Summary
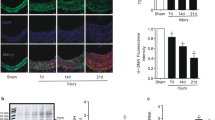
A20 was originally characterized as a TNF-inducible gene in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. It is also induced in many other cell types by a wide range of stimuli. Expression of A20 has been shown to protect from TNF-induced apoptosis and also functions via a negative-feedback loop to block NF-kappaB activation induced by TNF and other stimuli. However, there are no reports on whether A20 can inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in␣vivo. Here, we examined the effects of A20 on neointimal formation after balloon injury and TNF-α-induced vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) proliferation and migration, as well as related molecular mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. We introduced adenovirus expressing A20 or GFP into rat carotid arterial segments after balloon injury. The effects of A20 were evaluated 14 days after gene delivery with morphometry and immunohistochemical staining for proliferating and apoptotic cells. Ad-A20 infection resulted in a significantly lower intima to media ratio and a greater lumen area compared with Ad-GFP infected group. Proliferation index was significantly reduced 14 days in Ad-A20 infection group. However, apoptotic index and caspase-3 activity were not significantly different between any groups at 14 days. In vitro experiments were performed to show that A20 markedly inhibited TNF-α-induced proliferation and migration in VSMCs. Further studies showed that A20 expression blocked artery injury- and TNF-α-activated PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/CREB pathway in vivo and in vitro. In conclusion, A20 attenuates neointimal formation after arterial injury as well as cell proliferation and migration in response to TNF-α in VSMCs through blocking PI3K/Akt/GSKβ-dependent activation of CREB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hao H., Gabbiani G., Bochaton-Piallat M.L. 2003. Arterial smooth muscle cell heterogeneity: implications for atherosclerosis and restenosis development. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23:1510–1520
Davis C., Fischer J., Ley K., Sarembock I.J. 2003. The role of inflammation in vascular injury and repair. J. Thromb. Haemost. 1: 1699–1709
Clausell N., Molossi S., Sett S., et al. 1994. In vivo blockade of TNF-α in cholesterol-fed rabbits after cardiac transplant inhibits acute coronary artery neointimal formation. Circulation 89: 2768–2779
Rectenwald J.E., Moldawer L.L., Seeger J.M., Ozaki Ck 2000. Direct evidence for cytokines involvement in neointimal hyperplasia. Circulation 102: 1697–1702
Ono H., Ichiki T., Fukuyama K., et al. 2004. cAMP-response element-binding protein mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. .24:1634–1639
Sulser F. 2002. The role of CREB and other transcription factors in the pharmacotherapy and etiology of depression. Ann. Med. 34: 348–356
Sata M., Nagai R. 2002. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a key regulator of vascular tone? Circ. Res. 91:273–275
Beyaert R., Heyninck K., Van Huffel S. 2000. A20 and A20-binding proteins as cellular inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent gene expression and apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 60:1143–1151
Heyninck K., Beyaert R. 2005. A20 inhibits NF-kappaB activation by dual ubiquitin-editing functions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 30:1–4
Li H.L., Wang A.B., Zhang R., Wei Y.S., Chen H.Z., She Z.G., Huang Y., Liu D.P., Liang C.C. 2006. A20 inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis through negative Fas/Fas ligand-dependent activation of caspase-8 and mitochondrial pathways in murine RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Cell Physiol. 208: 307–318
Arvelo M.B., Badrichani A.Z., Stroka D.M., et al. 1999. A novel function for A20 in smooth muscle cells: inhibition of activation and proliferation. Transplant. Proc. 31: 858–859
Idel S., Dansky H.M., Breslow J.L. 2003. A20, a regulator of NFkappaB, maps to an atherosclerosis locus and differs between parental sensitive C57BL/6J and resistant FVB/N strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 14235–14240
Tulis D.A., Mnjoyan Z.H., Schiesser R.L., et al. 2003. Adenoviral gene transfer of fortilin attenuates neointima formation through suppression of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Circulation 107: 98–105
Li H.L., Huang Y., Zhang C.N., Liu G., Wei Y.S., Wang A.B., Liu Y.Q., Hui R.T., Wei C., Williams G.M., Liu D.P., Liang C.C. 2006. Epigallocathechin-3 gallate inhibits cardiac hypertrophy through blocking reactive oxidative species -dependent and -independent signal pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 40: 1756–1777
Li H.L., Wang A.B., Huang Y., Liu D.P., Wei C., Williams G.M., Zhang C.N., Liu G., Liu Y.Q., Hao D.L., Hui R.T., Lin M., Liang C.C. 2005. Isorhapontigenin, a new resveratrol analog, attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via blocking signaling transduction pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 38: 243–257
Kim S., Izumi Y., Yano M., et al. 1998. Angiotensin blockade inhibits activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in rat balloon-injured artery. Circulation 97:1731–1737
Garcia-Touchard A., Henry T.D., Sangiorgi G., et al. 2005. Extracellular proteases in atherosclerosis and restenosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25: 1119–1127
Patel V.I., Daniel S., Longo C.R., Shukri T., Motley-Dore C., Ramsey H.E., Fisher M.D., Grey S.T., Arvelo M.B., Ferran C. 2006. A20, a modulator of smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis, prevents and induces regression of neointimal hyperplasia. FASEB J. 20: 1418–1430
Tokunou T., Ichiki T., Takeda K., et al. 2001. cAMP response element-binding protein mediates thrombin-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 21:1764–1769
Tokunou T., Ichiki T., Takeda K., Funakoshi Y., et al. 2003. Apoptosis induced by inhibition of cyclic AMP response element-binding protein in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation 108:1246–1252
Klemm D.J., Watson P.A., Frid M.G., et al. 2001. cAMP response element-binding protein content is a molecular determinant of smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 46132–46141
Mayr B., Montminy M. 2001. Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2: 599–609
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Jing Huang (Peking University, Beijing) for his critical suggestions and providing the related plasmids.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ai-Bing Wang and Hong-Liang Li – contributed equally to this work.
Contract grant sponsor: “973” Basic Research Form of China Contract Grant Number: 2006CB503801 and 2005CB522507
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, AB., Li, HL., Zhang, R. et al. A20 attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through blocking PI3k/Akt singling in vitro and in vivo . J Biomed Sci 14, 357–371 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9150-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9150-x