Abstract
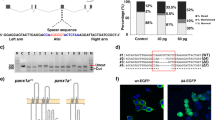
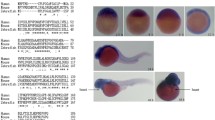
Although multiple subtypes of sodium channels are expressed in most neurons, the specific contributions of the individual sodium channels remain to be studied. The role of zebrafish Nav1.6 sodium channels in the embryonic locomotor movements has been investigated by the antisense morpholino (MO) knockdown. MO1 and MO2 are targeted at the regions surrounding the translation start site of zebrafish Nav1.6 mRNA. MO3 is targeted at the RNA splicing donor site of exon 2. The correctly spliced Nav1.6 mRNA of MO3 morphants is 6% relative to that of the wild-type embryos. Nav1.6-targeted MO1, MO2 and MO3 attenuate the spontaneous contraction, tactile sensitivity, and swimming in comparison with a scrambled morpholino and mutated MO3 morpholino. No significant defect is observed in the development of slow muscles, the axonal projection of primary motoneurons, and neuromuscular junctions. The movement impairments caused by MO1, MO2, and MO3 suggest that the function of Nav1.6 sodium channels is essential on the normal early embryonic locomotor activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tzoumaka E., Tischler A.C., Sangameswaran L., Eglen R.M., Hunter J.C., Novakovic S.D. (2000) Differential distribution of the tetrodotoxin-sensitive rPN4/NaCh6/Scn8a sodium channel in the nervous system. J. Neurosci. Res. 60:37–44
Caldwell J.H., Schaller K.L., Lasher R.S., Peles E., Levinson S.R. (2000) Sodium channel Na(v)1.6 is localized at nodes of ranvier, dendrites, and synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97:5616–5620
Krzemien D.M., Schaller K.L., Levinson S.R., Caldwell J.H. (2000) Immunolocalization of sodium channel isoform NaCh6 in the nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 420:70–83
Burgess D.L., Kohrman D.C., Galt J., Plummer N.W., Jones J.M., Spear B., Meisler M.H. (1995) Mutation of a new sodium channel gene, Scn8a, in the mouse mutant ‹motor endplate disease’. Nat. Genet. 10:461–465
Kearney J.A., Buchner D.A., De H.G., Adamska M., Levin S.I., Furay A.R., Albin R.L., Jones J.M., Montal M., Stevens M.J., Sprunger L.K., Meisler M.H. (2002) Molecular and pathological effects of a modifier gene on deficiency of the sodium channel Scn8a (Na(v)1.6). Hum. Mol. Genet. 11:2765–2775
Levin S.I., Khaliq Z.M., Aman T.K., Grieco T.M., Kearney J.A., Raman I.M., Meisler M.H. (2006) Impaired motor function in mice with cell-specific knockout of sodium channel Scn8a (NaV1.6) in cerebellar purkinje neurons and granule cells. J Neurophysiol 96:785–793
Raman I.M., Sprunger L.K., Meisler M.H., Bean B.P. (1997) Altered subthreshold sodium currents and disrupted firing patterns in Purkinje neurons of Scn8a mutant mice. Neuron 19:881–891
Garcia K.D., Sprunger L.K., Meisler M.H., Beam K.G. (1998) The sodium channel Scn8a is the major contributor to the postnatal developmental increase of sodium current density in spinal motoneurons. J. Neurosci. 18:5234–5239
Tsai C.W., Tseng J.J., Lin S.C., Chang C.Y., Wu J.L., Horng J.F., Tsay H.J. (2001) Primary structure and developmental expression of zebrafish sodium channel Na(v)1.6 during neurogenesis. DNA Cell Biol. 20:249–255
Novak A.E., Taylor A.D., Pineda R.H., Lasda E.L., Wright M.A., Ribera A.B. (2006) Embryonic and larval expression of zebrafish voltage-gated sodium channel alpha-subunit genes. Dev. Dyn. 235:1962–1973
Pineda R.H., Heiser R.A., Ribera A.B. (2005) Developmental, molecular, and genetic dissection of INa in␣vivo in embryonic zebrafish sensory neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 93:3582–3593
