Abstract
Purpose
Constructions of roadways have created many rock-cut slopes, and artificial soils have been sprayed onto the rock-cut slopes to promote re-vegetation. The aims of the study were to (1) understand the physicochemical properties, heavy metal enrichment and microbial community conditions of the artificial soil on the rock-cut slopes re-vegetated for different years and (2) analyze the associations between environmental factors and microbial communities, identify main environmental factors and provide suggestions to promote slope ecosystem restoration.
Materials and methods
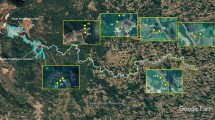
Nine rock-cut slopes located alongside railways constructed in different years (1996, 2003, 2007) were selected. Two natural slopes far away from the railways were selected as controls. At each rock slopes, five sampling transects with 1, 5, 15, 20, and 50 m from the track were created. At each transect, topsoil collected from 15 to 20 points along the transect comprised a soil sample. At the natural control slope, topsoil from more than 20 points scattered across the natural slope were collected and mixed together to obtain one soil sample. Total 47 soil samples were obtained. Soil physicochemical properties, microbial communities, accumulation of heavy metals and their relationships were investigated.
Results and discussions
The contents of clay and SOC, soil stability and erosion resistance ability increased with increasing re-vegetation time. However, there is a big gap that exists with natural slopes. The artificial soils were mainly polluted by Cd and Pb and tended to accumulate with increasing railway operation time. The dominant bacterial species of the study sites were similar but differed in abundance. Proteobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria at the phylum level and Sphingomonas, Haliangium, Bryobacter, and Gemmatimonas at the genus level dominated the soil microbial communities. The redundancy analysis results indicated that HCl-extractable Fe, AK and SOC were the most important factors affecting the microbial communities of the rock-cut slopes, and HCl-extractable Cd, HCl-extractable Cr, Cu and Cd also had some influence.
Conclusions
Monitoring heavy metal enrichment and managing soil nutrients, especially AK, SOC and Fe, are important to the successful re-vegetation of the rock-cut slopes. Slow releasing fertilizers and organic fertilizers should be used to provide long-term nutrient supply for the vegetation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [Chen Z. Q.], upon reasonable request.
References
Ai Y, Chen Z, Guo P, Zeng L, Liu H, Da Z, Li W (2012) Fractal characteristics of synthetic soil for cut slope revegetation in the Purple soil area of China. Can J Soil Sci 92(2):277-e284
Alvarez A, Saez JM, Costa JSD, Colin VL, Fuentes MS, Cuozzo SA, Benimeli CS, Polti MA, Amoroso MJ (2017) Actinobacteria: current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 166:41–62
Angers DA (1998) Water-stable aggregation of Québec silty clay soils: some factors controlling its dynamics. Soil till Res 47(1):91–96
Asano M, Wagai R (2014) Evidence of aggregate hierarchy at micro- to submicron scales in an allophanic Andisol. Geoderma 216:62–74
Bao SD (2000) Analysis of soil agrochemistry. China Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Baraniecki CA, Aislabie J, Foght JM (2002) Characterization of Sphingomonas sp. Ant 17, an aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from Antarctic soil. Microb Ecol 43(1):44–54
Bet WWA, Dong C, Wu J, Liu X, Wu Y, Chen X, Yu S (2017) Ecological effects of soil properties and metal concentrations on the composition and diversity of microbial communities associated with land use patterns in an electronic waste recycling region. Sci Total Environ 601–602:57–65
Buchmann C, Schaumann GE (2018) The contribution of various organic matter fractions to soil-water interactions and structural stability of an agriculturally cultivated soil. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 181(4):586–599
