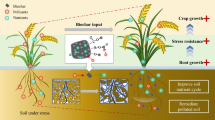
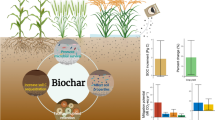
Abstract
Purpose
Environmentally friendly mulching material and appropriate tillage practice are needed to solve plastic film residues in agricultural production in ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting technology (RFRHT) in the Loess Plateau in China.
Materials and methods
A field experiment in randomized block design was conducted to (1) investigate the runoff coefficient for three ridge widths (30, 45, and 60 cm) using three ridge mulching materials (ridges compacted with soil (RCS), maize straw biochar-soil mixture (SBM), and cow dung biochar-soil mixture (DBM)); (2) the effects of three ridge widths using three ridge mulching materials on soil moisture, temperature, nutrients, fodder yield, quality, and water use efficiency (WUE) of sainfoin and conventional flat planting (FP) as a control, during two consecutive sainfoin-growing years: 2017 and 2018.
Results
The predicted runoff coefficient for RCS30, RCS45, RCS60, SBM30, SBM45, SBM60, DBM30, DBM45, and DBM60 (subscripts 30, 45, and 60 referred to ridge widths) was 0.31, 0.33, 0.34, 0.26, 0.30, 0.31, 0.22, 0.24, and 0.25, respectively, over 2 years. DBM had a higher concentration of total nitrogen and organic matter compared to SBM, while SBM had a higher concentration of Olsen phosphorus and available potassium compared to DBM. The higher runoff coefficient and soil moisture in SBM led to higher fodder yield, WUE, and condensed tannin content of sainfoin, compared to DBM. Compared to FP, in RCS, fodder yield and WUE of sainfoin decreased by 8.8–17.8% and 0.6–2.6 kg ha−1 mm−1, respectively. Condensed tannins concentration of sainfoin for RCS, SBM, and DBM increased by 4.1 −9.0%, 11.4 −21.8%, and 9.4 −15.2%, respectively. Fodder yield in SBM and DBM increased by 14.3 −19.5% and 7.1 −10.0%, respectively, while WUE in SBM and DBM increased by 6.7 −8.5 and 4.7 −5.5 kg ha−1 mm−1.
Conclusion
Ridges compacted with biochar-soil mixture, especially with maize straw biochar-soil mixture, increased fodder yield, WUE, and condensed tannin content of sainfoin. The optimum ridge width in SBM and DBM for sainfoin production was 46–49 and 41 cm, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- RFRHT:
-
Ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting technology
- RCS:
-
Ridges compacted with soil
- SBM:
-
Ridges compacted with maize straw biochar-soil mixture
- DBM:
-
Ridges compacted with cow dung biochar-soil mixture
- FP:
-
Conventional flat planting
- AFY:
-
Actual fodder yield
- ET:
-
Evapotranspiration
- WUE:
-
Water use efficiency
References
Abujabhah IS, Bound SA, Doyle R, Bowman JP (2016) Effects of biochar and compost amendments on soil physico-chemical properties and the total community within a temperate agricultural soil. Appl Soil Ecol 98:243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.10.021
Ahmadi SH, Ghasemi H, Sepaskhah AR (2020) Rice husk biochar influences runoff features, soil loss, and hydrological behavior of a loamy soil in a series of successive simulated rainfall events. CATENA 192:104587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104587
Blanco-Canqui H (2017) Biochar and soil physical properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 81:687–711. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2017.01.0017
Bordoloi S, Garg A, Sreedeep S, Lin P, Mei G (2018) Investigation of cracking and water availability of soil-biochar composite synthesized from invasive weed water hyacinth. Bioresour Technol 263:665–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.011
Brinkhaus AG, Wyss U, Arrigo Y, Girard M, Bee G, Zeitz JO, Kreuzer M (2017) In vitro ruminal fermentation characteristics and utilisable CP supply of sainfoin and birdsfoot trefoil silages and their mixtures with other legumes. Animal 11:580–590. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731116001816
Chen G, Gao K, Yan B, Dan Z, Zhou W, Cheng Z (2018) Estimation and emissions from crop straw and animal dung in Tibet. Sci Total Environ 631:1038–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.029
Cicek H, Ates S, Ozcan G, Tezel M, Kling JG, Louhaichi M, Keles G (2020) Effect of nurse crops and seeding rate on the persistence, productivity and nutritive value of sainfoin in a cereal-based production system. Grass Forage Sci 75:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/gfs.12467
Crutzen PJ (2006) Albedo enhancement by stratospheric sulfur injections: a contribution to resolve a policy dilemma? Climatic Change 77:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9101-y
Edeh IG, Mašek O, Buss W (2020) A meta-analysis on biochar’s effects on soil water properties – new insights and future research challenges. Sci Total Environ 714:136857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136857
El-Naggar A, Lee SS, Rinklebe J, Farooq M, Song H, Sarmah AK, Zimmerman AR, Ahmad M, Shaheen SM, Ok YS (2019) Biochar application to low fertility soils: a review of current status, and future prospects. Geoderma 337:536–554
Farhangi-Abriz S, Torabian S, Qin R, Noulas C, Lu Y, Gao S (2021) Biochar effects on yield of cereal and legume crops using meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 775:145869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145869
