Abstract
Purpose
Dissolved oxygen (DO) has important effects on microorganisms, phosphorus cycle genes, and phosphorus release from sediments. However, the mechanism by which DO affects the release of phosphorus through microorganisms and genes is not obvious. This paper aims to investigate how microorganisms and genes affect the release of phosphorus from sediments under different dissolved oxygen conditions.
Materials and methods
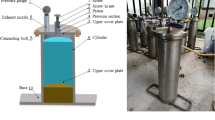
Sediment and water samples were collected and placed in incubators for 30 and 60 days of culture. Dissolved oxygen concentrations were maintained at 0.5 mg L−1, 1 mg L−1, 2 mg L−1, and 3 mg L−1. Fluorescence was used to quantitatively determine the number of functional genes, obtain microbial species through high-throughput sequencing, and analyze the correlation with phosphorus in sediments.
Results and discussion
At the genus level, Pseudomonas has a greater contribution to mineralization. On the 30th day, as the concentration of DO increased, the number of functional genes (phoD, ppk, and qppC) increased significantly. The expression of phoD (alkaline phosphatase gene) and pqqC (pyrroloquinoline quinone) together promoted the release of phosphorus. After 60 days culture, the ReP (the release of phosphorus from sediments) content decreased from 53.5 to 14.2 mg kg−1 with increasing DO concentration.
Conclusions
OrP (organic phosphorus) and AcP (acid extracted phosphorus) are converted to AlP (alkali extracted phosphorus) and thus lead to the reduction of ReP. The expression of ppk (polyphosphate kinase) gene was inhibited under low DO and promoted the release of phosphorus.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña JJ, Durán P, Lagos LM, Ogram A, de la Luz MM, Jorquera MA (2016) Bacterial alkaline phosphomonoesterase in the rhizospheres of plants grown in Chilean extreme environments. Biol Fertil Soils 52:763–773
Albrecht R, Le Petit J, Calvert V, Terrom G, Périssol C (2010) Changes in the level of alkaline and acid phosphatase activities during green wastes and sewage sludge co-composting. Bioresour Technol 101:228–233
Anderson DM, Glibert PM, Burkholder JM (2002) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 25:704–726
Bai X, Zhou Y, Ye W, Zhao H, Wang J, Li W (2021) Response of organic phosphorus in lake water to environmental factors: a simulative study. Sci Total Environ 785:147275
Cai O, Xiong Y, Yang H, Liu J, Wang H (2020) Phosphorus transformation under the influence of aluminum, organic carbon, and dissolved oxygen at the water-sediment interface: a simulative study. Front Environ Sci Eng 14:50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1227-z
Chen W, Yang F, Zhang L, Wang J (2016) Organic acid secretion and phosphate solubilizing efficiency of Pseudomonas sp. PSB12: effects of phosphorus forms and carbon sources. Geomicrobiol J 33:870–877
Chen X, Jiang N, Condron LM, Dunfield KE, Chen Z, Wang J, Chen L (2019) Impact of long-term phosphorus fertilizer inputs on bacterial phoD gene community in a maize field, Northeast China. Sci Total Environ 669:1011–1018
Dai Y, Yang Y, Wu Z, Feng Q, Xie S, Liu Y (2016) Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:4161–4175
De Prada P, Loveland-Curtze J, Brenchley JE (1996) Production of two extracellular alkaline phosphatases by a psychrophilic Arthrobacter strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3732–3738
Ding Y, Qin B, Xu H, Wang X (2016) Effects of sediment and turbulence on alkaline phosphatase activity and photosynthetic activity of phytoplankton in the shallow hyper-eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:16183–16193
Du H, Yang L, Wu J, Xiao L, Wang X, Jiang L (2012) Simultaneous removal of phosphorus and nitrogen in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor with transgenic bacteria expressing polyphosphate kinase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:265–272
Fan Y-Y, Li B-B, Yang Z-C, Cheng Y-Y, Liu D-F, Yu H-Q (2019) Mediation of functional gene and bacterial community profiles in the sediments of eutrophic Chaohu Lake by total nitrogen and season. Environ Pollut 250:233–240
Farhat MB et al (2009) Characterization of the mineral phosphate solubilizing activity of Serratia marcescens CTM 50650 isolated from the phosphate mine of Gafsa. Arch Microbiol 191:815–824
Fraser T, Lynch DH, Entz MH, Dunfield KE (2015) Linking alkaline phosphatase activity with bacterial phoD gene abundance in soil from a long-term management trial. Geoderma 257:115–122
Hooley P, Whitehead MP, Brown MR (2008) Eukaryote polyphosphate kinases: is the ‘Kornberg’complex ubiquitous?. Trends Biochem Sci 33:577–582
Huang L, Fang H, Reible D (2015) Mathematical model for interactions and transport of phosphorus and sediment in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water Res 85:393–403
Jiang X, Jin X, Yao Y, Li L, Wu F (2008) Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Res 42:2251–2259
Kang M, Peng S, Tian Y, Zhang H (2018) Effects of dissolved oxygen and nutrient loading on phosphorus fluxes at the sediment–water interface in the Hai River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 130:132–139
Le C, Zha Y, Li Y, Sun D, Lu H, Yin B (2010) Eutrophication of lake waters in China: cost, causes, and control. Environ Manag 45:662–668
Li S, Lin Z, Liu M, Jiang F, Chen J, Yang X, Wang S (2020) Effect of ferric chloride on phosphorus immobilization and speciation in Dianchi Lake sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110637
Li Y, Zhang J, Fu W, Wu D (2019) Diversity of glucose dehydrogenase gcd gene and its relationship with environmental factors in sediment of Sancha lake. Res Environ Sci 32:2040–2047