Pineda R.H., Svoboda K.R., Wright M.A., Taylor A.D., Novak A.E., Gamse J.T., Eisen J.S., Ribera A.B. (2006) Knockdown of Nav 1.6a Na+ channels affects zebrafish motoneuron development. Development 133:3827–3836
Saint-Amant L., Drapeau P. (1998) Time course of the development of motor behaviors in the zebrafish embryo. J. Neurobiol. 37:622–632
Buss R.R., Drapeau P. (2001) Synaptic drive to motoneurons during fictive swimming in the developing zebrafish. J. Neurophysiol. 86:197–210
Svoboda K.R., Linares A.E., Ribera A.B. (2001) Activity regulates programmed cell death of zebrafish Rohon-Beard neurons. Development 128:3511–3520
Devoto S.H., Melancon E., Eisen J.S., Westerfield M. (1996) Identification of separate slow and fast muscle precursor cells in␣vivo, prior to somite formation. Development 122:3371–3380
Crow M.T., Stockdale F.E. (1986) Myosin expression and specialization among the earliest muscle fibers of the developing avian limb. Dev. Biol. 113:238–254
Downes G.B., Granato M. (2004) Acetylcholinesterase function is dispensable for sensory neurite growth but is critical for neuromuscular synapse stability. Dev. Biol. 270:232–245
Saint-Amant L., Drapeau P. (2001) Synchronization of an embryonic network of identified spinal interneurons solely by electrical coupling. Neuron 31:1035–1046
Personius K.E., Balice-Gordon R.J. (2000) Activity-dependent editing of neuromuscular synaptic connections. Brain Res. Bull. 53:513–522
Bulman D.E. (1997) Phenotype variation and newcomers in ion channel disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 6:1679–1685
Lai J., Gold M.S., Kim C.S., Bian D., Ossipov M.H., Hunter J.C., Porreca F. (2002) Inhibition of neuropathic pain by decreased expression of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel, NaV1.8. Pain 95:143–152
Akopian A.N., Souslova V., England S., Okuse K., Ogata N., Ure J., Smith A., Kerr B.J., McMahon S.B., Boyce S., Hill R., Stanfa L.C., Dickenson A.H., Wood J.N. (1999) The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2:541–548
Escayg A., MacDonald B.T., Meisler M.H., Baulac S., Huberfeld G., An-Gourfinkel I., Brice A., LeGuern E., Moulard B., Chaigne D., Buresi C., Malafosse A. (2000) Mutations of SCN1A, encoding a neuronal sodium channel, in two families with GEFS+2. Nat. Genet. 24:343–345
Planells-Cases R., Caprini M., Zhang J., Rockenstein E.M., Rivera R.R., Murre C., Masliah E., Montal M. (2000) Neuronal death and perinatal lethality in voltage-gated sodium channel alpha(II)-deficient mice. Biophys. J. 78:2878–2891
Meisler M.H., Kearney J., Escayg A., MacDonald B.T., Sprunger L.K. (2001) Sodium channels and neurological disease: insights from Scn8a mutations in the mouse. Neuroscientist 7:136–145
Drapeau P., Saint-Amant L., Buss R.R., Chong M., McDearmid J.R., Brustein E. (2002) Development of the locomotor network in zebrafish. Prog. Neurobiol. 68:85–111
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yen-Jen Sung, Chen Jen Huang, and Sheng-Ping Huang for their technical assistance. The work was supported by grants from the National Science Council, ROC (NSC93–2321-B010–009; NSC94-2321-B-010-009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YH., Huang, FL., Cheng, YC. et al. Knockdown of zebrafish Nav1.6 sodium channel impairs embryonic locomotor activities. J Biomed Sci 15, 69–78 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9200-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9200-4