Feng W, Yang F, Cen R, Liu J, Qu Z, Miao Q, Chen H (2021) Effects of straw biochar application on soil temperature, available nitrogen and growth of corn. J Environ Manage 277:111331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111331
Gan Y, Siddique KHM, Turner NC, Li XG, Niu JY, Yang C, Liu L, Chai Q (2013) Ridge-furrow mulching systems-an innovative technique for boosting crop productivity in semiarid rain-fed environments. Adv Agron 118:429–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-405942-9.00007-4
Gao Y, Shao G, Lu J, Zhang K, Wu S, Wang Z (2020) Effects of biochar application on crop water use efficiency depend on experimental conditions: a meta-analysis. Field Crop Res 249:107763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2020
Gea A, Stringano E, Brown RH, Mueller-Harvey I (2011) In situ analysis and structural elucidation of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) tannins for high-throughput germplasm screening. J Agric Food Chem 59:495–503. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf103609p
Geist HJ, Lambin EF (2004) Dynamic causal patterns of desertification. Bioscience 54:817. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054
Głąb T, Palmowska J, Zaleski T, Gondek K (2016) Effect of biochar application on soil hydrological properties and physical quality of sandy soil. Geoderma 281:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.06.02
Gul S, Whalen JK (2016) Biochemical cycling of nitrogen and phosphorus in biochar-amended soils. Soil Biol Biochem 103:1–15
Hagemann N, Subdiaga E, Orsetti S, de la Rosa JM, Knicker H, Schmidt HP, Kappler A, Behrens S (2018) Effect of biochar amendment on compost organic matter composition following aerobic compositing of manure. Sci Total Environ 613–614:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.161
Han F, Ren L, Zhang XC (2016) Effect of biochar on the soil nutrients about different grasslands in the Loess Plateau. CATENA 137:554–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.11.002
Hatew B, Carbonero CH, Stringano E, Sales LF, Smith LMJ, Hendriks WH, Pellikaan WF (2014) Diversity of condensed tannin structures affects rumen in vitro methane production in sainfoin ( Onobrychis viciifolia ) accessions. Grass Forage Sci 70:474–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/gfs.12125
He G, Wang Z, Li F, Dai J, Li Q, Xue C, Cao H, Wang S, Malhi SS (2016) Soil water storage and winter wheat productivity affected by soil surface management and precipitation in dryland of the Loess Plateau, China. Agr Water Manage 171:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.03.005
Horta MDC, Torrent J (2007) The Olsen P method as an agronomic and environmental test for predicting phosphate release from acid soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosy 77:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-006-9066-2
Hossain MZ, Bahar MM, Sarkar B, Donne SW, Ok YS, Palansooriya KN, Kirkham MB, Chowdhury S, Bolan N (2020) Biochar and its importance on nutrient dynamics in soil and plant. Biochar 2:379–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-020-00065-z
Huang X, Niu R, Huang X, An Y, Li J, Li M, He H, Garg A (2021) Influence of sustainable biochars produced from kitchen waste, pig manure, and wood on soil erosion. Water 13:2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162296
Irani S, Majidi MM, Mirlohi A, Karami M, Zargar M (2015a) Response to drought stress in sainfoin: within and among ecotype variation. Crop Sci 55:1868–1880. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2014.07.0481
Irani S, Majidi MM, Mirlohi A, Zargar M, Karami M (2015b) Assessment of drought tolerance in sainfoin: physiological and drought tolerance indices. Agron J 107:1771–1781. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj15.0131
Khadem A, Raiesi F, Besharati H, Khalaj MA (2021) The effects of biochar on soil nutrients status, microbial activity and carbon sequestration potential in two calcareous soils. Biochar 3:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-020-00076-w
Kosiorek M, Wyszkowski M (2017) Content of organic carbon, total nitrogen and available forms of macronutrients in soil contaminated with cobalt. J Elem 22:1427–1437. https://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2016.21.4.1324
Koskei K, Munyasya AN, Wang YB, Zhao ZY, Zhou R, Indoshi SN, Wang W, Cheruiyot WK, Mburu DM, Nyende AB, Xiong YC (2021) Effects of increased plastic film residues on soil properties and crop productivity in agro-ecosystem. J Hazard Mater 414:125521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125521
Li Y, Feng G, Tewolde H, Yang M, Zhang F (2020) Soil, biochar, and nitrogen loss to runoff from loess soil amended with biochar under simulated rainfall. J Hydrol 591:125318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125318
Li Y, Zhang F, Yang M, Zhang J, Xie Y (2019) Impacts of biochar application rates and particle sizes on runoff and soil loss in small cultivated loess plots under simulated rainfall. Sci Total Environ 649:1403–1413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.415