Lin P, Klump JV, Guo L (2018) Variations in chemical speciation and reactivity of phosphorus between suspended-particles and surface-sediment in seasonal hypoxia-influenced Green Bay. J Great Lakes Res 44:864–874
Liu Y et al (2017) Distribution of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria in relation to fractionation and sorption behaviors of phosphorus in sediment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:17679–17687
McDowell RW, Hill S (2015) Speciation and distribution of organic phosphorus in river sediments: a national survey. J Soils Sediments 15:2369–2379
Meyer JB, Frapolli M, Keel C, Maurhofer M (2011) A novel molecular marker for studying phylogeny and diversity of phosphate-solubilizing pseudomonads: the pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthetic gene pqqC. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:7345–7354
Mondal S, Haque S, Kundu D, Dutta D, Ghosh AR (2018) Isolation and identification of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms and distribution of orthophosphate in different seasons from sewage-fed East Kolkata Wetland. Lakes Reservoirs Res Manage 23:261–270
Ni Z, Wang S, Wang Y (2016) Characteristics of bioavailable organic phosphorus in sediment and its contribution to lake eutrophication in China. Environ Pollut 219:537–544
Otieno N, Lally RD, Kiwanuka S, Lloyd A, Ryan D, Germaine KJ, Dowling DN (2015) Plant growth promotion induced by phosphate solubilizing endophytic Pseudomonas isolates. Front Microbiol 6:745
Qu J-H, Li H-F, Chen N, Yuan H-L (2013) Biogeochemical function of phosphorus-solubilising bacteria on cycling of phosphorus at the water-sediment interface under laboratorial simulated conditions. Int J Environ Pollut 52:104–116
Ruban V, López-Sánchez J, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller P (1999) Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. J Environ Monit 1:51–56
Sellner KG, Doucette GJ, Kirkpatrick GJ (2003) Harmful algal blooms: causes, impacts and detection. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:383–406
Smith VH, Tilman GD, Nekola JC (1999) Eutrophication: impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Pollut 100:179–196
Tapia-Torres Y, Rodríguez-Torres MD, Elser JJ, Islas A, Souza V, García-Oliva F, Olmedo-Álvarez G (2016) How to live with phosphorus scarcity in soil and sediment: lessons from bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:4652–4662
Trivedi P, Sa T (2008) Pseudomonas corrugata (NRRL B-30409) mutants increased phosphate solubilization, organic acid production, and plant growth at lower temperatures. Curr Microbiol 56:140–144
Wang C, Zhang Y, Li H, Morrison RJ (2013) Sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in sediment. Limnology 14:147–157
Wu Y, Wen Y, Zhou J, Wu Y (2014) Phosphorus release from lake sediments: effects of pH, temperature and dissolved oxygen. KSCE J Civ Eng 18:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-0192-0
Yang Q, Zhao H, Zhao N, Ni J, Gu X (2016) Enhanced phosphorus flux from overlying water to sediment in a bioelectrochemical system. Bioresour Technol 216:182–187
Zhang H, Yan M, Huang T, Huang X, Yang S, Li N, Wang N (2020) Water-lifting aerator reduces algal growth in stratified drinking water reservoir: novel insights into algal metabolic profiling and engineering applications. Environ Pollut 266:115384
Zhang H et al (2021) Biogeographic distribution patterns of algal community in different urban lakes in China: insights into the dynamics and co-existence. Global J Environ Sci 100:216–227
Zhang T, Wang X, Jin X (2007) Variations of alkaline phosphatase activity and P fractions in sediments of a shallow Chinese eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Environ Pollut 150:288–294
Zheng B-X, Ding K, Yang X-R, Wadaan MA, Hozzein WN, Peñuelas J, Zhu Y-G (2019a) Straw biochar increases the abundance of inorganic phosphate solubilizing bacterial community for better rape (Brassica napus) growth and phosphate uptake. Sci Total Environ 647:1113–1120
Zheng B-X et al (2019b) Responses to soil pH gradients of inorganic phosphate solubilizing bacteria community. Sci Rep 9:1–8
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U20A20316, No. 51509199, and No. 72091510) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No. E2020402074 and No. E2020402044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent publication
The manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Haihan Zhang
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Our work provides insights into the role of bacteria in phosphorus release from sediments at various levels of dissolved oxygen.
• The relative abundance of the four most abundant genera containing ppk, including Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Rhodococcus, and Luteitalea, was positively related to the content of OrP, but the relative abundance of Pseudomonas was negatively related to OrP content.
• Pseudomonas had a greater contribution in mineralization of OrP, but Variovorax, Rhodococcus, and Luteitalea mainly promoted OrP synthesis.
• Some genera containing pqqC, including Candidatus Solibacter, Luteitalea, Gemmatirosa, Pseudomonas, and Granulicella, may produce organic acids that do not bind phosphate to calcium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, Q. et al. Effects of dissolved oxygen on phosphorus transformation in reservoir sediments: novel insights on bacterial community and functional genes. J Soils Sediments 22, 2094–2104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03233-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03233-9