Abstract
Purpose
Runoff and soil erosion reflect the interactions of soil properties and rainfall. However, few researchers have investigated the forms of nitrogen lost, the first flush, and the relationships between nitrogen losses and rainfall, runoff duration, different slope gradients, and fertilizer rates on red soils and paddy soils.
Materials and methods
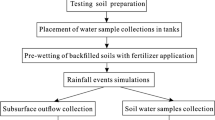
This study examined the nitrogen losses (NH4+-N, NO3--N, and TN) in runoff under simulated rainfall conditions with an intensity of 80 mm/h. The slope angles were set at 0°, 5°, and 15° for the red soil, and 0° and 5° for the paddy soil. The fertilizer was applied to the soils at 3 rates, i.e., 60, 180, and 300 kg N/hm2.
Results and discussion
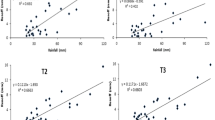
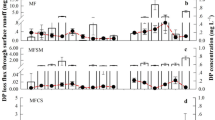
The results showed that the cumulative rainfall required to generate runoff differed significantly for different slope gradients, and the value for the red soil was 46.46 mm at 0°, which was 3.46 and 4.62 times of the rainfalls at 5° and 15°. The value for the paddy soil was 20.09 mm (average of 0° and 5°), which was half of red soil’s value. Of the TN lost in a 90-min event, 57.25 ± 12.62% was lost in the first 20 min of runoff generation, with the losses decreasing as the runoff generation time increased. The NH4+-N/TN and NO3−-N/TN differed significantly at different fertilizer N levels (P < 0.01). As the fertilizer application rate increased, the NH4+-N/TN tended to increase while the NO3−-N/TN tended to decrease. The NH4+-N/TN decreased exponentially, while NO3−-N/TN increased logarithmically, as the runoff duration time increased. A model, which included parameters to predict the initial losses of precipitation, was established to simulate the processes driving TN losses under different conditions. It is useful to analyze the TN losses from different soil types, slope gradients, and fertilizer rates.
Conclusion
The threshold slope gradient, first flush effect, and the TN loss process of the red and paddy soil were determined in this study. This information derived can potentially contribute to developing measures for reducing agricultural diffuse pollution and improving resource allocation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudi I, Carmi G, Berliner P (2012) Rainfall simulator for field runoff studies. J Hydrol 454:76–81
Anache JAA, Flanagan DC, Srivastava A, Wendland EC (2018) Land use and climate change impacts on runoff and soil erosion at the hillslope scale in the Brazilian Cerrado. Sci Total Environ 622:140–151
Arshad RR, Mahmoodabadi M, Farpoor MH, Fekri M (2019) Experimental investigation of rain-induced splash and wash processes under wind-driven rain. Geoderma 337:1164–1174
Assouline S, Ben-Hur M (2006) Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the dynamics of interrill erosion during soil surface sealing. Catena 66:211–220
Barbosa FT, Bertol I, Wolschick NH, Vazquez EV (2021) The effects of previous crop residue, sowing direction and slope length on phosphorus losses from eroded sediments under no-tillage. Soil Tillage Res 206
Boulange J, Malhat F, Jaikaew P, Nanko K, Watanabe H (2019) Portable rainfall simulator for plot-scale investigation of rainfall-runoff, and transport of sediment and pollutants. Int J Sedment Res 34:38–47
Deng L, Fei K, Sun T, Zhang L, Fan X, Ni L (2019) Characteristics of runoff processes and nitrogen loss via surface flow and interflow from weathered granite slopes of Southeast China. J Mt Sci 16:1048–1064
Ding X, Xue Y, Lin M, Jiang G (2017) Influence mechanisms of rainfall and terrain characteristics on total nitrogen losses from Regosol. Water 9:167
Efthimiou N, Psomiadis E, Papanikolaou I, Soulis KX, Borrelli P, Panagos P (2022) A new high resolution object-oriented approach to define the spatiotemporal dynamics of the cover-management factor in soil erosion modelling. Catena 213
Fang Q, Zhang L, Xu Z, Sun H, Wang G, Otsuk K (2015) A rainfall simulation study of soil erodibility and available nutrient losses from two contrasting soils in China. J Facul Agricult Kyushu Uni 60:235–242
Fu SH, Liu BY, Liu HP, Xu L (2011) The effect of slope on interrill erosion at short slopes. Catena 84:29–34
Galloway JN, Aber JD, Erisman JW, Seitzinger SP, Howarth RW, Cowling EB, Cosby BJ (2003) The nitrogen cascade. Bioscience 53:341–356
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai ZC, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–892
Guo ZL, Ma MJ, Cai CF, Wu YW (2018) Combined effects of simulated rainfall and overland flow on sediment and solute transport in hillslope erosion. J Soil Sediment 18:1120–1132
He JJ, Sun LY, Gong HL, Cai QG, Jia LJ (2016) The characteristics of rill development and their effects on runoff and sediment yield under different slope gradients. J Mt Sci 13:397–404
