Abstract
Purpose
Biological nitrogen fixation greatly contributes to crop nitrogen nutrition in the agricultural ecosystem. However, with the inevitable and increasing releases of nanoparticles, the responses of soil diazotrophs (nitrogen-fixing microbes) are still unclear. This study aimed to figure out the effects of nanoparticles on the soil diazotrophic community and the underlying assembly mechanisms in the maize rhizosphere.
Materials and methods
In this study, we investigated the effects of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) on the diazotrophic activity, abundance, community diversity, and composition of the maize rhizosphere by performing a pot experiment. We also proposed the ecological co-occurrence network and assembly processes.
Results
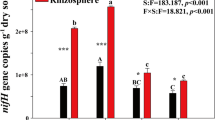
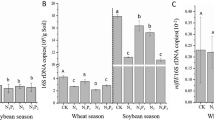
CuONPs increased the soil nitrogenase activity and the diazotrophic diversity, and they also shifted the taxonomic and phylogenetic community composition, with increases in the proportions of Bradyrhizobium, Geobacter, Methylomonas, and Azobacter. Additionally, the high centralization and complexity of the soil diazotrophic co-occurrence network implied that CuONPs destabilized the soil diazotrophic community. We evaluated the importance of deterministic and stochastic processes with βNTI values and found that the soil diazotrophic community assembly was mainly structured by determinism across all experiments, and did not change after treatment with CuONPs.
Conclusions
Our results suggested that CuONPs can shape the diazotrophic communities and destabilize the community, which might go against crop nutrition and soil biological functions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly due to privacy.
References
Afreen S, Omar RA, Talreja N, Chauhan D, Mangalaraja RV, Ashfaq M (2022) Nanostructured materials based on copper/carbon as a plant growth stimulant. Nanobiotechnology for Plant Protection. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 367–391
Alleman AB, Mohammed YA, Mcvay KA, Khan QA, Patrich C, Miller J, Miller Z, Torrion J, Lamb P, Mus F, Chen CC, Peters JW, (2021) Drivers of diazotroph community structure and co-occurrence in a Northern Great Plains pulse crop rotation system. Appl Soil Ecol 157:103737
Aroh K, Udensi JU (2021) Study on interactive effects of different levels of lead and mercury on nitrogen fixation of some diazotrophs. J Adv Biol Biotechnol 24:34–42
Bakshi M, Kumar A (2021) Copper-based nanoparticles in the soil-plant environment: assessing their applications, interactions, fate and toxicity. Chemosphere 281:130940
Birgander J, Olsson PA (2021) Temporal patterns of carbon flow from grassland vegetation to soil microorganisms measured using 13C-labelling and signature fatty acids. Plant Soil 462:245–255
Bray RH, Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci 59:39–45
Burachevskaya M, Minkina T, Mandzhieva S, Bauer T, Nevidomskaya D, Shuvaeva V, Sushhkova S, Kizilkaya R, Gülser C, Rajput V (2021) Transformation of copper oxide and copper oxide nanoparticles in the soil and their accumulation by Hordeum sativum. Environ Geochem Health 43:1655–1672
Cao JL, Lin T-C, Yang ZJ, Zheng Y, Xie L, Xiong DC, Yang YS (2020) Warming exerts a stronger effect than nitrogen addition on the soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community in a young subtropical Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation. Geoderma 367:114273
Caporaso JG et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of highthroughput community sequencing data. Nat Meth 7:335–336
Chaerun SK, Prabowo BA, Winarko R, (2022) Bionanotechnology: the formation of copper nanoparticles assisted by biological agents and their applications as antimicrobial and antiviral agents. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 18:100703
