Abstract
Purpose
In this study it is investigated whether typical pollution sources cause differences of heavy metal (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) pollution in the soil-leafy vegetable systems.
Materials and methods
Soil and leafy vegetable samples were collected in the fields contaminated by industrial operation sources (IOS) and organic fertilizer sources (OFS), respectively, in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) areas. The differences of heavy metal pollution were compared in soil-vegetable systems contaminated by IOS and OFS (IOS- and OFS-systems). Those mainly included (1) Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn contents in soils and vegetables; (2) heavy metal fractions distribution in soils and their connection with the heavy metal in leafy vegetables; (3) the key influential factor of heavy metal accumulation of leafy vegetable; and (4) the ecological risk of heavy metal pollution in soil-vegetable systems.
Results and discussion
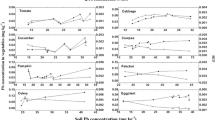
The mean pollution index (PI) of Cd, Pb, Cu, and Zn was 5.05, 1.89, 0.72, and 1.21 in IOS-soils (soils contaminated by IOS), and 2.51, 0.25, 0.64, and 0.71 in OFS-soils (soils contaminated by OFS), respectively. For PIS > 1, the percentages of Cd were 100% in both sources. The IOS caused more significant Cd and Pb pollution in vegetables, but OFS induced higher Cu and Zn accumulation. The Cd in soils had a relatively higher bioavailable fraction proportion (the sum of water-soluble, exchangeable and carbonate-bound fraction), mobility, and transferability in IOS-soils. Nevertheless, such indicators for Cu and Zn were higher in OFS-soils. Compared with IOS-soils, OFS-soils were characterized by a higher proportion of metals bound to humic acid and organic matter. Redundancy analysis (RDA) results showed that the accumulation of Cd, Pb, Cu, and Zn in IOS-vegetables (vegetables contaminated by IOS) was mainly controlled by F3-Cd, F5-Pb, F5-Cu, and F3-Zn in soils, respectively. Moreover, F1-Cd, F4-Pb, F2-Cu, and F2-Zn could be the dominant influential factors of Cd, Pb, Cu, and Zn absorption by OFS-vegetables (vegetables contaminated by OFS), respectively. Risk assessment results revealed that the IOS-systems had higher heavy metal pollution level than OFS-systems.
Conclusions
The source of heavy metals is one of the main factors for the mobility and transfer of heavy metals in the soil–plant systems. There are obvious differences in pollution characteristics between IOS- and OFS-soils. Compared with OFS, IOS caused the more serious ecological risk of heavy metal pollution to the soil-vegetable systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agrawal R, Kumar B, Priyanka K, Narayan C, Shukla K, Sarkar J (2016) Micronutrient fractionation in coal mine-affected agricultural soils. India Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96(4):449–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1745-3
Almaroai YA, Usman AR, Ahmad M, Kim K, Moon DH, Lee SS, Ok YS (2012) Effects of synthetic chelators and low-molecular-weight organic acids on chromium, copper, and arsenic uptake and translocation in maize (Zea mays L.). Soil Sci 177(11):655–663. https://doi.org/10.1097/SS.0b013e31827ba23f
Bai LY, Zeng XB, Su SM, Duan R, Wang YN, Gao X (2015) Heavy metal accumulation and source analysis in greenhouse soils of Wuwei District, Gansu Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5359–5369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3763-1
Baran A, Antonkiewicz J (2017) Phytotoxicity and extractability of heavy metals from industrial wastes. Environ Prot Eng 43(2):143–155. https://doi.org/10.5277/epe170212
Bouyoucos GJ (1951) A recalibration of the hydrometer method for making mechanical analysis of soils 1. Agron J 43(9):434–438
Cheng SW, Liu GJ, Zhou CC, Sun RY (2018) Chemical speciation and risk assessment of cadmium in soils around a typical coal mining area of China. Ecotox Environ Safe 160:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.022
CGS (2005) Geological survey technical standard. China Geological Survey
Cui LQ, Li LQ, Zhang AF, Pan GX, Bao DD, Chang A (2011) Biochar amendment greatly reduces rice Cd uptake in a contaminated paddy soil: a two-year field experiment. BioResources 6(3):2605–2618