Cagle G, Lin Q, Graham SA, Mendelssohn I, Fleeger JW, Deis D, Johnson DS, Zhou J, Hou A (2020) Planting Spartina alterniflora in a salt marsh denuded of vegetation by an oil spill induces a rapid response in the soil microbial community. Ecol Eng 151
Cederlund H, Thierfelder T, Stenstrom J (2008) Functional microbial diversity of the railway track bed. Sci Total Environ 397(1–3):205–214
Chen Z, Ai Y, Fang C, Wang K, Li W, Liu S, Li C, Xiao J, Huang Z (2014b) Distribution and phytoavailability of heavy metal chemical fractions in artificial soil on rock cut slopes alongside railways. J Hazard Mater 273(may 30):165–173
Chen Z, Luo R, Huang Z, Tu W, Chen J, Li W, Chen S, Xiao J, Ai Y (2015) Effects of different backfifill soils on artifificial soil quality for cut slope revegetation: soil structure, soil erosion, moisture retention and soil C stock. Ecol Eng 83:5–12
Chen Z, Wang K, Ai YW, Li W, Gao H, Fang C (2014a) The effects of railway transportation on the enrichment of heavy metals in the artifificial soil on railway cut slopes. Environ Monit Assess 186(2):1039-e1049
Chen LP, Ying-Wei AI, Yan-Hua YU, Liu H, Yang X, Zhang J (2008) Content and speciation of heavy metal in topsoil alongside railway in hills area in sichuan. Chem Res Application(Chinese)
Chodak M, Gołębiewski M, Morawska-Płoskonka J, Kuduk K, Niklińska M (2013) Diversity of microorganisms from forest soils differently polluted with heavy metals. Appl Soil Ecol 64(Complete):7–14
Cwiakala M, Korzeniowska J, Kraszewski C, Rafalski L (2019) Testing the concentration of trace metals in soils near roads with varied traffic intensity. Roads and Bridges-Drogi I Mosty 18(2):127–134
De Ona J, Ferrer A, Osorio F (2011) Erosion and vegetation cover in road slopes hydroseeded with sewage sludge. Transp Res Part D Transp Environ 16(6):465–468
Ded Ysh SN, Kulichevskaya IS, Huber KJ, Overmann J (2017) Defining the taxonomic status of described subdivision 3 Acidobacteria: proposal of Bryobacteraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67(2):498–501
Degens BP, Schipper LA, Sparling GP, Duncan LC (2001) Is the microbial community in a soil with reduced catabolic diversity less resistant to stress or disturbance? Soil Biol Biochem 33(9):1143–1153
Ding X, Liang C, Zhang B, Yuan Y, Hang XZ (2015) Higher rates of manure application lead to greater accumulation of both fungal and bacterial residues in macroaggregates of a clay soil. Soil Biol Biochem 84:137–146
Dong H, Li L, Lu Y, Cheng Y, Wang Y, Ning Q, Wang B, Zhang L, Zeng G (2019) Integration of nanoscale zero-valent iron and functional anaerobic bacteria for groundwater remediation: a review. Environ Int 124:265–277
Fajardo C, Costa G, Nande M, Botias P, Garcia-Cantalejo J, Martin M (2019) Pb, Cd, and Zn soil contamination: monitoring functional and structural impacts on the microbiome. Appl Soil Ecol 135:56–64
Gao GJ, Yuan JG, Han RH, Xin GR, Yang ZY (2007) Characteristics of the optimum combination of synthetic soils by plant and soil properties used for rock slope restoration. Ecol Eng 30:303–311
Garcia-Palacios P, Bowker MA, Chapman SJ, Maestre FT, Soliveres S, Gallardo A, Valladares F, Guerrero C, Escudero A (2011) Early-successional vegetation changes after roadside prairie restoration modify processes related with soil functioning by changing microbial functional diversity. Soil Biol Biochem 43(6):1245–1253
García-Palacios P, Soliveres S, Maestre FT, Escudero A, Castillo-Monroy AP, Valladares F (2010) Dominant plant species modulate responses to hydroseeding, irrigation and fertilization during the restoration of semiarid motorway slopes. Ecol Eng 36(10):1290–1298
Golebiewski M, Deja-Sikora E, Cichosz M, Tretyn A, Wrobel B (2014) 16S rDNA pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial community in heavy metals polluted soils. Microb Ecol 67:635–647
Gyasi-Agyei Y, Sibley J, Ashwath N (2001) Quantitative evaluation of strategies for erosion control on a railway embankment batter. Hydrol Process 15(17):3249–3268
