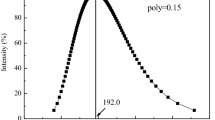
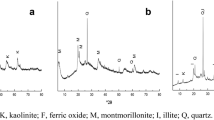
Abstract
Purpose
Understanding how anions affect the colloidal behavior of clay mineral is greatly important in determining soil particle dispersibility. The surface of soil particles, especially for silicate clay mineral components, is often net negatively charged. However, how anions influence soil particle interactions and affect soil structure has not been fully studied. This study investigated how specific anions (SO42−, Cl−, and phosphate) affect the aggregation of permanently charged montmorillonite particles.
Methods
The effects of anions on colloidal montmorillonite particle aggregation were investigated at different ionic strengths using dynamic light scattering. Anion adsorption on montmorillonite particles in equilibrated solutions was measured by ion chromatography.
Results
Anions were adsorbed onto a permanently charged clay mineral surface, which induced strong specific effects in inhibiting montmorillonite particle aggregation. Phosphate had the greatest inhibiting effect on coagulation, followed by Cl− and SO42−. The critical coagulation ionic strength (CCIS) for K2SO4, KCl, and KH2PO4 was 9.915, 11.38, and 180.7 mmol/L, respectively. The activation energy between particles in the different anion solutions quantitatively characterized this specific anion effect. The difference in the various anion solutions increased with decreasing ionic strength (i.e., increasing electric field). Second, the amount of phosphate adsorbed by montmorillonite was the greatest among the three anions, followed by Cl− and SO42−, under the given solution conditions, consistent with the observed specific anion effects.
Conclusions
Phosphate, Cl−, and SO42− adsorbed onto the surface of permanently charged mineral particles and increased the negative surface charge through non-classic polarization. The strength of the electric field strongly influenced this polarization. The combined roles of cations and anions regulate aggregation, whereas CCIS is determined by specific ion adsorption. Our findings emphasize the importance of specific anion adsorption and double-layer interfacial effects on the aggregation of permanently charged clay mineral colloids. Our findings have important implications for interpreting the behavior of clay minerals in the environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sagheer F, Hey M (2004) Hofmeister anion effects on aqueous solutions of poly (ethylene oxide) studied by attenuated total reflectance FT-IR spectroscopy. Colloid Surface A 245:99–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2004.08.001
Borukhov I, Andelman D, Orland H (1997) Steric Effects in Electrolytes: A Modified Poisson-Boltzmann Equation. Phys Rev Lett 79:435–438. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.79.435
Boström M, Williams D, Ninham B (2001a) Specific ion effects: why DLVO theory fails for biology and colloid systems. Phys Rev Lett 87:168103. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.168103
Boström M, Williams DRM, Ninham BW (2001b) Surface tension of electrolytes: specific ion effects explained by dispersion forces. Langmuir 17:4475–4478. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0102298
Flores SC, Kherb J, Cremer PS (2012) Direct and reverse Hofmeister effects on interfacial water structure. J Phys Chem C 116:14408–14413. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3029352
Gao XD, Li S, Liu XM, Hu FN, Tian R, Li H (2019) The effects of NO3- and Cl- on negatively charged clay aggregation. Soil till Res 186:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.10.025
Gokarn YR, Fesinmeyer RM, Saluja A, Razinkov V, Chase SF, Laue TM, Brems DN (2011) Effective charge measurements reveal selective and preferential accumulation of anions, but not cations, at the protein surface in dilute salt solutions. Protein Sci 20:580–587. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.591
Haldar SK, Tišljar J (2014) Introduction to Mineralogy and Petrology: Chapter 2 - Basic Mineralogy. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hou Y, Yu CQ, Liu GM, Ngai T, Zhang GZ (2010) Effects of anions on the aggregation of charged microgels. J Phys Chem B 114(11):3799. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9121694
Jia M, Li H, Zhu HL, Tian R, Gao XD (2013) An approach for the critical coagulation concentration estimation of polydisperse colloidal suspensions of soil and humus. J Soil Sediment 13:325–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-012-0608-8