Chandra P, Rai AK, Sundha P, Basak N, Kaur H (2022) Rhizospheric soil–plant-microbial interactions for abiotic stress mitigation and enhancing crop performance. In: Shit PK, Adhikary PP, Bhunia GS, Sengupta D (eds) Soil health and environmental sustainability. Springer, New York, pp 593–614
Chen H, Zheng CY, Qiao YQ, Du SZ, Li W, Zhang XQ, Zhao ZS, Cao XF, Zhang WJ (2020) Long-term organic and inorganic fertilization alters the diazotrophic abundance, community structure, and co-occurrence patterns in a vertisol. Sci Total Environ 766:142441
Cook J, Pawar S, Rg E (2021) Thermodynamic constraints on the diversity of microbial ecosystems. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory 16:1–23
Dai XL, Song DL, Guo QK, Zhou W, Liu GR, Ma RP, Liang GQ, He P, Sun G, Yuan FS, Liu Zb DA, B, Qg A et al (2021) Predicting the influence of fertilization regimes on potential N fixation through their effect on free-living diazotrophic community structure in double rice cropping systems. Soil Biol Biochem 156:108220
Deng Y, Jiang YH, Yang YF, He ZL, Luo F, Zhou JZ (2012) Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform 13:113
Dhevagi P, Priyatharshini S, Ramya A, Sudhakaran M (2021) Biosorption of lead ions by exopolysaccharide producing Azotobacter sp. J Environ Biol 1:40–50
Dong K, Yu Z, Kerfahi D, Lee S, Li N, Yang T, Adams JM (2022) Soil microbial co-occurrence networks become less connected with soil development in a high Arctic glacier foreland succession. Sci Total Environ 813:152565
Etto RM, Jesus EC, Cruz LM, Schneider BSF, Tomachewshi D, Urrea-Valencia S, Goncalves DRP, Galvao F, Ayub RA, Curcio GR, Steffens MBR, Galvao CW (2022) Influence of environmental factors on the tropical peatlands diazotrophic communities from the Southern Brazilian Atlantic Rain Forest. Lett Appl Microbiol 3:543–554
Faria M, Costa L, Chiaramonte JB, Bettiol W, Mendes R (2021) The rhizosphere microbiome: functions, dynamics, and role in plant protection. Trop Plant Pathol 46:13–25
Feng MM, Adams JM, Fan KK, Shi Y, Sun RB, Wang DZ, Chu H (2018) Long-term fertilization influences community assembly processes of soil diazotrophs. Soil Biol Biochem 126:151–158
Feng YZ, Guo ZY, Zhong LH, Zhao F, Zhang JB, Lin XG (2017) Balanced fertilization decreases environmental filtering on soil bacterial community assemblage in north China. Front Microbiol 8:2376
Gao Q, Gao SH, Bates CL, Zeng YF, Lei JS, Dong Q, Qin ZY, Zhao JS, Ning DL, Huang Y, Zhou JZ, Yang YF (2020) The microbial network property as a bio-indicator of antibiotic transmission in the environment. Sci Total Environ 758:143712
Gomes DG, Pieretti JC, Loureno IM, Lourenco IM, Oliveira HC, Seabra AB (2022) Copper-based nanoparticles for pesticide effects. In: de Lima R, Ghoshal S, Santaella C (eds) Fernandes FL, Pereira dCHW. Inorganic nanopesticides and nanofertilizers. Springer, New York, pp 187–212
Goyal D, Prakash O, Pandey J (2019) Rhizospheric microbial diversity: an important component for abiotic stress management in crop plants toward sustainable agriculture. New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 115–134
Guan XY, Gao XY, Avellan A, Spielman-Sun E, Xu J, Laughton S, Yun J, Zhang YL, Bland GD, Zhang Y, Wang XS, Casman EA, Lowry GV (2020) CuO nanoparticles alter the rhizospheric bacterial community and local nitrogen cycling for wheat grown in a calcareous soil. Environ Sci Technol 54:8699–8709
He G, Shu S, Liu G, Zhang QF, Liu Y, Jiang YH, Liu WZ (2022) Aquatic macrophytes mitigate the short-term negative effects of silver nanoparticles on denitrification and greenhouse gas emissions in riparian soils. Environ Pollut 293:118611
Hou J, Wang XX, Hayat T, Wang XK (2017) Ecotoxicological effects and mechanism of CuO nanoparticles to individual organisms. Environ Pollut 221:209–217
Hu JL, Richwine JD, Keyser PD, Li LD, Yao F, Jagadamma S, Debruyn JM (2021) Nitrogen fertilization and native C4 grass species alter abundance, activity, and diversity of soil diazotrophic communities. Front Microbiol 12:675693