He XL, Zheng ZC, Li TX, He SQ (2020) Effect of slope gradient on phosphorus loss from a sloping land of purple soil under simulated rainfall. Pol J Environ Stud 29:1637–1647
Huang J, Wu P, Zhao X (2013) Effects of rainfall intensity, underlying surface and slope gradient on soil infiltration under simulated rainfall experiments. Catena 104:93–102
Huo J, Liu C, Yu X, Chen L, Zheng W, Yang Y, Yin C (2020) Direct and indirect effects of rainfall and vegetation coverage on runoff, soil loss, and nutrient loss in a semi-humid climate. Hydrol Process 35
Khan MN, Gong YB, Hu TX, Lal R, Zheng JK, Justine MF, Azhar M, Che MX, Zhang HT (2016) Effect of slope, rainfall intensity and mulch on erosion and infiltration under simulated rain on purple soil of south-western sichuan province. China Water 8:528
Kinnell PIA (2016) A review of the design and operation of runoff and soil loss plots. Catena 145:257–265
Li CJ, Pan CZ (2018) The relative importance of different grass components in controlling runoff and erosion on a hillslope under simulated rainfall. J Hydrol 558:90–103
Li JM, Wang WL, Guo MM, Kang HL, Wang ZG, Huang JQ, Sun BY, Wang K, Zhang GH, Bai Y (2020a) Effects of soil texture and gravel content on the infiltration and soil loss of spoil heaps under simulated rainfall. J Soil Sediment 20:3896–3908
Li L, Nearing MA, Polyakov VO, Nichols MH, Pierson FB, Cavanaugh ML (2020b) Evolution of rock cover, surface roughness, and its effect on soil erosion under simulated rainfall. Geoderma 379
Li Y, Feng G, Tewolde H, Yang M, Zhang F (2020c) Soil, biochar, and nitrogen loss to runoff from loess soil amended with biochar under simulated rainfall. J Hydrol 591
Li ZY, Fang HY (2016) Impacts of climate change on water erosion: A review. Earth Sci Rev 163:94–117
Liang ZS, Liu HW, Zhao YB, Wang QD, Wu ZR, Deng L, Gao HY (2020) Effects of rainfall intensity, slope angle, and vegetation coverage on the erosion characteristics of Pisha sandstone slopes under simulated rainfall conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:17458–17467
Lintern A, Webb JA, Ryu D, Liu S, Bende-Michl U, Waters D, Leahy P, Wilson P, Western AW (2018) Key factors influencing differences in stream water quality across space. WIREs Water 5
Liu J, Zhou Z, Liu Je, Su X (2022) Effects of root density on soil detachment capacity by overland flow during one growing season. J Soil Sediment 22
Liu JG, You LZ, Amini M, Obersteiner M, Herrero M, Zehnder AJB, Yang H (2010) A high-resolution assessment on global nitrogen flows in cropland. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107:8035–8040
Liu YF, Liu Y, Wu GL, Shi ZH (2019a) Runoff maintenance and sediment reduction of different grasslands based on simulated rainfall experiments. J Hydrol 572:329–335
Liu YX, Xin Y, Xie Y, Wang WT (2019b) Effects of slope and rainfall intensity on runoff and soil erosion from furrow diking under simulated rainfall. Catena 177:92–100
Luo Z, Liang X, Lam SK, Mosier AR, Hu S, Chen D (2021) Hotspots of reactive nitrogen loss in China: Production, consumption, spatiotemporal trend and reduction responsibility. Environ Pollut 284
Mamedov AI, Huang C, Levy GJ (2006) Antecedent moisture content and aging duration effects on seal formation and erosion in smectitic soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:832–843
Mhaske SN, Pathak K, Basak A (2019) A comprehensive design of rainfall simulator for the assessment of soil erosion in the laboratory. Catena 172:408–420
Misagh P, Mahmood S, Esteban LBM, Antonio ZD, Siyue L, Nobuaki T, Artemio C (2021) Effects of length and application rate of rice straw mulch on surface runoff and soil loss under laboratory simulated rainfall. Int J Sedment Res 36:468–478
Pan C, Shangguan Z (2006) Runoff hydraulic characteristics and sediment generation in sloped grassplots under simulated rainfall conditions. J Hydrol 331:178–185
Qi SC, Vanapalli SK (2018) Simulating hydraulic and mechanical responses of unsaturated expansive soil slope to rainfall: case study. Int J Geomech 18:05018002
Qian J, Zhang LP, Wang WY, Liu Q (2014) Effects of vegetation cover and slope length on nitrogen and phosphorus loss from a sloping land under simulated rainfall. Pol J Environ Stud 23:835–843
Qiu Y, Wang X, Xie Z, Wang Y (2021) Effects of gravel-sand mulch on the runoff, erosion, and nutrient losses in the Loess Plateau of north-western China under simulated rainfall. Soil Water Res 16:22–28
Shi P, Schulin R (2018) Erosion-induced losses of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals from agricultural soils of contrasting organic matter management. Sci Total Environ 618:210–218
