Abstract
Purpose
Traditional measurement for soil properties is time-consuming and costly, while visible–near-infrared spectroscopy enables the rapid prediction of soil properties. In this study, visible–near-infrared spectroscopy was used to predict these four soil properties including OC (organic carbon) content, TN (total nitrogen) content, pH value, and clay content in rare earth mining areas based on different spectral transformation and calibration methods.
Materials and methods
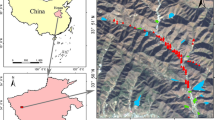
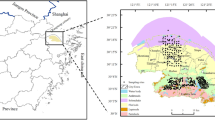
A total of 232 soil samples were collected from unexploited, in situ leaching, and heap leaching mining areas in southern Jiangxi Province, China. The chemical properties and reflectance spectra of air-dried samples were measured. Spectral transformations including first-order derivative (FOD), continuum removal (CR), and continuous wavelet transform (CWT) were selected to improve the prediction accuracy of the model. Partial least-squares regression (PLSR), the support vector machine (SVM), and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) were used to construct prediction models.
Results and discussion
The highest prediction accuracies in terms of the coefficient of determination (R2), root mean square error (RMSE), and relative prediction deviation (RPD) were obtained using CWT spectra with XGBoost for organic carbon content (R2 = 0.89, RMSE = 0.24, RPIQ = 4.67), total nitrogen content (R2 = 0.86, RMSE = 0.01, RPIQ = 4.14), and pH value (R2 = 0.73, RMSE = 0.19, RPIQ = 1.66). The best prediction result for clay content was obtained using CWT spectra with the SVM (R2 = 0.67, RMSE = 6.45, RPIQ = 2.75).
Conclusions
The CWT coupled with a non-linear model, such as XGBoost, is an effective method for the accurate prediction of soil properties in rare earth mining areas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Dor E, Inbar Y, Chen Y (1997) The reflectance spectra of organic matter in the visible near-infrared and short wave infrared region (400–2500 nm) during a controlled decomposition process. Remote Sens Environ 61:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(96)00120-4
Bishop JL, Pieters CM, Edwards JO (1994) Infrared spectroscopic analyses on the nature of water in montmorillonite. Clay Clay Miner 42:702–716. https://doi.org/10.1346/ccmn.1994.0420606
Bronick CJ, Lal R (2005) Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma 124:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.03.005
Chen CT, Landgrebe DA, Szilagyi A, Henderson TL, Baumgardner MF (1989) Spectral band selection for classification of soil organic matter content. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:1778–1784. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300060028x
Chen T, Guestrin C (Ed.) (2016) Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM
Cheng T, Rivard B, Sánchez-Azofeifa A (2011) Spectroscopic determination of leaf water content using continuous wavelet analysis. Remote Sens Environ 115:659–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.11.001
Chen Y, Li YQ, Wang XY, Wang JL, Gong XW, Niu YY, Liu J (2020) Estimating soil organic carbon density in Northern China’s agro-pastoral ecotone using vis-NIR spectroscopy. J Soils Sediments 20:3698–3711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02977-0
Clark RN, Roush TL (1984) Reflectance spectroscopy: quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing applications. J Geophys Res-Sol Ea 89:6329–6340. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB089iB07p06329
Conforti M, Castrignanò A, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F, Stelluti M, Buttafuoco G (2015) Laboratory-based Vis-NIR spectroscopy and partial least square regression with spatially correlated errors for predicting spatial variation of soil organic matter content. CATENA 124:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.09.004
Dalal RC, Henry RJ (1986) Simultaneous determination of moisture, organic carbon, and total nitrogen by near infrared reflectance spectrophotometry. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:120–123. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000010023x
Dong ZY, Wang N, Liu JB, Xie JC, Han JC (2021) Combination of machine learning and VIRS for predicting soil organic matter. J Soils Sediments 21:2578–2588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02977-0
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2000) Additive logistic regression: a statistical view of boosting. Ann Stat 28:337–374. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1016218223
Friedman JH (2001) Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Ann Stat 29:1189–1232. https://doi.org/10.2307/2699986
Greenberg I, Linsler D, Vohland M, Ludwig B (2020) Robustness of visible near-infrared and mid-infrared spectroscopic models to changes in the quantity and quality of crop residues in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 84:963–977. https://doi.org/10.1002/saj2.20067
