Abstract
Purpose
The present study aims to investigate the effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) Enterobacter sp. Zm-123 and a heavy metal adsorption biomass spent mushroom substrate (SMS) on the growth promotion of rape and reduction of cadmium (Cd) toxicity in contaminated soil.
Materials and methods
The Zm-123 fermentation broth (Zm-123) and SMS were made into three kinds of solid microbial agents by spray-mixing granulation (SG), coating granulation (CG), and semi-solid fermentation (SSF), then Zm-123, SMS, and the three kinds of solid microbial agents were applied to the rapes growing in simulated Cd-contaminated soil pots, respectively.
Results and discussion
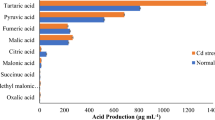
All treatment groups significantly recovered soil physical–chemical properties and decreased exchangeable Cd (SE-Cd) in the soil (P < 0.05). All five treatment groups significantly increased the biomass and chlorophyll content of rape compared with the CK group (P < 0.05). In addition, all treatments effectively increased the activities of antioxidant enzymes catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD), reduced the accumulation of proline and malondialdehyde (MDA), and reduced the Cd content of the edible parts of rape. Among the five treatment groups, the SSF group showed the strongest effect, reducing soil SE-Cd by 19.56–21.94% and the Cd content in the edible part by 30.53–49.06%.
Conclusions
SMS as the substrate of the semi-solid fermentation Zm-123 treatment group can effectively remediate soil Cd contamination and promote the growth of rape.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkrim S, Jebara SH, Saadani O, Abid G, Taamalli W, Zemni H, Mannai K, Louati F, Jebara M (2020) In situ effects of Lathyrus sativus- PGPR to remediate and restore quality and fertility of Pb and Cd polluted soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 192
Abei H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Ali J, Ali F, Ahmad I, Rafique M, Munis MFH, Hassan SW, Sultan T, Iftikhar M, Chaudhary HJ (2021) Mechanistic elucidation of germination potential and growth of Sesbania sesban seedlings with Bacillus anthracis PM21 under heavy metals stress: An in vitro study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208
Ambrosini A, de Souza R, Passaglia LMP (2016) Ecological role of bacterial inoculants and their potential impact on soil microbial diversity. Plant Soil 400:193–207
Bao SD (2007) Soil agro-chemistrical analysis [M], vol 268–270, 3rd edn. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, pp 30–34;76–78;106–108;154–159 in Chinese
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:305–307
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Braud A, Jezequel K, Bazot S, Lebeau T (2009) Enhanced phytoextraction of an agricultural Cr- and Pb-contaminated soil by bioaugmentation with siderophore-producing bacteria. Chemosphere 74:280–286
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil - ScienceDirect. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Cui H, Zhou J, Zhao Q, Si Y, Mao J, Fang G, Liang J (2013) Fractions of Cu, Cd, and enzyme activities in a contaminated soil as affected by applications of micro- and nanohydroxyapatite. J Soils Sediments 13:742–752
Cuypers A, Plusquin M, Remans T, Jozefczak M, Keunen E, Gielen H, Opdenakker K, Nair AR, Munters E, Artois TJ, Nawrot T, Vangronsveld J, Smeets K (2010) Cadmium stress: an oxidative challenge. Biometals 23:927–940
Dabrowska G, Hrynkiewicz K, Trejgell A, Baum C (2017) The effect of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on the phytoextraction of Cd and Zn by Brassica napus L. Int J Phytorem 19:597–604
Dai M, Lu H, Liu W, Jia H, Hong H, Liu J, Yan C (2017) Phosphorus mediation of cadmium stress in two mangrove seedlings Avicennia marina and Kandelia obovata differing in cadmium accumulation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:272–279
Demiral T, Turkan I (2005) Comparative lipid peroxidation, antioxidant defense systems and proline content in roots of two rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 53:247–257