Dong B, Zhang RZ, Gan YD, Cai LQ, Freidenreich A, Wang KP, Guo TW, Wang HB (2019) Multiple methods for the identification of heavy metal sources in cropland soils from a resource-based region. Sci Total Environ 651:3127–3138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.130
Fan Y, Li H, Xue ZJ, Zhang Q, Cheng FQ (2017) Accumulation characteristics and potential risk of heavy metals in soil-vegetable system under greenhouse cultivation condition in Northern China. Ecol Eng 102:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.02.032
Formentini TA, Mallmann FJK, Pinheiro A, Fernandes CVS, Bender MA, Da Veiga M, Dos Santos DR, Doelsch E (2015) Copper and zinc accumulation and fractionation in a clayey Hapludox soil subject to long-term pig slurry application. Sci Total Environ 536:831–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.110
Guo T, Lou CL, Zhai WW, Tang XJ, Hashmi MZ, Murtaza R, Li Y, Liu XM, Xu JM (2018) Increased occurrence of heavy metals, antibiotics and resistance genes in surface soil after long-term application of manure. Sci Total Environ 635:995–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.194
Haider FU, Liqun C, Coulter JA, Cheema SA, Wu J, Zhang R, Wenjun M, Farooq M (2021) Cadmium toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotox Enivron Safe 211:111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111887
Hao XZ, Zhou DM, Huang DQ, Zhang HL, Wang YJ (2007) The growth and Cu and Zn uptake of pakchois (Brassica chinesis L.) in an acidic soil as affected by chicken or pig manure. J Environ Sci Heal B 42(8): 905–912. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230701623571
Hou QY, Yang ZF, Ji JF, Yu T, Chen GG, Li J, Xia XQ, Zhang M, Yuan XY (2014) Annual net input fluxes of heavy metals of the agro-ecosystem in the Yangtze River delta, China. J Geochem Explor 139:68–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.08.007
Huang SW, Tang JW, Li CH (2017) Status of heavy metals, nutrients, and total salts in commercial organic fertilizers and organic wastes in China(in Chinese). J Plant Nutr Fertil 23(1):162–173
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing. China Environ Pollut 152(3):686–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.056
Laborda F, Bolea E, Gorriz MP, Martin-Ruiz MP, Ruiz-Begueria S, Castillo JR (2008) A speciation methodology to study the contributions of humic-like and fulvic-like acids to the mobilization of metals from compost using size exclusion chromatography-ultraviolet absorption-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and deconvolution analysis. Anal Chim Acta 606:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.10.048
Li J, Zhu L, Tong LH, Lv YZ, Li J (2018a) Risk assessment of heavy metals accumulation in soils under long-term greenhouse vegetable cultivation conditions(in Chinese). Journal of Agro-Environment Science 37(05):2159–2165
Li T, Tao Q, Liang C, Shohag MJI, Yang X, Sparks DL (2013) Complexation with dissolved organic matter and mobility control of heavy metals in the rhizosphere of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Environ Pollut 182:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.07.025
Li G, Khan S, Ibrahim M, Sun T, Tang J, Cotner JB, Xu Y (2018b) Biochars induced modification of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in soil and its impact on mobility and bioaccumulation of arsenic and cadmium. J Hazard Mater 348:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.031
Li XY, Li ZG, Lin CJ, Bi XY, Liu JL, Feng X, Zhang H, Chen J, Wu TT (2018c) Health risks of heavy metal exposure through vegetable consumption near a large-scale Pb/Zn smelter in central China. Ecotox Environ Safe 161:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.080
Liao JB, Wen ZW, Ru X, Chen JD, Wu HZ, Wei CH (2016) Distribution and migration of heavy metals in soil and crops affected by acid mine drainage: Public health implications in Guangdong Province, China. Ecotox Environ Safe 124:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.11.023
Lu RK (2000) Analytical methods for soil and agrochemistry. Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing
Mamindy-Pajany Y, Sayen S, Mosselmans JFW, Guillon E (2014) Copper, nickel and zinc speciation in a biosolid-amended soil: pH adsorption edge, μ-XRF and μ-XANES investigations. Environ Sci Technol 48:7237–7244. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5005522