Jungwirth P, Tobias DJ (2001) Molecular structure of salt solutions: A new view of the interface with implications for heterogeneous atmospheric chemistry. J Phys Chem B 105:10468–10472. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp012750g
Jungwirth P, Tobias DJ (2006) Specific ion effects at the air/water interface. Chem Rev 106:1259–1281. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0403741
Katana B, Takács D, Bobbink FD, Dyson PJ, Alsharif NB, Tomšič M, Szilagyi I (2020) Masking specific effects of ionic liquid constituents at the solid-liquid interface by surface functionalization. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22(42):24764–24770. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp02805c
Kim HK, Tuite E, Nordén B, Ninham B (2001) Co-ion dependence of DNA nuclease activity suggests hydrophobic cavitation as a potential source of activation energy. Eur Phys J E 4:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s101890170096
Kunz W, Lo Nostro P, Ninham BW (2004) The present state of affairs with Hofmeister effects. Curr Opin Colloid in 9:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2004.05.004
Li H, Hou J, Liu XM, Li R, Zhu HL, Wu LS (2011) Combined determination of specific surface area and surface charge properties of charged particles from a single experiment. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:2128–2135. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2010.0301
Ling JY, Zheng SH, Sheng F, Wu H, Chen ZH, Gu C, Jin X (2021) Effect of common inorganic anions on iron-catalyzed secondary brown carbon formation from guaiacol. Sci Total Environ 770:145206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145206
Liu XM, Li H, Du W, Tian R, Li R, Jiang XJ (2013) Hofmeister Effects on Cation Exchange Equilibrium: Quantification of Ion Exchange Selectivity. J Phys Chem C 117:6245–6251. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp312682u
Liu XM, Li H, Li R, Tian R, Hou J (2012) A new model for cation exchange equilibrium considering the electrostatic field of charged particles. J Soil Sediment 12:1019–1029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-012-0517-x
Liu XM, Li H, Li R, Xie DT, Ni JP, Wu LS (2014) Strong non-classical induction forces in ion-surface interactions: General origin of Hofmeister effects. Sci Rep-UK 4. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05047
López-León T, Santander-Ortega MJ, Ortega-Vinuesa JL, Bastos-González D (2008) Hofmeister effects in colloidal systems: influence of the surface nature. J Phys Chem C 112:16060–16069. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp803796a
Moreira L, Boström M, Ninham B, Biscaia E, Tavares F (2006) Hofmeister effects: Why protein charge, pH titration and protein precipitation depend on the choice of background salt solution. Colloid Surface A 282:457–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.11.021
Murphy E, Zachara J (1995) The role of sorbed humic substances on the distribution of organic and inorganic contaminants in groundwater. Geoderma 67:103–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7061(94)00055-F
Newton AG, Kwon KD, Cheong DK (2016) Edge structure of montmorillonite from atomistic simulations. Minerals 6(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020025
Nguyen MN, Dultz S, Tran TTT, Bui ATK (2013) Effect of anions on dispersion of a kaolinitic soil clay: A combined study of dynamic light scattering and test tube experiments. Geoderma 209:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.06.024
Ninham BW (2002) Physical chemistry: The loss of certainty. Progress in Colloid & Polymer Ence 120:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45291-5_1
Ninham BW, Duignan TT, Parsons DF (2011) Approaches to hydration, old and new: Insights through Hofmeister effects. Curr Opin Colloid in 16:612–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2011.04.006
Nucci NV, Vanderkooi JM (2008) Effects of salts of the Hofmeister series on the hydrogen bond network of water. J Mol Liq 143(2–3):160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2008.07.010
Oncsik T, Trefalt G, Borkovec M, Szilagyi I (2015) Specific ion effects on particle aggregation induced by monovalent salts within the Hofmeister series. Langmuir 31(13):3799–3807. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00225