Ibrahim AS, Ali GA, Hassanein A, Attia AM, Marzouk ER (2022) Toxicity and uptake of CuO nanoparticles: evaluation of an emerging nanofertilizer on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plant. Sustainability 14:1–20
Indhira D, Krishnamoorthy M, Ameen F, Bhat SA, Arumugam K, Ramalingam S, Priyan SR, Kumar GS (2022) Biomimetic facile synthesis of zinc oxide and copper oxide nanoparticles from Elaeagnus indica for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Environ Res 212:113323
Inoue T, Shimono A, Akaji Y, Baba S, Takenaka A, Chan HT (2020) Mangrove–diazotroph relationships at the root, tree and forest scales: diazotrophic communities create high soil nitrogenase activities in Rhizophora stylosa rhizospheres. Ann Bot 125:131–144
Jabir T, Vipindas PV, Krishnan KP, Hatha AAM (2021) Abundance and diversity of diazotrophs in the surface sediments of Kongsfjorden, an Arctic fjord. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37:41
Jagpreet S, Kumar S, Alok A, Upadhyay SK, Rawat M, Tsang DCW, Bolan N, Kim KH (2019) The potential of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nutrient source for plant growth. J Clean Prod 214:1061–1070
Jan-Roblero J, Cancino-Díaz JC, García-Mena J, Nirmalkar K, Zárate-Segura P, Ordaz A, Guerrero-Barajas C (2020) Assessment of the tolerance to Fe, Cu and Zn of a sulfidogenic sludge generated from hydrothermal vents sediments as a basis for its application on metals precipitation. Mol Biol Rep 47:6165–6177
Jiang YM, Huang HY, Tian YR, Xu X, Li XK (2020) Stochasticity versus determinism: microbial community assembly patterns under specific conditions in petrochemical activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 407:124372
Jo´sko I, Oleszczuk P, Dobrzynska J, Futa B, Joniec J, Dobrowolski R, (2019) Longterm effect of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles on soil microbial community in different types of soil. Geoderma 352:204–212
Kalu CM, Ogola HJ, Selvarajan R, Tekere M, Ntushelo K (2022) Correlations between root metabolomics and bacterial community structures in the phragmites australis under acid mine drainage-polluted wetland ecosystem. Current Microbiol 79:34
Kariman K, Moreira-Grez B, Scanlan C, Rahimlou S, Boitt G, Rengel Z (2022) Synergism between feremycorrhizal symbiosis and free-living diazotrophs leads to improved growth and nutrition of wheat under nitrogen deficiency conditions. Biol Fert Soils 58:121–133
Kaur H, Kalia A, Sandhu JS, Dheri GS, Kuaur G, Pathania S (2022) Interaction of TiO2 nanoparticles with soil: effect on microbiological and chemical traits. Chemosphere 301:134629
Kerfahi D, Ogwu MC, Ariunzaya D, Balt A, Davaasuren D, Enkhmandal O, Purevsuren T, Batbaatar A, Tibbett M, Undrakhbold S, Boldgiv B, Adams JM (2020) Metal-tolerant fungal communities are delineated by high zinc, lead, and copper concentrations in metalliferous gobi desert soils. Microb Ecol 79:420–431
Kumar M, Ambika S, Hassani A, Nidheesh PV (2023) Waste to catalyst: role of agricultural waste in water and wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 858:159762
Kumar U, Nayak AK, Sahoo S, Kumar A, Kaviraj M, Shahid M (2020) Combined effects of elevated CO2, N fertilizer and water deficit stress on diazotrophic community in sub-humid tropical paddy soil. Appl Soil Ecol 155:103682
Latora V, Marchiori M (2001) Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett 87:1–5
Li YY, Pan F, Yao H (2019) Response of symbiotic and asymbiotic nitrogen-fixing microorganisms to nitrogen fertilizer application. J Soil Sediment 19:1948–1958
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Liu Y, Li Y, Pan B, Zhang XY, Zhang H, Steinberg CEW, Qiu H, Vijver MG, Peijnenburg WJGM (2021) Application of low dosage of copper oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles boosts bacterial and fungal communities in soil. Sci the Total Environ 757:143807