Sun L, Fang H, Cai Q, Yang X, He J, Zhou JL, Wang X (2019) Sediment load change with erosion processes under simulated rainfall events. J Geogr Sci 29:1001–1020
Wang G, Wu B, Zhang L, Jiang H, Xu Z (2014) Role of soil erodibility in affecting available nitrogen and phosphorus losses under simulated rainfall. J Hydrol 514:180–191
Wang J, Huang J, Wu PT, Zhao XN (2016) Application of neural network and grey relational analysis in ranking the factors affecting runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall. Soil Res 54:291–301
Wang L, Liang T, Zhang Q (2013) Laboratory experiments of phosphorus loss with surface runoff during simulated rainfall. Environ Earth Sci 70:2839–2846
Wang LH, Dalabay N, Lu P, Wu FQ (2017) Effects of tillage practices and slope on runoff and erosion of soil from the Loess Plateau, China, subjected to simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res 166:147–156
Wang QH, Li C, Pang Z, Wen HF, Zheng RL, Chen J, Ma XJ, Que XE (2018) Effect of grass hedges on runoff loss of soil surface-applied herbicide under simulated rainfall in Northern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 253:1–10
Wang XX, Bi HX (2020) The effects of rainfall intensities and duration on SCS-CN model parameters under simulated rainfall. Water 12:1595
Wu L, Peng ML, Qiao SS, Ma XY (2018a) Assessing impacts of rainfall intensity and slope on dissolved and adsorbed nitrogen loss under bare loessial soil by simulated rainfalls. Catena 170:51–63
Wu L, Qiao S, Peng M, Ma X (2018b) Coupling loss characteristics of runoff-sediment-adsorbed and dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus on bare loess slope. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:14018–14031
Wu XY, Zhang LP, Yu XX (2012) Impacts of surface runoff and sediment on nitrogen and phosphorus loss in red soil region of southern China. Environ Earth Sci 67:1939–1949
Xiao P, Yao W, Shen Z, Yang C, Lyu X, Jiao P (2017) Effects of shrub on runoff and soil loss at loess slopes under simulated rainfall. Chin Geogr Sci 27:589–599
Xing W, Yang P, Ren S, Ao C, Li X, Gao W (2016) Slope length effects on processes of total nitrogen loss under simulated rainfall. Catena 139:73–81
Xu G, Tang S, Lu K, Li P, Li Z, Gao H, Zhao B (2015) Runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall on sand-covered slopes in a region subject to wind–water erosion. Environ Earth Sci 74:2523–2530
Yan Y, Dai Q, Yuan Y, Peng X, Zhao L, Yang J (2018) Effects of rainfall intensity on runoff and sediment yields on bare slopes in a karst area, SW China. Geoderma 330:30–40
Yang T, Wang Q, Wu L, Zhao G, Liu Y, Zhang P (2016) A mathematical model for soil solute transfer into surface runoff as influenced by rainfall detachment. Sci Total Environ 557–558:590–600
Yuan Z, Liao Y, Zheng M, Zhuo M, Huang B, Nie X, Wu X, Li D (2020) Relationships of nitrogen losses, phosphorus losses, and sediment under simulated rainfall conditions. J Soil Water Conserv 75:231–241
Zhang FB, Yang MY, Li BB, Li ZB, Shi WY (2017) Effects of slope gradient on hydro-erosional processes on an aeolian sand-covered loess slope under simulated rainfall. J Hydrol 553:447–456
Zhang R, Li M, Yuan X, Pan Z (2019) Influence of rainfall intensity and slope on suspended solids and phosphorus losses in runoff. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:33963–33975
Zhang X, Davidson EA, Mauzerall DL, Searchinger TD, Dumas P, Shen Y (2015) Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 528:51–59
Zhang XQ, Hu MC, Guo XY, Yang H, Zhang ZK, Zhang KL (2018) Effects of topographic factors on runoff and soil loss in Southwest China. Catena 160:394–402
Zheng HJ, Zuo JC, Wang LY, Li YJ, Liao KT (2016) 15N isotope tracing of nitrogen runoff loss on red soil sloping uplands under simulated rainfall conditions. Plant Soil Environ 62:416–421
Zhou P, Zhang D, Zhuang L, Zhang L, Yuan W, Singh RP (2021) Assessment of runoff nutrients loss in Phyllostachys praecox cv. prevernalis forest land under simulated rainfall conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:21874–21886
Zhuang XH, Wang W, Ma YY, Huang XF, Lei TW (2018) Spatial distribution of sheet flow velocity along slope under simulated rainfall conditions. Geoderma 321:1–7
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: U20A20114 and 31572208); the Taishan Industry Leading Talents High-Efficiency Agriculture Innovation Project (grant number: LJNY202125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Weixin Ding
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Li, B., Lei, Q. et al. The effects of slope and fertilizer rates on nitrogen losses in runoff from red soil and paddy soil during simulated rainfall. J Soils Sediments 22, 2354–2364 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03236-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03236-6