Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to clarify the influx/efflux of nitrogen and the dominant influencing factors of nitrogen transformation at the sediment–water interface (SWI).
Materials and methods
Two intact sediment cores were collected from Dongfeng Reservoir (DFR) in the Wujiang River basin in December 2018 and July 2019. The cores were immediately sliced upon collection. Pore water samples were obtained by centrifugation. Different forms of inorganic nitrogen were exacted and measured by an analytical continuous flow analyzer (SEAL Analytical Limited, Germany). Particulate organic nitrogen (PON) samples were obtained after the removal of inorganic carbon and inorganic nitrogen. Stable isotopes (δ15N-PON) and the ratios of C/N were measured by a stable isotopic mass spectrometer (MAT-253) and an elemental analyzer (Elementar, Rhine main, Germany). The estimation of mineralization and diffusion flux was conducted using a first-order kinetic model and Fick’s first law, respectively.
Results and discussion
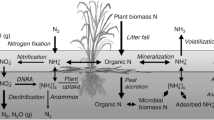
Significant seasonal variations in the concentration of nitrogen species in the pore waters of the sediment indicated that dissolved oxygen (DO) was the primary environmental factor controlling nitrogen transformation and transportation at the SWI. Mineralization and nitrification were identified as the dominant processes in the sediment profile and SWI of the DFR. The δ15N-PON and C/N ratios provided insights into the sources of PON in the sediment, with soil organic matter and livestock waste being identified as the primary contributors. The estimated endogenous diffusion fluxes of NH4+-N from sediment were 34.69 mg m−2 d−1 and 29.21 mg m−2 d−1 in the stratified period (SP) and non-stratified period (NSP), respectively. These fluxes were notably higher than those observed in most eutrophic aquatic systems, suggesting that the role of sedimentary nitrogen reservoirs in nitrogen accumulation in oligotrophic/mesotrophic environments may have been significantly underestimated.
Conclusions
Mineralization of PON and nitrification were the main processes of nitrogen transformation at the SWI in DFR. As a dominant component of inorganic nitrogen, NH4+-N exhibits high levels of endogenous release.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalto SL, Saarenheimo J, Ropponen J, Juntunen J, Rissanen AJ, Tiirola M (2018) Sediment diffusion method improves wastewater nitrogen removal in the receiving lake sediments. Water Res 138:312–322
Cai Y, Cao Y, Tang C (2019) Evidence for the primary role of phytoplankton on nitrogen cycle in a subtropical reservoir reflected by the stable isotope ratios of particulate nitrogen and total dissolved nitrogen. Front Microbiol 10
Chowdhury M, Bakri DA (2006) Diffusive nutrient flux at the sediment-water interface in Suma Park Reservoir. Australia Hydrol Sci J 51(1):144–156
Deemer BR, Harrison JA, Li S, Beaulieu JJ, DelSontro T, Barros N, Bezerra-Neto JF, Powers SM, dos Santos MA, Vonk JA (2016) Greenhouse gas emissions from reservoir water surfaces: a new global synthesis. Bioscience 66(11):949–964
Ellert BH, Bettany JR (1988) Comparison of kinetic models for describing net sulfur and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52(6):1692–1702
Feng X, Jiang H, Qiu G, Yan H, Li G, Li Z (2009) Geochemical processes of mercury in Wujiangdu and Dongfeng reservoirs, Guizhou. China Environ Pollut 157(11):2970–2984
Gao D, Chen S, Li S, Liu X, Li J, Bai L, Yang J, Wang Z (2020) Nitrous oxide production and emission mechanisms in key interfaces of canyon-reservoirs during stratification period. Chin J Ecol 39(8):2737–2747
Gao Y, Wang B, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhang J, Jiang Y, Wang F (2013) Impacts of river impoundment on the riverine water chemistry composition and their response to chemical weathering rate. Front Earth Sci 7(3):351–360
Guo W, Hu J, Wang H (2022) Analysis of runoff variation characteristics and influencing factors in the Wujiang River Basin in the past 30 years. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(1):372
Han G, Tang Y, Liu M, Van Zwieten L, Yang X, Yu C, Wang H, Song Z (2020) Carbon-nitrogen isotope coupling of soil organic matter in a karst region under land use change, Southwest China. Agric, Ecosyst Environ 301
Hardison AK, Algar CK, Giblin AE, Rich JJ (2015) Influence of organic carbon and nitrate loading on partitioning between dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) and N2 production. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 164:146–160
Hong Y, Wu J, Guan F, Yue W, Long A (2019) Nitrogen removal in the sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China: evidence from the distribution and forms of nitrogen in the sediment cores. Mar Pollut Bull 138:115–124
Hou Y, Liu X, Chen S, Ren J, Bai L, Li J, Gu Y, Wei L (2021) Effects of seasonal thermal stratification on nitrogen transformation and diffusion at the sediment-water interface in a deep canyon artificial reservoir of Wujiang River Basin. Water 13(22):3194
Lavery PS, Oldham CE, Ghisalberti M (2001) The use of Fick’s first law for predicting porewater nutrient fluxes under diffusive conditions. Hydrol Process 15(13):2435–2451
Lei P, Zhu J, Zhong H, Pan K, Zhang L, Zhang H (2021) Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in pore water profiles and estimation of their diffusive fluxes and annual loads in Guanting Reservoir (GTR). Northern China Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106(1):10–17
Li S, Jiang Z, Ji G (2022) Effect of sulfur sources on the competition between denitrification and DNRA. Environ Pollut 305