Madanayake NH, Perera N, Adassooriya NM (2022) Engineered nanomaterials: threats, releases, and concentrations in the environment. In: Sarma H, Dominguez DC, Lee WY (eds) Emerging contaminants in the environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 225–240
Madline A, Benidire L, Boularbah A (2021) Alleviation of salinity and metal stress using plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from semiarid Moroccan copper-mine soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:67185–67202
Mäkipää R, Huhtiniemi S, Kaseva J, Smolander A (2017) Asymbiotic nitrogen fixation on woody roots of Norway spruce and silver birch. Can J Forest Res 48:172–179
Marchi LD, Coppola F, Soares AMVM, Pretti C, Monserrat JM, Torre CD, Freitas R (2019) Engineered nanomaterials: from their properties and applications, to their toxicity towards marine bivalves in a changing environment. Environ Res 178:108683
Newman ME (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8577–8582
Nogueira EW, Godoi L, Yabuki L, Brucha G, Damianovic MHRZ (2021) Sulfate and metal removal from acid mine drainage using sugarcane vinasse as electron donor: performance and microbial community of the down-flow structured-bed bioreactor. Bioresource Technol 330:124968
Oghenerume P, Eduok S, Ita B, Johan O, Bassey I (2020) Influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles on soil physicochemical properties and arachis hypogea rhizosphere microbial community. Int J Plant Soil Sci 32:88–100
Olesen JM, Bascompte J, Dupont YL, Jordano P (2007) The modularity of pollination networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19891–19896
Orr CH, Leifert C, Cummings SP, Cooper JM (2012) Impacts of organic and conventional crop management on diversity and activity of free-living nitrogen fixing bacteria and total bacteria are subsidiary to temporal effects. PLoS ONE 7:e52891
Pande S, Kost C (2017) Bacterial unculturability and the formation of intercellular metabolic networks. Trends Microbiol 25:349–361
Parada J, Rubilar O, Fernández-Baldo MA, Bertolino FA, Durán N, Seabra AB, Tortella GR (2019) The nanotechnology among us: are metal and metal oxides nanoparticles a nano or mega risk for soil microbial communities?. Crit Rev Biotechnol 39:157–172
Peixoto S, Henriques I, Loureiro S (2021) Long-term effects of Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide exposure on soil microbial communities. Environ Pollut 269:116113
Peng JL, Ma J, Wei XY, Zhang CM, Jia N, Wang X, Wang ET, Hu D, Wang ZW (2021) Accumulation of beneficial bacteria in the rhizosphere of maize (Zea mays L.) grown in a saline soil in responding to a consortium of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Ann Microbiol 71:40
Pérez-Hernández H, Fernández-Luqueño F, Huerta-Lwanga E, Mendoza-Vega J, José DA (2020) Effect of engineered nanoparticles on soil biota: do they improve the soil quality and crop production or jeopardize them? Land Degrad Dev 31:2213–2230
Prasanna NR (2007) Soil pH and its role in cyanobacterial abundance and diversity in rice field soils. Appl Ecol Environ Res 5:103–113
Qu HJ, Ma CX, Xing WL, Xue LH, Liu HJ, White JC, Chen GC, Xing BS (2022) Effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on Salix growth, soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition in a wetland mesocosm. J Hazard Mater 424:127676
Raja MA, Husen A (2020) Role of nanomaterials in soil and water quality management. In: Husen A, Jawaid M (eds) Nanomaterials for agriculture and forestry applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 491–503
Rajput V, Minkina T, Ahmed B, Sushkova S, Singh R, Soldatov M, Laratte B, Fedorenko A, Mandzhieva S, Blicharska E, Musarrat J (2019) Interaction of copper-based nanoparticles to soil, terrestrial, and aquatic systems: critical review of the state of the science and future perspectives. Rev Environ Contam T 252:51–96