Meng L, Huang TH, Shi JC, Chen J, Zhong FL, Wu LS, Xu JM (2019) Decreasing cadmium uptake of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the cadmium-contaminated paddy field through different cultivars coupling with appropriate soil amendments. J Soil Sediment 19(4):1788–1798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2186-x
MEPPRC (2018) Soil environmental quality: risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land, GB15618, Beijing
MHPRC (1991) Maximum levels of contaminants in food, GB13106, Beijing
MHPRC (1994) Maximum levels of contaminants in food, GB15199, Beijing
MHPRC (2017) Maximum levels of contaminants in food, GB2762, Beijing
Michel K, Roose M, Ludwig B (2007) Comparison of different approaches for modelling heavy metal transport in acidic soils. Geoderma 140:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.04.005
Mohamed I, Ahamadou B, Li M, Gong CX, Cai P, Liang W, Huang QY (2010) Fractionation of copper and cadmium and their binding with soil organic matter in a contaminated soil amended with organic materials. J Soil Sediment 10(6):973–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0199-1
Moturi MCZ, Rawat M, Subramanian V (2004) Distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in solid waste from selected sites in the industrial belt of Delhi, India. Environ Monit Assess 95:183–199. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EMAS.0000029900.86810.85
Perin G, Craboledda L, Lucchese M, Cirillo R, Dotta L, Zanette ML, Orio AA (1985) Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of northern Adriatic Sea. A new approach for environmental toxicity determination. Heavy metals in the environment 2(1):454–456
Phillips RP, Fahey TJ (2006) Tree species and mycorrhizal associations influence the magnitude of rhizosphere effects. Ecology 87:1302–1313. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1302:TSAMAI]2.0.CO;2
Plaza C, Senesi N, García-Gil JC, Polo A (2005) Copper(II) complexation by humic and fulvic acids from pig slurry and amended and non-amended soils. Chemosphere 61:711–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.046
Qian M, Wu H, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Lin H, Ma J (2016) Occurrence of trace elements and antibiotics in manure-based fertilizers from the Zhejiang Province of China. Sci Total Environ 559:174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.123
Qian XY, Wang ZQ, Shen GX, Chen XH, Tang ZZ, Guo CX, Gu HR, Fu K (2018) Heavy metals accumulation in soil after 4 years of continuous land application of swine manure: a field-scale monitoring and modeling estimation. Chemosphere 210:1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.107
Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J (2015) Impact of emerging and low cost alternative amendments on the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of Cd and Pb in a contaminated floodplain soil. Ecol Eng 74:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.10.024
Shan H, Su SM, Liu RL, Li ST (2016) Cadmium availability and uptake by radish (Raphanus sativus) grown in soils applied with wheat straw or composted pig manure. Environ Sci Pollut R 23(15):15208–15217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6464-0
Taghipour M, Jalali M (2020) Effects of some industrial and organic wastes application on growth and heavy metal uptake by tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum) grown in a greenhouse condition. Environ Sci Pollut R 27(5):5353–5366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07017-6
Tandi NK, Nyamangara J, Bangira C (2004) Environmental and potential health effects of growing leafy vegetables on soil irrigated using sewage sludge and effluent: a case of Zn and Cu. J Environ Sci Heal B 39(3):461–471. https://doi.org/10.1081/PFC-120035930
Tang X, Li X, Liu X, Hashmi MZ, Xu J, Brookes PC (2015) Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the uptake of lead and trace elements by Brassica chinensis grown in an acidic red soil. Chemosphere 119:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.081
Wan YN, Huang QQ, Wang Q, Yu Y, Su DC, Qiao YH, Li HF (2020) Accumulation and bioavailability of heavy metals in an acid soil and their uptake by paddy rice under continuous application of chicken and swine manure. J Hazard Mater 384:121293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121293
Wang H, Dong YH, Yang YY, Toor GS, Zhang XM (2013) Changes in heavy metal contents in animal feeds and manures in an intensive animal production region of China. J Environ Sci-China 25(12):2435–2442. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60473-8