Liu J, Han G (2021a) Tracing riverine sulfate source in an agricultural watershed: constraints from stable isotopes. Environ Pollut 288
Liu J, Han G (2021b) Tracing riverine particulate black carbon sources in Xijiang River Basin: insight from stable isotopic composition and Bayesian mixing model. Water Res 194
Liu C-Q, Li S-L, Lang Y-C, Xiao H-Y (2006) Using δ15N- and δ18O-values to identify nitrate sources in karst ground water, Guiyang. Southwest China Environ Sci Technol 40(22):6928–6933
Liu M, Han G, Zhang Q (2020) Effects of agricultural abandonment on soil aggregation, soil organic carbon storage and stabilization: results from observation in a small karst catchment, Southwest China. Agric, Ecosyst Environ 288
Liu X-L, Han G, Zeng J, Liu M, Li X-Q, Boeckx P (2021) Identifying the sources of nitrate contamination using a combined dual isotope, chemical and Bayesian model approach in a tropical agricultural river: case study in the Mun River. Thailand Sci Total Environ 760
Liu X-L, Liu C-Q, Li S-L, Wang F-S, Wang B-L, Wang Z-L (2011) Spatiotemporal variations of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from two reservoirs in SW China. Atmos Environ 45(31):5458–5468
Luo J, Hu Z, Chen X, Li X, Liu L, Yang M, Miao H, Chu Y, Xu P, Wang F (2022) Chlorophyll maxima layer in a large subtropical reservoir (Xinanjiang Reservoir): spatial development process and limitation by CO2 and phosphorus. Water Res 222
Mulligan M, van Soesbergen A, Sáenz L (2020) GOODD, a global dataset of more than 38,000 georeferenced dams. Sci Data 7(1):31
Ni Z, Zhang L, Yu S, Jiang Z, Zhang J, Wu Y, Zhao C, Liu S, Zhou C, Huang X (2017) The porewater nutrient and heavy metal characteristics in sediment cores and their benthic fluxes in Daya Bay. South China Mar Pollut Bull 124(1):547–554
Qu R, Han G (2022) Potassium isotopes in herbaceous plants: a potential new tool for C3 and C4 plant research. J Geophy Res Biogeosci 127(11):e2021JG006682
Qu R, Han G (2023) Potassium isotopes of fertilizers as potential markers of anthropogenic input in ecosystems. Environ Chem Lett 21(1):41–45
Stanford G, Smith SJ (1972) Nitrogen mineralization potentials of soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 36(3):465–472
Su M, Andersen T, Burch M, Jia Z, An W, Yu J, Yang M (2019) Succession and interaction of surface and subsurface cyanobacterial blooms in oligotrophic/mesotrophic reservoirs: a case study in Miyun Reservoir. Sci Total Environ 649:1553–1562
Wang H, Gao Y, Han Y (2022) Determining the main controlling factors of nitrogen diffusion fluxes at sediment-water interface by grey correlation analysis. Water Resour Manag 36(13):4951–4964
Wang Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Yan S, Guo J (2013) Nitrogen removal from Lake Caohai, a typical ultra-eutrophic lake in China with large scale confined growth of Eichhornia crassipes. Chemosphere 92(2):177–183
Winton RS, Calamita E, Wehrli B (2019) Reviews and syntheses: dams, water quality and tropical reservoir stratification. Biogeosci 16(8):1657–1671
Xiao H-Y, Liu C-Q (2010) Identifying organic matter provenance in sediments using isotopic ratios in an urban river. Geochem J 44(3):181–187
Xu S, Lu J, Chen L, Luo W, Zhu S (2023) Experiment on sediment ammonia nitrogen release of Chaohu Lake in varying hydrodynamic disturbance. Sustainability 15(2):1581
Yu N, Qin Y, Hao F, Lang Y, Wang F (2019) Using seismic surveys to investigate sediment distribution and to estimate burial fluxes of OC, N, and P in a canyon reservoir. Acta Geochim 38(6):785–795
Yue Y, Wang F, Fu Z, Tang Y, Ma J, Qin Y, Li M, Yang M, Chen X-P (2021) Differential response of microbial diversity and abundance to hydrological residual time and age in cascade reservoirs. J Soils Sediments 21(2):1290–1301
Zeng J, Han G (2020) Tracing zinc sources with Zn isotope of fluvial suspended particulate matter in Zhujiang River, southwest China. Ecol Indic 118
Zeng J, Han G, Yang K (2020) Assessment and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a tropical catchment. Northeast Thailand J Cleaner Prod 265
Zeng L, Luo G, He T, Guo Y, Qian X (2016) Effects of sulfate-reducing bacteria on methylmercury at the sediment–water interface. J Environ Sci 46:214–219
Zhang Y, Wu Z, Xu M, Pei Z, Lu X, Zhang D, Wu T, Li B, Xu S (2021) Nutrient deposition over the past 60 years in a reservoir within a medium-sized agricultural catchment. Sci Total Environ 764
Zhao H, Zhang L, Wang S, Jiao L (2018) Features and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus diffusive fluxes at the sediment-water interface of Erhai Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(2):1933–1942
Zhao K, Fu H, Wang Q, Lu H (2021) Determination of water quality characteristics and nutrient exchange flux at the sediment-water interface of the Yitong River in Changchun City. China Water 13(24):3555
Zhu Y, Tang W, Jin X, Shan B (2019) Using biochar capping to reduce nitrogen release from sediments in eutrophic lakes. Sci Total Environ 646:93–104
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Yongbo Gu and Lai Wei for field sampling and Yongmei Hou and Yusi Wang for laboratory analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41661144029 and 41672351) and the Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (Grant No. 2021FY101000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philip N. Owens
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Han, G. & Liu, X. Controlling processes and key factors of nitrogen efflux at the sediment–water interface in a mesotrophic artificial reservoir. J Soils Sediments 23, 3527–3538 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03610-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03610-y