Liang J, Li Y, Si B, Wang Y, Chen X, Wang X, Chen H, Wang H, Zhang F, Bai Y, Biswas A (2021) Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline-alkali soils. Sci Total Environ 771:144802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144802
Libutti A, Francavilla M, Monteleone M (2021) Hydrological properties of a clay loam soil as affected by biochar application in a pot experiment. Agronomy 11:489. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030489
Liu X, Wang Y, Yan X, Hou H, Liu P, Cai T, Zhang P, Jia Z, Ren X, Chen X (2020) Appropriate ridge-furrow ratio can enhance crop production and resource use efficiency by improving soil moisture and thermal condition in a semi-arid region. Agr Water Manage 240:106289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106289
Liu Y, Yang S, Lu H, Wang Y (2018) Effects of biochar on spatial and temporal changes in soil temperature in cold waterlogged rice paddies. Soil till Res 181:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.04.008
Luo CL, Zhang XF, Duan HX, Zhou R, Mo F, Mburu DM, Wang BZ, Wang W, Kavagi L, Xiong YC (2021) Responses of rainfed wheat productivity to varying ridge-furrow size and ratio in semiarid eastern African Plateau. Agr Water Manage 249:106813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106813
Ma G, Mao H, Bu Q, Han L, Shabbir A, Gao F (2020) Effect of compound biochar substrate on the root growth of cucumber plug seedlings. Agronomy 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10081080
Malisch CS, Salminen JP, Kölliker R, Engström MT, Suter D, Studer B, Lüscher A (2016) Drought effects on proanthocyanidins in sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia Scop.) are dependent on the plant’s pntogenetic stage. J Agric Food Chem 64:9307–9316. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02342
Obia A, Cornelissen G, Martinsen V, Smebye AB, Mulder J (2020) Conservation tillage and biochar improve soil water content and moderate soil temperature in a tropical Acrisol. Soil till Res 197:104521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104521
Obia A, Mulder J, Martinsen V, Cornelissen G, Børresen T (2016) In situ effects of biochar on aggregation, water retention and porosity in light-textured tropical soils. Soil till Res 155:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.08.002
Oram NJ, Van de Voorde TFJ, Ouwehand GJ, Bezemer TM, Mommer L, Jeffery S, Van GJW (2014) Soil amendment with biochar increases the competitive ability of legumes via increased potassium availability. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.03.031
Pandit NR, Schmidt HP, Mulder J, Hale SE, Husson O, Cornelissen G (2020) Nutrient effect of various composting methods with and without biochar on soil fertility and maize growth. Arch Agron Soil Sci 66:250–265. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1610168
Qi Y, Yang X, Mejia A, Huerta E, Beriot N, Gertsen H, Garbeva P, Geissen V (2018) Macro-and micro-plastics in soil-plant system : effects of plastic mulch film residues on wheat ( Triticum aestivum ) growth. Sci Total Environ 645:1048–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.229
Rawat J, Saxena J, Sanwal P (2019) Biochar: a sustainable approach for improving plant growth and soil properties. Biochar-an Imperative Amendment for Soil and the Environment. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.82151
Schofield P, Mbugua DM, Pell AN (2001) Analysis of condensed tannins: a review. Anim Feed Sci Technol 91:21–40
Sheppard SC, Cattani DJ, Ominski KH, Biligetu B, Bittman S, McGeough EJ (2019) Sainfoin production in western Canada: a review of agronomic potential and environmental benefits. Grass Forage Sci 74:6–18
Sun CX, Huang GH, Fan Y, Zhou X, Lu C, Wang XQ (2019) Drought occurring with hot extremes : changes under future climate change on Loess Plateau, China. Earth s Futur 7:587–604. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018EF001103
Wang Q, Zhang EH, Li FM, Li FR (2008) Runoff efficiency and the technique of microwater harvesting with ridges and furrows, for potato production in semi-arid areas. Water Resour Manage 22:1431–1443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-007-9235-3
Wang Q, Li F, Zhang D, Liu Q, Li G, Liu X, Li X, Chen J (2018) Sediment control and fodder yield increase in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L) production with tied-ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting on sloping land. Field Crop Res 225:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.05.017
Wang Q, Song X, Li F, Hu G, Liu Q, Zhang E, Wang H, Davies R (2015a) Optimum ridge-furrow ratio and suitable ridge-mulching material for Alfalfa production in rainwater harvesting in semi-arid regions of China. Field Crop Res 180:186–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.06.004
Wang Y, Huang T, Liu J, Lin Z, Li S, Wang R, Ge Y (2015b) Soil pH value, organic matter and macronutrients contents prediction using optical diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Comput Electron Agr 111:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2014.11.019