Gu BJ, Chen DL, Yang Y, Vitousek P, Zhu YG (2021) Soil-food-environment-health nexus for sustainable development. Research. 2021:9804807. https://doi.org/10.34133/2021/9804807
Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Shen JL, Han WX, Zhang WF, Christie P, Goulding KWT, Vitousek PM, Zhang FS (2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327:1008–1010. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1182570
Hong YS, Chen YY, Yu L, Liu YF, Liu YL, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Cheng H (2018) Combining fractional order derivative and spectral variable selection for organic matter estimation of homogeneous soil samples by VIS-NIR spectroscopy. Remote Sens-Basel 10:479. https://doi.org/10.3965/10.3390/rs10030479
Ji WJ, Adamchuk VI, Chen SC, Mat Su AS, Ismail A, Gan QJ, Shi Z, Biswas A (2019) Simultaneous measurement of multiple soil properties through proximal sensor data fusion: a case study. Geoderma 341:111–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.01.006
Jiang QH, Li QX, Wang XG, Wu Y, Yang XL, Liu F (2017) Estimation of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in different soil layers using VNIR spectroscopy: effects of spiking on model applicability. Geoderma 293:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.01.030
Kennard RW, Stone LA (1969) Computer aided design of experiments. Technometrics 11:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1969.10490666
Kilmer VJ, Alexander LT (1949) Methods of making mechanical analysis of soils. Soil Sci 68:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-194907000-00003
Kovačević M, Bajat B, Gajić B (2010) Soil type classification and estimation of soil properties using support vector machines. Geoderma 154:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.11.005
Kuang BY, Tekin Y, Mouazen AM (2015) Comparison between artificial neural network and partial least squares for on-line visible and near infrared spectroscopy measurement of soil organic carbon, pH and clay content. Soil till Res 146:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.11.002
Levene H (1960) Robust tests for equality of variances. Stanford University Press
Li MYH, Zhou MF (2020) The role of clay minerals in formation of the regolith-hosted heavy rare earth element deposits. Am Miner 105:92–108. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2020-7061
Ludwig B, Vormstein S, Niebuhr J, Heinze S, Marschner B, Vohland M (2017) Estimation accuracies of near infrared spectroscopy for general soil properties and enzyme activities for two forest sites along three transects. Geoderma 288:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.10.022
Mallat SG (1989) A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE T Pattern Anal 11:674–693. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.192463
Nawar S, Mouazen AM (2017) Predictive performance of mobile vis-near infrared spectroscopy for key soil properties at different geographical scales by using spiking and data mining techniques. CATENA 151:118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.12.014
Nawar S, Buddenbaum H, Hill J, Kozak J, Mouazen AM (2016) Estimating the soil clay content and organic matter by means of different calibration methods of vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Soil till Res 155:510–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.07.021
Palacios-Orueta A, Ustin SL (1998) Remote sensing of soil properties in the Santa Monica Mountains I. spectral analysis. Remote Sens Environ 65:170–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00024-8
Paustian K, Lehmann J, Ogle S, Reay D, Robertson GP, Smith P, Smith P (2016) Climate-smart soils. Nature 532:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17174
Peng Y, Knadel M, Gislum R, Schelde K, Thomsen A, Greve MH (2014) Quantification of SOC and clay content using visible near-infrared reflectance-mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy with Jack-Knifing partial least squares regression. Soil Sci 179:325–332. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0000000000000074
Saeys W, Mouazen AM, Ramon H (2005) Potential for onsite and online analysis of pig manure using visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Biosys Eng 91:393–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.05.001
Savitzky A, Golay MJE (1964) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem 36:1627–1639. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60214a047
Shi TZ, Cui LJ, Wang JJ, Fei T, Chen YY, Wu GF (2013) Comparison of multivariate methods for estimating soil total nitrogen with visible/near-infrared spectroscopy. Plant Soil 366:363–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1436-8
Smola AJ, Schölkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14:199–222. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88
Song X, Chen C, Arthur E, Tuller M, Zhou H, Ren TS (2021) Effects of increasing water activity on the relationship between water vapor sorption and clay content. Soil Sci Soc Am J 85:520–525. https://doi.org/10.1002/saj2.20236