Warne MSJ, Heemsbergen D, Mclaughlin M, Bell M, Broos K, Whatmuff M, Barry G, Nash D, Pritchard D, Penney N (2008) Models for the field-based toxicity of copper and zinc salts to wheat in 11 Australian soils and comparison to laboratory-based models. Environ Pollut 156:707–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.012
Wei FS, Chen JS (1991) Study on the background value of soil environment in China(in Chinese). Environmental Science 4:12–19
Wu LH, Tan CY, Liu L, Zhu P, Peng C, Luo YM, Christie P (2012) Cadmium bioavailability in surface soils receiving long-term applications of inorganic fertilizers and pig manure. Geoderma 173:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.12.003
Xiao L, Guan D, Peart MR, Chen Y, Li Q (2017) The respective effects of soil heavy metal fractions by sequential extraction procedure and soil properties on the accumulation of heavy metals in rice grains and brassicas. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:2558–2571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8028-8
Yang JJ, Regier T, Dynes JJ, Wang J, Shi JY, Peak D, Zhao YD, Hu TD, Chen YX, Tse JS (2011) Soft X-ray induced photoreduction of organic Cu(II) compounds probed by X-ray absorption near-edge (XANES) spectroscopy. Anal Chem 83(20):7856–7862. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac201622g
Yi KX, Fan W, Chen JY, Jiang SH, Huang SJ, Peng L, Zeng QR, Luo S (2018) Annual input and output fluxes of heavy metals to paddy fields in four types of contaminated areas in Hunan Province, China. Sci Total Environ 634:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.294
Yu HY, Liu CP, Zhu JS, Li FB, Deng DM, Wang Q, Liu CS (2016) Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: the effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value. Environ Pollut 209:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.021
Yu HY, Chang CY, Li FB, Wang Q, Chen M, Zhang J (2018) Thallium in flowering cabbage and lettuce: Potential health risks for local residents of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 241:626-635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.090
Zeng FR, Ali S, Zhang HT, Ouyang YB, Qiu BY, Wu FB, Zhang GP (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.019
Zeng XY, Xiao ZH, Zhang GL, Wang AD, Li ZH, Liu YH, Wang H, Zeng QR, Liang YS, Zou DS (2018) Speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in pyrolytic biochar of swine and goat manures. J Anal Appl Pyrol 132:82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2018.03.012
Zhang JR, Li HZ, Zhou YZ, Dou L, Cai LM, Mo LP, You J (2018) Bioavailability and soil-to-crop transfer of heavy metals in farmland soils: a case study in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 235:710–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.106
Zhao KL, Liu XM, Zhang WW, Xu JM, Wang F (2011) Spatial dependence and bioavailability of metal fractions in paddy fields on metal concentrations in rice grain at a regional scale. J Soil Sediment 11(7):1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0408-6
Zheng SN, Wang Q, Yu HY, Huang XZ, Li FB (2020) Interactive effects of multiple heavy metal(loid)s on their bioavailability in cocontaminated paddy soils in a large region. Sci Total Environ 708:135126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135126
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly thank all the people for giving help to this research.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0800306) and Science and Technology Program of Jiangsu (BE2018679).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HW, FS, HD, TS, HL, JW, and XH. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HW. The final manuscript was critically revised by LL, MD, SJ, CD, and GP. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
This manuscript is new and not being considered elsewhere. All authors have approved the submission of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Sui, F., Duan, H. et al. Comparison of heavy metal speciation, transfer and their key influential factors in vegetable soils contaminated from industrial operation and organic fertilization. J Soils Sediments 22, 1735–1745 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03187-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03187-y