3, respectively. The molecular weight analysis showed that these three mutant proteins form the dimer. Kinetic data demonstrated that the Kcat of forward reaction of all mutants, except T148 mutants, were decreased dramatically. The results of kinetic study suggest that T148 is not important to E3 catalytic function and R281 play a role in the catalytic function of the E3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reed L.J. (1974) Multienzyme complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 7: 40–46
Yeaman S.J. (1986) The mammalian 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases: a complex family. Trends Biochem. Sci. 11: 293–296
Yeaman S.J. (1989) The 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes: recent advances. Biochem. J. 257: 625–632
Walker J.L., Oliver D.J. (1986) Glycine decarboxylase multienzyme complex. Purification and partial characterization from leaf mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 2214–2221
Williams C.H. Jr. (1976) Flavin containing dehydrogenases. In: Boyer P. (ed) Enzymes. Academic Press, New York, USA, pp. 89–173
Mattevi A., Schierbeek A.J., Hol W.G. (1991) Refined crystal structure of lipoamide dehydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii at 2.2 Å resolution. A comparison with the structure of glutathione reductase. J. Mol. Biol. 220: 975–994
Kikuchi G., Hiraga K. (1982) The mitochondrial glycine cleavage system. Unique features of the glycine decarboxylation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 45: 137–149
de Kok A., van Berkel W.J.H. (1996) Lipoamide dehydrogenase. In: Patel M.S., Roche T.E., Harris R.A. (Eds), Alpha-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase Complexes. Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, Switzerland, pp. 53–70
Mattevi A., Obmolova G., Sokatch J.R., Betzel C., Hol W.G. (1992) The refined crystal structure of Pseudomonas putida lipoamide dehydrogenase complexed with NAD+ at 2.45 Å resolution. Proteins 13: 336–351
Mattevi A., Obmolova G., Kalk K.H., van Berkel W.J., Hol W.G. (1993) Three-dimensional structure of lipoamide dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens at 2.8 Å. Analysis of redox and thermostability properties. J. Mol. Biol. 230: 1200–1215
Brautigam C.A., Chuang J.L., Tomchick D.R., Machius M., Chuang D.T. (2005) Crystal structure of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: NAD+/NADH binding and the structure basis of disease-causing mutations. J. Mol. Biol. 350: 543–552
Jentoft J.E., Shoham M., Hurst D., Patel M.S. (1992) A structural model for human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. Proteins 14: 88–101
Pons G., Raefsky-Estrin C., Catothers D.J., Repin R.A., Javed A.A., Jesse B.W., Ganapathi M.K., Samols D., Patel M.S. (1988) Cloning and cDNA sequence of the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase component of human ketoacid dehydrogenase complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 1422–1426
Liu T.C., Kim H., Arizmendi C., Kitano A., Patel M.S. (1993) Identification of two missense mutations in a dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase-deficient patient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 5186–5190
Shaag A., Saada A., Berger I., Mandel H., Joseph A., Feigenbaum A., Elpeleg O.N. (1999) Molecular basis of lipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency in Ashkenazi Jews. Am. J. Med. Genet. 82: 177–182
Cerna L., Wenchich L., Hansikova H., Kmoch S., Peskova K., Chrastina P., Brynda J., Zeman J. (2001) Novel mutations in a boy with dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency. Med. Sci. Monit. 7: 1319–1325
Cameron J.M., Levandovskiy V., Mackay N., Raiman J., Renaud D.L., Clarke J.T.R., Feigenbaum A., Elpeleg O., Robinson B.H. (2006) Novel mutations in dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency in two cousins with borderline-normal complex activity. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 140A: 1542–1552
Hong Y.S., Kerr D.S., Craigen W.J., Tan J., Pan Y., Lusk M., Patel M.S. (1996) Identification of two mutations in a compound heterozygous child with dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency. Hum. Mol. Genet. 5: 1925–1930
Hong Y.S., Kerr D.S., Liu T.C., Lusk M., Powell B.R., Patel M.S. (1997) Deficiency of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase due to two mutant alleles (E340K and G101del). Analysis of a family and prenatal testing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1362: 160–168
Grafakou O., Oexle K., van den Heuvel L., Smeets R., Trijbels F., Goebel H.H., Bosshard N., Superti-Furga A., Steinmann B., Smeitink J. (2003) Leigh syndrome due to compound heterozygosity of dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase gene mutations. Description of the first E3 splice site mutation. Eur. J. Pediatr. 162: 714–718
Shany E., Saada A., Landau D., Shaag A., Hershkovitz E., Elpeleg O.N. (1999) Lipoamide dehydrogenase deficiency due to a novel mutation in the interface domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 262: 163–166
Odievre M.H., Chretien D., Munnich A., Robinson BH., Dumoulin R., Masmoudi S., Kadhom N., Rotig A., Rustin P., Bonnefont J.P. (2005) A novel mutation in the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase E3 subunit gene (DLD) resulting in an atypical form of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase deficiency. Hum. Mutat. 25: 323–324
Liu T.C., Hong Y.S., Korotchkina L.G., Vettakkorumakankav N.N., Patel M.S. (1999) Site-directed mutagenesis of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase: role of lysine-54 and glutamate-192 in stabilizing the thiolate-FAD intermediate. Protein Expr. Purif. 16: 27–39
Kim H. (2006) Activity of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase is largely reduced by mutation at isoleucine-51 to alanine. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39: 223–227
Kim H. (2002) Activity of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase is reduced by mutation at threonine-44 of FAD-binding region to valine. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 35: 437–441
Kim H., Patel M.S. (1992) Characterization of two site-specifically mutated human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases (His-452→Gln and Glu-457→Gln). J. Biol. Chem. 267: 5128–5132
Kim H. (2005) Asparagine-473 residue is important to the efficient function of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 38: 248–452
Wang Y.C., Wang S.T., Li C., Liu W.H., Chen P.R., Chen L.Y., Liu T.C. (2007) The role of N286 and D320 in the reaction mechanism of human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3) center domain. J. Biomed. Sci. 14: 203–210
Liu T.C., Korotchkina L.G., Hyatt S.L., Vettakkorumakankav N.N., Patel M.S. (1995) Spectroscopic studies of the characterization of recombinant human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase and its site-directed mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 15545–15550
Sambrook J., Fritsh E.F., Maniatis T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Mannual, 2nd edn, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 7.43–7.45
Bradford M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YC., Wang, ST., Li, C. et al. The role of amino acids T148 and R281 in human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. J Biomed Sci 15, 37–46 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9208-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9208-9