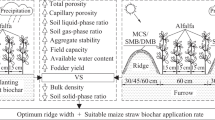
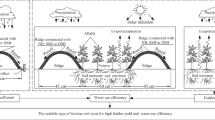
Abstract
Purpose
Drought and soil erosion are significant environmental challenges to agricultural production in the Loess Plateau of China. We hypothesized that ridge-furrow rainwater-harvesting, especially tied-ridge-furrow rainwater-harvesting, with biochar application would increase soil moisture, temperature, and alfalfa fodder yield, and reduce runoff and sediment yield.
Materials and methods
A split-plot design experiment was conducted to determine the effects of biochar application patterns (biochar application pattern and no biochar application pattern) and tillage practices (tied-ridging, open-ridging, and flat-planting) on soil temperature, moisture, runoff, sediment yield, fodder yield, and water use efficiency (WUE) of alfalfa during two consecutive alfalfa-growing years: 2019 and 2020.
Results
Biochar application decreased runoff, sediment yield, soil temperature, and increased soil water storage, compared to no biochar application. Open-ridging and tied-ridging significantly increased soil water storage, fodder yield, WUE of alfalfa, and decreased runoff and sediment yield, compared to flat-planting. Compared to no biochar application, soil water storage for biochar application increased by 34.51 mm during alfalfa growing season over two years. The mean runoff and sediment yield for no biochar application were 1.48–1.69 and 1.94–2.25 times greater than that for biochar application, respectively. Compared to flat-planting, the mean decrease of runoff and sediment yield was 27.4–31.9% and 60.1–64.7%, respectively, for open-ridging, while it was 37.1–55.2% and 71.8–82.4% for tied-ridging. The mean increase of soil water storage, fodder yield, and WUE of alfalfa for open-ridging was 39.5–52.1 mm, 26.2–31.7%, and 10.07–14.86 kg ha−1 mm−1, respectively, while it for tied-ridging was 31.2–60.5 mm, 26.5–35.2%, and 12.14–16.55 kg ha−1 mm−1 over two years.
Conclusions
Tied-ridge-furrow rainwater-harvesting with biochar application is a potentially effective adaptation technology that could control soil erosion and increase alfalfa fodder yield in semiarid regions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RFRH:
-
Ridge-furrow rainwater-harvesting
- TRFRH:
-
Tied-ridge-furrow rainwater-harvesting
- WUE:
-
Water use efficiency
- NFY:
-
Net fodder yield
- AFY:
-
Actual fodder yield
References
Abrol V, Ben-Hur M, Verheijen FGA, Keizer JJ, Martins MAS, Tenaw H, Tchehansky L, Graber ER (2016) Biochar effects on soil water infiltration and erosion under seal formation conditions: rainfall simulation experiment. J Soils Sediments 16(12):2709–2719
Acosta-Rangel A, Li R, Mauk P, Santiago L, Lovatt CJ (2021) Effects of temperature, soil moisture and light intensity on the temporal pattern of floral gene expression and flowering of avocado buds. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 280:109940
Araya A, Stroosnijder L (2010) Effects of tied-ridges and mulch on barley (Hordeum vulgare) rainwater use efficiency and production in Northern Ethiopia. Agr Water Manage 97(6):841–847
Chen Z, Cao XL, Niu JP (2021) Effects of exogenous ascorbic acid on seed germination and seedling salt-tolerance of alfalfa. PLoS One 16(4):0250926
Faloyea OT, Alatisea MO, Ajayia AE, Ewulo BS (2019) Effects of biochar and inorganic fertiliser applications on growth, yield and water use efficiency of maize under deficit irrigation. Agr Water Manage 217:165–178
Fang S, Zhao C, Jian S (2016) Canopy transpiration of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation forest in the Loess Plateau region of China. Environ Earth Sci 75(5):376
Feng WY, Yang F, Cen R, Liu J, Qu ZY, Miao QF, Chen HY (2021) Effects of straw biochar application on soil temperature, available nitrogen, and growth of corn. J Environ Manage 277:111331
Fister W, Heckrath G, Greenwood P, Kuhn NJ (2013) Erodibility of biochar from a sandy soil in Denmark, united nations convention to combat desertification, the economics of desertification, land degradation and drought: methodologies and analysis for decision-making. extended abstracts. UNCCD 2nd scientific conference
Fu GQ, Qiu XN, Xu XY, Zhang W, Zang F, Zhao CY (2021) The role of biochar particle size and application rate in promoting the hydraulic and physical properties of sandy desert soil. Catena 207(1):105607
Fu Q, Zhao H, Li H, Li TX, Hou RJ, Liu D, Ji Y, Gao Y, Yu PF (2019) Effects of biochar application during different periods on soil structures and water retention in seasonally frozen soil areas. Sci Total Environ 694:133732