El-Esawi MA, Elkelish A, Soliman M, Elansary HO, Zaid A, Wani SH (2020) Serratia marcescens BM1 enhances cadmium stress tolerance and phytoremediation potential of soybean through modulation of osmolytes, leaf gas exchange, antioxidant machinery, and stress-responsive genes expression. Antioxidants 9
Fang L, Cai P, Chen W, Liang W, Hong Z, Huang Q (2009) Impact of cell wall structure on the behavior of bacterial cells in the binding of copper and cadmium. Colloids Surf A 347:50–55
Fang XZ, Tian WH, Liu XX, Lin XY, Jin CW, Zheng SJ (2016) Alleviation of proton toxicity by nitrate uptake specifically depends on nitrate transporter 1.1 in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 211:149–158
Ghosh A, Pramanik K, Bhattacharya S, Mondal S, Ghosh SK, Maiti TK (2022) A potent cadmium bioaccumulating Enterobacter cloacae strain displays phytobeneficial property in Cd-exposed rice seedlings. Current Research in Microbial Sciences 3:100101–100101
Guo J, Lv X, Jia H, Hua L, Ren X, Muhammad H, Wei T, Ding Y (2020) Effects of EDTA and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on plant growth and heavy metal uptake of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance. J Environ Sci 88:361–369
Guo X, Wei Z, Penn CJ, Xu T, Wu Q (2013) Effect of soil washing and liming on bioavailability of heavy metals in acid contaminated soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77:432–441
Gupta P, Rani R, Chandra A, Kumar V (2018) Potential applications of Pseudomonas sp (strain CPSB21) to ameliorate Cr6+ stress and phytoremediation of tannery effluent contaminated agricultural soils. Sci Rep 8
Hassan W, Bano R, Bashir F, David J (2014) Comparative effectiveness of ACC-deaminase and/or nitrogen-fixing rhizobacteria in promotion of maize (Zea mays L.) growth under lead pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10983–10996
He X, Xu M, Wei Q, Tang M, Guan L, Lou L, Xu X, Hu Z, Chen Y, Shen Z, Xia Y (2020) Promotion of growth and phytoextraction of cadmium and lead in Solanum nigrum L. mediated by plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 205
Jin CW, Liu Y, Mao QQ, Wang Q, Du ST (2013) Mild Fe-deficiency improves biomass production and quality of hydroponic-cultivated spinach plants (Spinacia oleracea L.). Food Chem 138:2188–2194
Jin K, Sleutel S, Buchan D, De Neve S, Cai DX, Gabriels D, Jin JY (2009) Changes of soil enzyme activities under different tillage practices in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Soil Tillage Res 104:115–120
Ju W, Liu L, Fang L, Cui Y, Duan C, Wu H (2019) Impact of co-inoculation with plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and rhizobium on the biochemical responses of alfalfa-soil system in copper contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:218–226
Kanu AS, Ashraf U, Mo Z, Sabir SuR, Baggie I, Charley CS, Tang X (2019) Calcium amendment improved the performance of fragrant rice and reduced metal uptake under cadmium toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:24748–24757
Khakimova L, Chubukova O, Vershinina Z, Maslennikova D (2023) Effects of Pseudomonas sp. OBA 2.4.1 on growth and tolerance to cadmium stress in Pisum sativum L. Biotech (Basel (Switzerland)) 12
Khan AR, Ullah I, Khan AL, Hong SJ, Waqas M, Park GS, Kwak Y, Choi J, Jung BK, Park M, Lee IJ, Shin JH (2014) Phytostabilization and physicochemical responses of korean ecotype Solanum nigrum L. to cadmium contamination. Water Air Soil Pollut 225
Li X, Ma H, Li L, Gao Y, Li Y, Xu H (2019) Subcellular distribution, chemical forms and physiological responses involved in cadmium tolerance and detoxification in Agrocybe Aegerita. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:66–74
Li X, Zhang X, Yang Y, Li B, Wu Y, Sun H, Yang Y (2016) Cadmium accumulation characteristics in turnip landraces from China and assessment of their phytoremediation potential for contaminated soils. Front Plant Sci 7
Manoj SR, Karthik C, Kadirvelu K, Arulselvi PI, Shanmugasundaram T, Bruno B, Rajkumar M (2020) Understanding the molecular mechanisms for the enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals through plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: a review. J Environ Manage 254