Padmanabhan V, Daillant J, Belloni L, Mora S, Alba M, Konovalov O (2007) Specific ion adsorption and short-range interactions at the air aqueous solution interface. Phys Rev Lett 99:086105. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.086105
Parsons DF, Boström M, Nostro PL, Ninham BW (2011) Hofmeister effects: interplay of hydration, nonelectrostatic potentials, and ion size. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:12352–12367. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP20538B
Pavlovic M, Huber R, Adok-Sipiczki M, Nardin C, Szilagyi I (2016) Ion specific effects on the stability of layered double hydroxide colloids. Soft Matter 12(17):4024–4033. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5sm03023d
Peula-García JM, Ortega-Vinuesa JL, Bastos-González D (2010) Inversion of Hofmeister series by changing the surface of colloidal particles from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. J Phys Chem C 114: 11133–11139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp912035v
Pfaff JD (1993) US EPA Method 300 Revision 2.1: Determination of Inorganic Anions by Ion Chromatography. Method 300.0. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, U.S. Cincinnati, Ohio
Ruiz-Agudo E, Urosevic M, Putnis CV, Rodríguez-Navarro C, Cardell C, Putnis A (2011) Ion-specific effects on the kinetics of mineral dissolution. Chem Geol 281:364–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.01.003
Schwierz N, Horinek D, Netz RR (2013) Anionic and cationic Hofmeister effects on hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces. Langmuir 29: 2602–2614. https://doi.org/10.1021/la303924e
Takeshita C, Masuda K, Kobayashi M (2019) The effect of monovalent anion species on the aggregation and charging of allophane clay nanoparticles. Colloid Surface A 557:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.05.054
Tian R, Yang G, Li H, Gao XD, Liu XM, Zhu HL, Tang Y (2014) Activation energies of colloidal particle aggregation: towards a quantitative characterization of specific ion effects. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:8828–8836. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp54813a
Tielrooij K, Garcia-Araez N, Bonn M, Bakker H (2010) Cooperativity in ion hydration. Science 328:1006–1009. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183512
Tobias DJ, Hemminger JC (2008) Getting specific about specific ion effects. Science 319:1197–1198. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1152799
Wang H, Han XJ, Chen Y, Guo WJ, Zheng WL, Cai N, Guo QW, Zhao XL, Wu FC (2021) Effects of F-, Cl-, Br-, NO3-, and SO42- on the colloidal stability of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in the aqueous phase. Sci Total Environ 757:143962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143962
Weissenborn PK, Pugh RJ (1995) Surface tension and bubble coalescence phenomena of aqueous solutions of electrolytes. Langmuir 11: 1422–1426. https://doi.org/10.1021/la00005a002
Weissenborn PK, Pugh RJ (1996) Surface tension of aqueous solutions of electrolytes: relationship with ion hydration, oxygen solubility, and bubble coalescence. J Colloid Interf Sci 184:550–563. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1996.0651
Xiong Y, Chen JF, Zhang JS (1985) Soil Colloid (2): Methods for soil colloid research (In Chinese). Science Press, Beijing
Yang Q, Zhao J (2011) Hofmeister effect on the interfacial dynamics of single polymer molecules. Langmuir 27:11757–11760. https://doi.org/10.1021/la202510d
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for the financial support from the Scientific Research Fund of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (LSNQN202001), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1500202), and the 2020 Open Project of Chongqing Key Laboratory of Soil Multi-scale Interfacial Process. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaodan Gao: conceptualization, methodology, and writing—original draft. Kailu Ren: investigation. Zhihong Zhu: investigation. Jin Zhang: formal analysis. Song Li: data curation. Jingkuan Wang: supervision. Yingde Xu: conceptualization and writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jianming Xu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Ren, K., Zhu, Z. et al. Specific ion effects: The role of anions in the aggregation of permanently charged clay mineral particles. J Soils Sediments 23, 263–272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03309-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03309-6