Ge JM, Fan J, Yuan HY, Yang XT, Jin M, Wang S (2020a) Soil water depletion and restoration under inter-conversion of food crop and alfalfa with three consecutive wet years. J Hydrol 585:124851
Ge XG, Cao YH, Zhou BZ, Xiao WF, Tian XK, Li MH (2020b) Combined application of biochar and N increased temperature sensitivity of soil respiration but still decreased the soil CO2 emissions in moso bamboo plantations. Sci Total Environ 730:139003
Guo L, Liu Y, Wu GL, Huang Z, Cui Z, Cheng Z, Zhang RQ, Tian FP, He H (2019) Preferential water flow: Influence of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) decayed root channels on soil water infiltration. J Hydrol 578:124019
Gupta A, Rico-Medina A, Cao-Delgado AI (2020) The physiology of plant responses to drought. Science 368(6488):266–269
Habtemariam LT, Mgeni CP, Mutabazi KD, Sieber S (2019) The farm income and food security implications of adopting fertilizer micro-dosing and tied-ridge technologies under semi-arid environments in central Tanzania. J Arid Environ 166:60–67
Haider FU, Coulter JA, Cai LQ, Saddam H, Sardar AC, J W, Zhang RZ, (2021) An overview on biochar production, its implications, and mechanisms of biochar-induced amelioration of soil and plant characteristics. Pedosphere 32(1):107–130
Han DD, Deng JC, Gu CJ, Mu XM, Gao P, Gao JJ (2020) Effect of shrub-grass vegetation coverage and slope gradient on runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall. Int J Sediment Res 36(1):29–37
Han FP, Zhang RLL, XC, (2016) Effect of biochar on the soil nutrients about different grasslands in the Loess Plateau. CATENA 137:554–562
He T, Liu D, Yuan J, Luo J, Lindsey S, Bolan N, Ding W (2018) Effects of application of inhibitors and biochar to fertilizer on gaseous nitrogen emissions from an intensively managed wheat field. Sci Total Environ 628–629:121–130
Hossain MZ, Bahar MM, Sarkar B, Donne SW, Ok YS, Palansooriya KN, Kirkham MB, Chowdhury S, Bolan N (2020) Biochar and its importance on nutrient dynamics in soil and plant. Biochar 2:379–420
Hou RJ, Li TX, Fu Q, Liu D, Li M, Zhou ZQ, Li QL, Zhao H, Yu PF, Yan JW (2020) Effects of biochar and straw on greenhouse gas emission and its response mechanism in seasonally frozen farmland ecosystems. Catena 194:104735
Hu YJ, Ma PH, Wu SF, Sun BH, Feng H, Pan XL, Zhang BB, Chen GJ, Duan CX, Lei Q, Siddique KHM, Liu BY (2020) Spatial-temporal distribution of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) roots and water use efficiency under ridge-furrow dual mulching. Agr Water Manage 240:106301
Hu A, Stroosnijder L (2010) Effects of tied ridges and mulch on barley (Hordeum vulgare) rainwater use efficiency and production in Northern Ethiopia. Agr Water Manage 97:841–847
Hu Y, Sun B, Wu S, Feng H, Gao M, Zhang B, Liu Y (2021) After-effects of straw and straw-derived biochar application on crop growth, yield, and soil properties in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) -maize (Zea mays L.) rotations: a four-year field experiment. Sci Total Environ 780:146560
Kan ZR, Liu QY, Wu G, Ma ST, Virk AL, Qi JY, Zhao X, Zhang HL (2021) Temperature and moisture driven changes in soil carbon sequestration and mineralization under biochar addition. J Environ Manage 277:111331
Kumar K, Dhorde A (2021) Impact of Land use Land cover change on Storm Runoff Generation: A case study of suburban catchments of Pune, Maharashtra, India. Environ Dev Sustain 23:4559–4572
Lee CH, Wang CC, Lin HH, Lee SS, Tsang DCW, Jien SH, Ok YS (2018) In-situ biochar application conserves nutrients while simultaneously mitigating runoff and erosion of an Fe-oxide-enriched tropical soil. Sci Total Environ 620:665–671
Li QL, Wang M, Fu Q, Li TX, Liu D, Hou RJ, Li H, Cui S, Ji Y (2020a) Short-term influence of biochar on soil temperature, liquid moisture content and soybean growth in a seasonal frozen soil area. J Environ Manage 266:110609
Li T, Cao XS, Qiu ML, Li Y (2020b) Exploring the spatial determinants of rural poverty in the interprovincial border areas of the loess plateau in China: a village-level analysis using geographically weighted regression. Int J Geo-Inf 9(6):345
Li XY, Gong JD (2002) Effect of different ridge: furrow ratios and supplement irrigation on crop production in ridge and furrow rainfall harvesting system with mulches. Agr Water Manage 54(3):243–254
Li YY, Zhang FB, Yang MY, Zhang JQ, Xie YG (2019) Impacts of biochar application rates and particle sizes on runoff and soil loss in small cultivated loess plots under simulated rainfall. Sci Total Environ 649:1403–1413
Li ZG, Gu CM, Zhang RH, Ibrahim M, Zhang GS, Wang L, Zhang RQ, Chen F, Liu Y (2017) The benefic effect induced by biochar on soil erosion and nutrient loss of slopping land under natural rainfall conditions in central China. Agr Water Manage 185:145–150