Maslennikova D, Nasyrova K, Chubukova O, Akimova E, Baymiev A, Blagova D, Ibragimov A, Lastochkina O (2022) Effects of Rhizobium leguminosarum Thy2 on the Growth and Tolerance to Cadmium Stress of Wheat Plants. Life-Basel 12
Mitra S, Pramanik K, Sarkar A, Ghosh PK, Soren T, Maiti TK (2018) Bioaccumulation of cadmium by Enterobacter sp. and enhancement of rice seedling growth under cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:672–673
Moreira H, Pereira SIA, Marques APGC, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2016) Selection of metal resistant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for the growth and metal accumulation of energy maize in a mine soil - Effect of the inoculum size. Geoderma 278:1–11
Neubauer U, Furrer G, Schulin R (2002) Heavy metal sorption on soil minerals affected by the siderophore desferrioxamine B: the role of Fe (III)(hydr) oxides and dissolved Fe (III). Eur J Soil Sci 53:45–55
Ngan NM, Riddech N (2021) Use of spent mushroom substrate as an inoculant carrier and an organic fertilizer and their impacts on roselle growth (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) and soil quality. Waste Biomass Valorization 12:3801–3811
Pan F, Meng Q, Wang Q, Luo S, Chen B, Khan KY, Yang X, Feng Y (2016) Endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 promotes cadmium accumulation by increasing glutathione biosynthesis in Sedum alfredii Hance. Chemosphere 154:358–366
Patel M, Patel K, Al-Keridis LA, Alshammari N, Badraoui R, Elasbali AM, Abu Al-Soud W, Hassan M I, Yadav DK, Adnan M (2022) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria Curtobacterium oceanosedimentum improves growth attributes and strengthens antioxidant system in Chili (Capsicum frutescens). Sustainability 14
Podazza G, Arias M, Prado FE (2012) Cadmium accumulation and strategies to avoid its toxicity in roots of the citrus rootstock Citrumelo. J Hazard Mater 215:83–89
Pramanik K, Mitra S, Sarkar A, Maiti TK (2018) Alleviation of phytotoxic effects of cadmium on rice seedlings by cadmium resistant PGPR strain Enterobacter aerogenes MCC 3092. J Hazard Mater 351:317–329
Pramanik K, Mitra S, Sarkar A, Soren T, Maiti TK (2017) Characterization of cadmium-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae MCC 3091 promoted rice seedling growth by alleviating phytotoxicity of cadmium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24419–24437
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2010) Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends in Biotechnol 28:142–149
Ran J, Zheng W, Wang H, Wang H, Li Q (2020) Indole-3-acetic acid promotes cadmium (Cd) accumulation in a Cd hyperaccumulator and a non-hyperaccumulator by different physiological responsesy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191
Ribas LCC, de Mendonca MM, Camelini CM, Soares CHL (2009) Use of spent mushroom substrates from Agaricus subrufescens (syn. A. blazei, A. brasiliensis) and Lentinula edodes productions in the enrichment of a soil-based potting media for lettuce (Lactuca sativa) cultivation: Growth promotion and soil bioremediation. Bioresour Technol 100:4750–4757
Sessitsch A, Kuffner M, Kidd P, Vangronsveld J, Wenzel WW, Fallmann K, Puschenreiter M (2013) The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 60:182–194
Sun Y, Zheng S, Wang L, Liang X, Xu Y (2020) Changes of enzymatic activities, substrate utilization pattern, and microbial community diversity in heavy metal-contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 231
Tapia Y, Cala V, Eymar E, Frutos I, Garate A, Masaguer A (2010) Chemical characterization and evaluation of composts as organic amendments for immobilizing cadmium. Bioresour Technol 101:5437–5443
Tessier AP, Campbell P, Bisson MX (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Ullah I, Al-Johny BO, Al-Ghamdi KMS, Al-Zahrani HAA, Anwar Y, Firoz A, Al-Kenani N, Almatry MAA (2019) Endophytic bacteria isolated from Solanum nigrum L., alleviate cadmium (Cd) stress response by their antioxidant potentials, including SOD synthesis by sodA gene. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:197–207
