Abstract
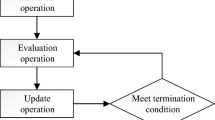
This paper presents an approach to develop an intelligent master–slave system between agricultural vehicles, which will enable a semi-autonomous agricultural vehicle (slave) to follow a leading tractor (master) with a given lateral and longitudinal offset. In our study not only the follow-up motions but also the site-specific control of the apparatus such as rear and front power lift was considered. In the first part of this paper, the recent research works in the area autonomous farming were discussed and the restrictions of these research works were illustrated. In the second part an approach, to construct a master–slave system between two agricultural vehicles was demonstrated. In the next part, the mathematic modeling of this master–slave system and the simulation results about the control algorithm were demonstrated. Afterwards, the result of a real field test was presented and the safety considerations about such an intelligent vehicle system were made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muhr T, Noack PO (2006) Mobile data repeaters enhancing the availability of RTK correction data in the field. In: Proceedings of the 2006 automation technology for off-road equipment conference. Bonn, Germany, pp 65–69, Sep 2006
O’Connor M, Bell T, Elkaim G, Parkinson BW (1996) Automatic steering of farm vehicles using GPS. In: Proceedings of the Third international conference on precision agriculture. Minneapolis, MN, pp 767–778, 23–26 June 1996
Noguchi N, Reid JF, Zhang Q, Will JD, Ischii K (2001) Development of robot tractor based on RTK-GPS and gyroscope. ASAE Paper 01-1195
Benson ER, Reid JF, Zhang Q (2003) Machine vision-based guidance system for agricultural grain harvesters using cut-edge detection. Biosyst Eng 86(4): 389–398
Tsubota R, Noguchi N, Mizushima A (2004) Automatic guidance with a laser scanner for a robot tractor in an orchard. In: Proceedings of the automation technology for off-road equipment conference. Kyoto, Japan
Noack PO, Kammerbauer B, Schönfelder M (2010) Path planning algorithms for a GPS based electronic tow bar. In: Proceedings of the second international conference on machine control and guidance. Bonn, Germany
Wang D, Qi F (2001) Trajectory planning for a four-wheel-steering vehicle. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Seoul Korea, 21–26 May 2001
Murakami N, Ito A, Will JD, Steffen M, Inoue K, Kita K, Miyaura S (2008) Development of a teleoperation system for agricultural vehicles. Comput Electron Agric 63: 81–88
IEC 61508. Functional safety of electrical/electronic/ programmable electronic safety-related systems. International Electrotechnical Commission, Switzerland
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Geimer, M., Noack, P.O. et al. A semi-autonomous tractor in an intelligent master–slave vehicle system. Intel Serv Robotics 3, 263–269 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-010-0071-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-010-0071-6