Stenberg B, Viscarra Rossel RA, Mouazen AM, Wetterlind J (2010) Visible and near infrared spectroscopy in soil science. Adv Agron 107:163–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(10)07005-7
Stoner ER, Baumgardner MF (1981) Characteristic variations in reflectance of surface soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45:1161–1165. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1981.03615995004500060031x
Torrence C, Compo GP (1998) A practical guide to wavelet analysis. B Am Meteorol Soc 79:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079%3c0061:APGTWA%3e2.0.CO;2
Tsakiridis NL, Keramaris KD, Theocharis JB, Zalidis GC (2020) Simultaneous prediction of soil properties from VNIR-SWIR spectra using a localized multi-channel 1-D convolutional neural network. Geoderma 367:114208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114208
Tziolas N, Tsakiridis N, Ogen Y, Kalopesa E, Ben-Dor E, Theocharis J, Zalidis G (2020) An integrated methodology using open soil spectral libraries and Earth Observation data for soil organic carbon estimations in support of soil-related SDGs. Remote Sens Environ 244:111793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111793
Vašát R, Kodešová R, Borůvka L, Klement A, Jakšík O, Gholizadeh A (2014) Consideration of peak parameters derived from continuum-removed spectra to predict extractable nutrients in soils with visible and near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (VNIR-DRS). Geoderma 232–234:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.05.012
Viscarra Rossel RA, Behrens T (2010) Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 158:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.12.025
Vohland M, Besold J, Hill J, Fründ H (2011) Comparing different multivariate calibration methods for the determination of soil organic carbon pools with visible to near infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 166:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.08.001
Vohland M, Ludwig M, Harbich M, Emmerling C, Thiele-Bruhn S (2016) Using variable selection and wavelets to exploit the full potential of visible-near infrared spectra for predicting soil properties. J Near Infrared Spec. 24:255–269. https://doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.1233
Wang SJ, Chen YH, Wang MG (2019) Performance comparison of machine learning algorithms for estimating the soil salinity of salt-affected soil using field spectral data. Remote Sens-Basel 11:2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11222605
Wang LX, Pang XY, Li N, Qi KB, Huang JS, Yin CY (2020) Effects of vegetation type, fine and coarse roots on soil microbial communities and enzyme activities in eastern Tibetan plateau. CATENA 194:104694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104694
Wei LF, Yuan ZR, Yu M, Huang C, Cao LQ (2019) Estimation of arsenic content in soil based on laboratory and field reflectance spectroscopy. Sensors 19:3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19183904
Whiting ML, Li L, Ustin SL (2004) Predicting water content using Gaussian model on soil spectra. Remote Sens Environ 89:535–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.11.009
Wilding LP (1985) Spatial variability: Its documentation, accommodation and implication to soil surveys. In: Nielsen DR, Bouma J (eds) Soil Spatial Variability. Pudoc, Wageningen, pp 166–187
Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L (2001) PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometr Intell Lab 58:109–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7439(01)00155-1
Yang MH, Xu DY, Chen SC, Li HY, Shi Z (2019) Evaluation of machine learning approaches to predict soil organic matter and pH using Vis-NIR spectra. Sensors 19:263. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19020263
Yang XJ, Lin A, Li X, Wu Y, Zhou W, Chen Z (2013) China’s ion-adsorption rare earth resources, mining consequences and preservation. Environ Dev 8:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2013.03.006
Zhang Y, Li MZ, Zheng LH, Qin QM, Lee WS (2019) Spectral features extraction for estimation of soil total nitrogen content based on modified ant colony optimization algorithm. Geoderma 333:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.07.004
Zhong L, Guo X, Xu Z, Ding M (2021) Soil properties: Their prediction and feature extraction from the LUCAS spectral library using deep convolutional neural networks. Geoderma 402:115366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115366
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFD1100603-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Xiuping Jia
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Zhao, X., Guo, X. et al. Inversion of soil properties in rare earth mining areas (southern Jiangxi, China) based on visible–near-infrared spectroscopy. J Soils Sediments 22, 2406–2421 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03242-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03242-8