Hahn AS, Quideau SA (2013) Long-term effects of organic amendments on the recovery of plant and soil microbial communities following disturbance in the Canadian boreal forest. Plant Soil 363(1–2):331–344
He L, Zhu Q, Wang Y, Chen C, He M, Tan F (2021) Irrigating digestate to improve cadmium phytoremediation potential of Pennisetum hybridum. Chemosphere 279
Hu Y, Zhang Z, Huang L, Qi Q, Liu L, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Zhou H, Lv X, Mao Z, Yang Y, Zhou J, Kardol P (2019) Shifts in soil microbial community functional gene structure across a 61-year desert revegetation chronosequence. Geoderma 347:126–134
Huang D, Liu L, Zeng G, Xu P, Jia W (2017a) The effects of rice straw biochar on indigenous microbial community and enzymes activity in heavy metal-contaminated sediment. Chemosphere 174:545–553
Huang Z, Chen J, Ai X, Li R, Ai Y, Li W (2017b) The texture, structure and nutrient availability of artificial soil on cut slopes restored with OSSS - influence of restoration time. J Environ Manage 200:502–510
Jiang B, Adebayo A, Jia JL, Xing Y, Deng SQ, Guo LM, Liang YT, Zhang DY (2019) Impacts of heavy metals and soil properties at a Nigerian e-waste site on soil microbial community. J Hazard Mater 362:187–195
Jim CY (2001) Ecological and landscape rehabilitation of a quarry site in Hong Kong. Restor Ecol 9(1):85–94
Kenarova A, Radeva G, Traykov I, Boteva S (2014) Community level physiological profiles of bacterial communities inhabiting uranium mining impacted sites. Ecotox Environ Safe 100(feb.):226–232
Krailertrattanachai N, Ketrot D, Wisawapipat W (2019) The distribution of trace metals in roadside agricultural soils, Thailand. Int J Env Res Pub He 16(5)
Li S, Wu J, Huo Y, Zhao X, Xue L (2020) Profiling multiple heavy metal contamination and bacterial communities surrounding an iron tailing pond in Northwest China. Sci Total Environ 752(2):14187
Liao M, Xie XM (2007) Effect of heavy metals on substrate utilization pattern, biomass, and activity of microbial communities in a reclaimed mining wasteland of red soil area. Ecotox Environ Safe 66(2):217–223
Liu H, Chen LP, Ai YW, Yang X, Yu YH, Zuo YB, Fu GY (2009) Heavy metal contamination in soil alongside mountain railway in Sichuan, China. Environ Monit Assess 152:25–33
Liu J, He X-X, Lin X-R, Chen W-C, Zhou Q-X, Shu W-S, Huang L-N (2015) Ecological effects of combined pollution associated with E-waste recycling on the composition and diversity of soil microbial communities. Environ Sci Technol 49(11):6438–6447
Meng Q, Sun Y, Zhao J, Zhou L, Ma X, Zhou M, Gao W, Wang G (2014) Distribution of carbon and nitrogen in water-stable aggregates and soil stability under long-term manure application in solonetzic soils of the Songnen plain, northeast China. J Soil Sediment 14(6):1041–1049
Mohammadi J, Motaghian MH (2011) Spatial prediction of soil aggregate stability and aggregate-associated organic carbon content at the catchment scale using geostatistical techniques. Pedosphere 21:389–399
Olsen SR (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Miscellaneous Paper Institute for Agricultural Research Samaru Pp
Regelink IC, Stoof CR, Rousseva S, Weng L, Lair GJ, Kram P, Nikolaidis NP, Kercheva M, Banwart S, Comans R (2015) Linkages between aggregate formation, porosity and soil chemical properties. Geoderma 247–248:24–37
Rivera D, Mejias V, Jauregui BM, Costa-Tenorio M, Isabel Lopez-Archilla A Peco B ( 2014) Spreading topsoil encourages ecological restoration on embankments: soil fertility, microbial activity and vegetation cover. Plos One 9(7)
Shang J, Liu B (2021) Application of a microbial consortium improves the growth of Camellia sinensis and influences the indigenous rhizosphere bacterial communities. J Appl Microbiol 130(6):2029–2040
Shrestha P, Gautam R, Ashwath N (2019) Effects of agronomic treatments on functional diversity of soil microbial community and microbial activity in a revegetated coal mine spoil. Geoderma 338:40–47