Rath KM, Fierer N, Murphy DV, Rousk J (2019) Linking bacterial community composition to soil salinity along environmental gradients. ISME J 13:836–846
Renjini A, Swapna MS, Raj V, Kumar KS, Sankararaman S (2022) Complex network-based pertussis and croup cough analysis: a machine learning approach. Physica D 433:133184
Rizvi A, Ahmed B, Zaidi A, Khan MS (2020) Biosorption of heavy metals by dry biomass of metal tolerant bacterial biosorbents: an efficient metal clean-up strategy. Environ Monit Assess 192:801
Salas-Leiva J, Salas-Leiva DE, Tovar-Ramirez D, Herrera-Pérez G, Tarango-Rivero S, Luna-Velasco A, Orrantia-Borund E (2021) Copper oxide nanoparticles slightly affect diversity and metabolic profiles of the prokaryotic community in pecan tree (Carya illinoinensis) rhizospheric soil. Appl Soil Ecol 157:103772
Samarajeewa AD, Velicogna JR, Schwertfeger DM, Subasinghe RP, Beaudette SLA (2020) Ecotoxicological effects of copper oxide nanoparticles (nCuO) on the soil microbial community in a biosolids-amended soil. Sci the Total Environ 763:143037
Serban M (2020) Exploring modularity in biological networks. Philos T R Soc B 1796:20190316
Simonin M, Cantarel AAM, Crouzet A, Gervaix J, Martins JMF, Richaume A (2018) Negative effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on carbon and nitrogen cyclemicrobial activities in contrasting agricultural soils and in presence of plants. Front Microbiol 3:3102
Sneha GR, Swarnalakshmi K, Sharma M, Reddy K, Bhoumik A, Suman A, Kannepalli A (2021) Soil type influence nutrient availability, microbial metabolic diversity, eubacterial and diazotroph abundance in chickpea rhizosphere. World J Microb Biot 37:167
Stegen JC, Lin XJ, Konopka AE, Fredrickson JK (2012) Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J 6:1653–1664
Sumbul A, Ansari RA, Rizvi R, Mahmood I (2020) Azotobacter: a potential bio-fertilizer for soil and plant health management. Saudi J Biol Sci 27:3634–3640
Sun W, Shahrajabian MH, Cheng QI (2021) Nitrogen fixation and diazotrophs—a review. Rom Biotech Lett 26:2834–2845
Swamy BK, Bura R, Godela R, Ratnam KV, Babu KS (2021) Preparation and evaluation of antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles of nickel, copper and zinc. Int J Current Pharmaceutical Rev Res 13:156–160
Tang HQ, Zhang N, Ni HW, Xu XF, Wang XY, Sui YY, Sun B, Liang YT (2021) Increasing environmental filtering of diazotrophic communities with a decade of latitudinal soil transplantation. Soil Biol Biochem 154:108119
Tao J, Wang S, Liao T, Luo HW (2021) Evolutionary origin and ecological implication of a unique nif island in free-living Bradyrhizobium lineages. ISME J 15:11
Tripathi BM, Stegen JC, Kim M, Dong K, Adams JM, Lee YK (2018) Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J 12:1072–1083
Trivedi M, Kedari S, Nikalje GC (2022) Role of nanoparticles in remediation of contaminated soil. In: Rajput VD, Verma KK, Sharma N, Minkina T (eds) The role of nanoparticles in plant nutrition under soil pollution. Springer, New York, pp 353–370
Upton RN, Sielaff AC, Hofmockel KS, Xu X, Polley HW, Wilsey BJ (2020) Soil depth and grassland origin cooperatively shape microbial community co-occurrence and function. Ecosphere 11:e02973
Wang Q, Wang J, Li Y, Chen D, Ao J, Zhou W, Shen D, Li Q, Huang Z, Jiang Y (2017) Influence of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on N2-fixation activity, abundance, and composition of diazotrophic communities in a Chinese fir plantation. Sci Total Environ 619–620:1530–1537
Wang YN, O’Connor D, Shen ZT, Lo IMC, Tsang DCW, Pehkonen S, Pu SY, Hou DY (2019a) Green synthesis of nanoparticles for the remediation of contaminated waters and soils: constituents, synthesizing methods, and influencing factors. J Clean Prod 226:540–549