Wang YP, Li XG, Hai L, Siddique KHM, Gan Y, Li FM (2014) Film fully-mulched ridge-furrow cropping affects soil biochemical properties and maize nutrient uptake in a rainfed semi-arid environment. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 60:486–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2014.909709
Wang Z, Han L, Sun K, Jin J, Ro KS, Libra JA, Liu X, Xing B (2016) Sorption of four hydrophobic organic contaminants by biochars derived from maize straw, wood dust and swine manure at different pyrolytic temperatures. Chemosphere 144:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.042
Xiong J, Yu R, Islam E, Zhu F, Zha J, Sohail MI (2020) Effect of biochar on soil temperature under high soil surface temperature in coal mined arid and semiarid regions. Sustainability 12:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198238
Xu X, Zheng F, Wilson GV, He C, Lu J, Bian F (2018) Comparison of runoff and soil loss in different tillage systems in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil till Res 177:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.10.005
Yang Y, Du W, Cui Z, Lei S, Lei T, Lv J (2020) Effects of plastic film mulching on soil water use efficiency and wheat yield in the Loess Plateau of China. Arid Land Res Manag 34:405–418. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324982.2020.1738593
Yang CD, Lu SG (2021) Effects of five different biochars on aggregation, water retention and mechanical properties of paddy soil: a field experiment of three-season crops. Soil till Res 205:104798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104798
Zhang C, Li X, Yan H, Ullah I, Zuo Z, Li L, Yu J (2020a) Effects of irrigation quantity and biochar on soil physical properties, growth characteristics, yield and quality of greenhouse tomato. Agr Water Manage 241:106263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106263
Zhang D, Wang Q, Li G, Li X, J. Sample D (2019a) Optimum ridge width and suitable mulching material for sainfoin production with ridge–furrow rainwater harvesting in semiarid regions of China. Arid Land Res Manag 33:274–296. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324982.2018.1563241
Zhang DK, Wang Q, Zhou XJ, Wang XY, Zhao XL, Zhao WC, Lei J (2020b) Effects of ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting with biochar-soil crust mulching on ridge runoff, soil hydrothermal properties, and sainfoin yield. Chinese J Eco-Agriculture 28:272–285. https://doi.org/10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.190707
Zhang LH, Shao HB, Ye GF, Lin YM (2012) Effects of fertilization and drought stress on tannin biosynthesis of Casuarina equisetifolia seedlings branchlets. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1639–1649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-0958-2
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Wu Y, Wang X, Du Z, Liu X, Song J (2013) Effects of biochar amendment on soil thermal conductivity, reflectance, and temperature. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77:1478–1487. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2012.0180
Zhang S, Wang H, Sun X, Fan J, Zhang F, Zheng J, Li Y (2021) Effects of farming practices on yield and crop water productivity of wheat, maize and potato in China : a meta-analysis. Agr Water Manage 243:106444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106444
Zhang X, Zhao J, Yang L, Kamran M, Xue X, Dong Z, Jia Z, Han Q (2019b) Ridge-furrow mulching system regulates diurnal temperature amplitude and wetting-drying alternation behavior in soil to promote maize growth and water use in a semiarid region. Field Crop Res 233:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.01.009
Zhao B, Xu R, Ma F, Li Y, Wang L (2016) Effects of biochars derived from chicken manure and rape straw on speciation and phytoavailability of Cd to maize in artificially contaminated loess soil. J Environ Manag 184:569–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.10.020
Zhou LM, Jin SL, Liu CA, Xiong YC, Si JT, Li XG, Gan YT, Li FM (2012) Ridge-furrow and plastic-mulching tillage enhances maize-soil interactions: opportunities and challenges in a semiarid agroecosystem. Field Crop Res 126:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.10.010
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to Maureen M. Vance, ex-Manager Adult Reading Assistance Scheme, Christchurch, New Zealand, for improving the English in this paper.
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (42061050) and (41661059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript for publication. Dengkui Zhang set up the experiment, conducted fieldwork and data analysis, and wrote and revised the manuscript. Xujiao Zhou assisted with fieldwork and manuscript revision. Wucheng Zhao, Xiaole Zhao, and Xiaoyun Wang sampled and analyzed data. Erastus Mak-Mensah assisted in editing the manuscript. Qi Wang and Qinglin Liu reviewed and revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Wang, Q., Zhou, X. et al. Suitable biochar type and optimum ridge width for sainfoin production in ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting in the Loess Plateau in China. J Soils Sediments 23, 206–222 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03331-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03331-8