Vance E (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19
Walker DJ, Clemente R, Roig A, Bernal MP (2003) The effects of soil amendments on heavy metal bioavailability in two contaminated Mediterranean soils. Environ Pollut 122:303–312
Wang F, Ouyang W, Hao F, Lin C, Song N (2014) In situ remediation of cadmium-polluted soil reusing four by-products individually and in combination. J Soils Sediments 14:451–461
Wei Y, Jin Z, Zhang M, Li Y, Huang S, Liu X, Jin Y, Wang H, Qu J (2020) Impact of spent mushroom substrate on Cd immobilization and soil property. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:3007–3022
Wu F, Fan J, Ye X, Yang L, Hu R, Ma J, Ma S, Li D, Zhou J, Nie G, Zhang X (2022) Unraveling cadmium toxicity in Trifolium repens L. seedling: insight into regulatory mechanisms using comparative transcriptomics combined with physiological analyses. Int J Mol Sci 23
Xiao L, Yu Z, Liu H, Tan T, Yao J, Zhang Y, Wu J (2020) Effects of Cd and Pb on diversity of microbial community and enzyme activity in soil. Ecotoxicology 29:551–558
Xu Q, Pan W, Zhang R, Lu Q, Xue W, Wu C, Song B, Du S (2018) Inoculation with Bacillus subtilis and Azospirillum brasilense produces abscisic acid that reduces Irt1-mediated cadmium uptake of roots. J Agric Food Chem 66:5229–5236
Yang W, Wang S, Ni W, Rensing C, Xing S (2019) Enhanced Cd-Zn-Pb-contaminated soil phytoextraction by Sedum alfredii and the rhizosphere bacterial community structure and function by applying organic amendments. Plant Soil 444:101–118
Yang X, Feng Y, He ZL, Stoffella PJ (2005) Molecular mechanisms of heavy metal hyperaccumulation and phytoremediation. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18:339–353
Yu S, Liang J, Bai X, Dong L, Liu X, Wei Y, Li Y, Huang S, Qu J (2018) Inoculation of plant growth-promoting bacteria Bacillus sp YM-1 alleviates the toxicity of Pb to pakchoi. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:28216–28225
Yu Z, Zhou Q (2009) Growth responses and cadmium accumulation of Mirabilis jalapa L. under interaction between cadmium and phosphorus. J Hazard Mater 167:38–43
Zeng X, Xu H, Lu J, Chen Q, Li W, Wu L, Tang J, Ma L (2020) The immobilization of soil cadmium by the combined amendment of bacteria and hydroxyapatite. Sci Rep 10
Zhang C, Xue S, Liu GB, Song ZL (2011) A comparison of soil qualities of different revegetation types in the Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil 347:163–178
Zhang M, Jin Z, Zhang X, Wang G, Li R, Qu J, Jin Y (2020) Alleviation of Cd phytotoxicity and enhancement of rape seedling growth by plant growth-promoting bacterium Enterobacter sp. Zm-123. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:33192–33203
Zhang YJ, Xie M, Li CY, Wu G, Peng DL (2014) Impacts of the transgenic CrylAc and CpTI insect-resistant cotton SGK321 on selected soil enzyme activities in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil Environ 60:401–406
Zhao H, Sun S, Zhang L, Yang J, Wang Z, Ma F, Li M (2020) Carbohydrate metabolism and transport in apple roots under nitrogen deficiency. Plant Physiol Biochem 155:455–463
Zhu HJ, Sun LF, Zhang YF, Zhang XL, Qiao JJ (2012) Conversion of spent mushroom substrate to biofertilizer using a stress-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing Pichia farinose FL7. Bioresour Technol 111:410–416
Zhu X, Lv B, Shang X, Wang J, Li M, Yu X (2019) The immobilization effects on Pb, Cd and Cu by the inoculation of organic phosphorus-degrading bacteria (OPDB) with rapeseed dregs in acidic soil. Geoderma 350:1–10
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China (Grant No. LH2020D002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Dong-Mei Zhou
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Yang, R., Guan, Y. et al. Effects of Enterobacter sp. Zm-123 and spent mushroom substrate on rape growth promotion and cadmium toxicity reduction in cadmium-contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 23, 2783–2797 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03515-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03515-w