Wang YS, Li CN, Tu B, Kou YP, Li XZ (2021) Species pool and local ecological assembly processes shape the β-diversity of diazotrophs in grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 160:108338
Wang YY, Jiang FP, Ma CX, Rui YK, Tsang DCW, Xing BS (2019b) Effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on amino acids in wheat grains (Triticum aestivum) in a life cycle study. J Environ Manag 241:319–327
Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 33:475–505
Whiteside MD, Werner GDA, Caldas VEA, Av P, Dupin SE, Elbers B, Bakker M, Wyatt GAK, Klein M, Hink MA, Postma M, Vaitla B, Noë R, Shimizu TS, West SA, Kiers ET (2019) Mycorrhizal fungi respond to resource inequality by moving phosphorus from rich to poor patches across networks. Current Biol 29:2043–2050
Wu H, Li Y, Zhang W, Wang C, Wang P, Niu L, Du J, Gao Y (2019) Bacterial community composition and function shift with the aggravation of water quality in a heavily polluted river. J Environ Manage 237:433–441
Wyszkowska J, Borowik A, Kucharski M, Kucharski J (2013) Effect of cadmium, copper and zinc on plants, soil microorganisms and soil enzymes. J Elem 18:769–796
Xiao ZG, Fan NK, Yue L, Chen FR, Ji HH, Shu YH, Rasmann S, Wang ZY (2021) Dose-dependent effects of CeO2 nanomaterials on tomato plant chemistry and insect herbivore resistance. Environ Sci: Nano 8:3577
Xu M, Liu Y, Deng Y, Zhang SY, Hao XD, Zhu P, Zhou JY, Yin HQ, Liang YL, Liu HW, Liu XD, Bai LY, Jiang LH, Jiang HD (2020) Bioremediation of cadmium-contaminated paddy soil using an autotrophic and heterotrophic mixture. RSC Adv 10:26090
Yadav A, Singh RP, Singh AL, Singh M (2021) Identification of genes involved in phosphate solubilization and drought stress tolerance in chickpea symbiont Mesorhizobium ciceri Ca181. Arch Microbiol 203:1167–1174
Yu FM, Lin JM, Xie DY, Yao YW, Wang XR, Huang YY, Xin MF, Yang FF, Liu KH, Li Y (2020) Soil properties and heavy metal concentrations affect the composition and diversity of the diazotrophs communities associated with different land use types in a mining area. Appl Soil Ecol 155:103669
Yusefi-Tanha E, Fallah S, Rostamnejadi A, Pokhrel LR (2020) Particle size and concentration dependent toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) on seed yield and antioxidant defense system in soil grown soybean (Glycine max cv. Kowsar). Sci Total Environ 715:136994
Zhang JW, Tang HY, Zhu JG, Lin XG, Feng YZ (2019) Effects of elevated ground-level ozone on paddy soil bacterial community and assembly mechanisms across four years. Sci Total Environ 654:505–513
Zhang X, Ward BB, Sigman DM (2020) Global nitrogen cycle: critical enzymes, organisms, and processes for nitrogen budgets and dynamics. Chem Rev 120:5308–5341
Zhao S, Su X, Wang Y, Yang X, Bi M, He Q, Chen Y (2020) Copper oxide nanoparticles inhibited denitrifying enzymes and electron transport system activities to influence soil denitrification and N2O emission. Chemosphere 245:125394
Zhao X, Yang Y, Feng K, Wang KJ, Wang XH, Liu BF, Xie GJ, Xing DF (2021) Self-regulating microbiome networks ensure functional resilience of biofilms in sand biofilters during manganese load fluctuations. Water Res 188:116473
Zhou JZ, Ning DL (2017) Stochastic community assembly: does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol Mol Biol R 81:e00002-17
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800520), the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (YDZJ202201ZYTS512), and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of Jiangxi Agricultural University (9232308147).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Dan Tsang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Liu, Z., Zhao, H. et al. Effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on soil diazotrophic communities in maize rhizosphere. J Soils Sediments 23, 1760–1774 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03430-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03430-0