Stefanowicz AM, Kapusta P, Zubek S, Stanek M, Woch MW (2020) Soil organic matter prevails over heavy metal pollution and vegetation as a factor shaping soil microbial communities at historical Zn-Pb mining sites. Chemosphere 240
Tang J, Zhang J, Ren L, Zhou Y, Gao J, Luo L, Yang Y, Peng Q, Huang H, Chen A (2019) Diagnosis of soil contamination using microbiological indices: a review on heavy metal pollution. J Environ Manage 242(JUL.15):121–130
Wenfeng W, Zhiqi Q, Hongming T, Lixiang and Cao (2014) Siderophore production by actinobacteria. Biometals 27(4):623–631
Wu B, Hou S, Peng D, Wang Y, Wang C, Xu F, Xu H (2018) Response of soil micro-ecology to different levels of cadmium in alkaline soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 166:116–122
Xu Y, Seshadri B, Sarkar B, Wang H, Rumpel C, Sparks D, Farrell M, Hall T, Yang X, Bolan N (2018) Biochar modulates heavy metal toxicity and improves microbial carbon use efficiency in soil. Sci Total Environ 621:148–159
Yan S, Zhao J, Ren T, Liu G (2020) Correlation between soil microbial communities and tobacco aroma in the presence of different fertilizers. Ind Crop Prod 151:112454
Yeomans JC, Bremner JM (1988) A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plan 19(13):1467–1476
Yurong Y, Miao D, Yaping C, Jinlong W, Ming T, Yihui B (2017) Comparisons of soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial communities in heavy metal contaminated bulk and rhizosphere soils of Robinia pseudoacacia L. in the Northern Foot of Qinling Mountain. Forests 8(11):430
Zeng Q, An S, Yang L (2017) Soil bacterial community response to vegetation succession after fencing in the grassland of China. Sci Total Environ 609(dec.31):2–10
Zhan HY, Jiang YF, Yuan J, Hu XF, Nartey OD, Wang BL (2014) Trace metal pollution in soil and wild plants from lead–zinc smelting areas in Huixian County, Northwest China. J Geochem Explor 147:182–188
Zhang W, Chen L, Zhang R, Lin KF (2016a) High throughput sequencing analysis of the joint effects of BDE209-Pb on soil bacterial community structure. J Hazard Mater 301:1–7
Zhang C, Nie S, Liang J, Zeng G, Wu H, Hua (2016b) Effects of heavy metals and soil physicochemical properties on wetland soil microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Sci Total Environ 557–558:785–790
Zhao X, Huang J, Lu J, Sun Y (2019) Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotox Environ Safe 170(APR):218–226
Zhao L, Liu Y, Yuan S, Li Z, Li X (2020) Development of archaeal communities in biological soil crusts along a revegetation chronosequence in the Tengger Desert, north central China. Soil till Res 196:104443
Zhen S, Wang S, Luo L, Ren Y, Liang Y, Yang R (2019) Significant impacts of both total amount and availability of heavy metals on the functions and assembly of soil microbial communities in different land use patterns. Front Microbiol 10:2293–2293
Zheng YJ, Chen YP, Maltby L, Jin XL (2016) Highway increases concentrations of toxic metals in giant panda habitat. Environ Sci Pollut R 23(21):1–11
Zhou X, Zhang J, Pan D, Ge X, Jin X (2018) p-Coumaric acid can alter the composition of cucumber rhizosphere microbial communities and induce negative plant-microbial interactions. Biol Fert Soils 54:363
Acknowledgements
The authors show our gratitude to all those helped us during the conduction of this project and writing of the paper.
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Key Research Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Department, China [grant no. 2022YFS0498] and the financial support of the National Science Foundation of China [grant no. 41501112].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Girish Choppala.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
You, A., Tang, J., Shu, J. et al. The impacts of soil properties and heavy metals on soil microbial communities in the artificial soils on railway rock-cut slopes. J Soils Sediments 23, 1820–1831 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03420-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03420-8