Lim TJ, Spokas KA, Feyereisen G, Novak JM (2016) Predicting the impact of biochar additions on soil hydraulic properties. Chemosphere 142:136–144
Liu HQ, Yang JH, Diao YF, Lei TW, Rahma AE (2021) The hydrodynamic mechanism of rainfall runoff from loess slope incorporated with straw. Land Degrad Dev 32(14):3812–3822
Liu XL, Wang YD, Yan XQ, Hou HZ, Liu P, Cai T, Zhang P, Jia ZK, Ren XL, Chen XL (2020) Appropriate ridge-furrow ratio can enhance crop production and resource use efficiency by improving soil moisture and thermal condition in a semi-arid region. Agr Water Manage 240:106289
Mailapalli DR, Thompson AM (2011) Polyacrylamide coated Milorganite™ and gypsum for controlling sediment and phosphorus loads. Agr Water Manage 101(1):27–34
Major J, Rondon M, Molina D, Riha S, Lehmann J (2010) Maize yield and nutrition during 4 years after biochar application to a Colombian savanna oxisol. Plant Soil 333:117–128
Meng XP, Lian YH, Liu Q, Zhang P, Jia ZK, Han QF (2020) Optimizing the planting density under the ridge and furrow rainwater harvesting system to improve crop water productivity for foxtail millet in semiarid areas. Agr Water Manage 238:106220
Mesfin T, Tesfahunegn GB, Wortmann CS, Nikus O, Mamo M (2009) Tied-ridging and fertilizer use for sorghum production in semi-arid Ethiopia. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 85(1):87–94
Narjary B, Aggarwal P, Singh A, Chakraborty D, Singh R (2012) Water availability in different soils in relation to hydrogel application. Geoderma 187–188:94–101
Nyamangara J, Nyagumbo I (2010) Interactive effects of selected nutrient resources and tied-ridging on plant growth performance in a semi-arid smallholder farming environment in central Zimbabwe. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 88:103–109
Obia A, Børresen T, Martinsen V, Cornelissen G, Mulder J (2017) Effect of biochar on crust formation, penetration resistance and hydraulic properties of two coarse-textured tropical soils. Soil till Res 170:114–121
Palangi S, Bahmani O, Atlassi-Pak V (2021) Effects of wheat straw biochar amendments to soil on the fate of deltamethrin and soil properties. Environ Technol Inno 23(6):101681
Peng X, Ye LL, Wang CH, Zhou H, Sun B (2011) Temperature and duration dependent rice straw-derived biochar: characteristics and its effects on soil properties of an Ultisol in southern China. Soil till Res 112:159–166
Qiu LJ, Wu YP, Shi ZY, Yu MZ, Zhao FB, Guan YH (2021) Quantifying spatiotemporal variations in soil moisture driven by vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau of China. J Hydrol 600(8):126580
Usowicz B, Lipiec J, Łukowski M, Marczewski W, Usowicz J (2016) The effect of biochar application on thermal properties and albedo of loess soil under grassland and fallow. Soil till Res 164:45–51
Usowicz B, Lipiec J, Usowicz JB, Marczewski W (2013) Effects of aggregate size on soil thermal conductivity: comparison of measured and model-predicted data. Int J Heat Mass Tran 57:536–541
Wang C, Walter MT, Parlange JY (2013a) Modeling simple experiments of biochar erosion from soil. J Hydrol 499:140–145
Wang JY, Mo F, Zhou H, Kavagi L, Nguluu SN, Xiong YC (2021a) Ridge-furrow with grass straw mulching farming system to boost rainfed wheat productivity and water use efficiency in semiarid Kenya. J Sci Food Agr 101(7):3030–3040
Wang J, Zhao WW, Jia LZ, Hu XP, Cherubini F (2021b) Soil desiccation trends after afforestation in the Loess Plateau of China. J Soils Sediments 21:1165–1176
Wang L, Wei SP, Horton R, Shao MA (2011) Effects of vegetation and slope aspect on water budget in the hill and gully region of the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 87(1):90–100
Wang Q, Li FC, Zhang DK, Liu QL, Li G, Liu XN, Li XL, Chen J (2018) Sediment control and fodder yield increase in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L) production with tied-ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting on sloping land. Field Crop Res 225:55–63
Wang B, Zhang GH, Shi YY, Zhang XC, Ren ZP, Zhu LJ (2013b) Effect of natural restoration time of abandoned farmland on soil detachment by overland flow in the Loess Plateau of China. Earth Surf Proc Land 38(14):1725–1734
Wei WL, Yang HQ, Fan MS, Chen HQ, Guo DY, Cao J, Yakov K (2020) Biochar effects on crop yields and nitrogen loss depending on fertilization. Sci Total Environ 702:134423
Wu S, Wu P, Feng H, Merkley GP (2011) Effects of alfalfa coverage on runoff, erosion and hydraulic characteristics of overland flow on loess slope plots. Front Env Sci Eng 5(1):76–83
Xin X, Sun Z, Xiao J, Feng LS, Yang N, Liu Y (2021) Ridge-furrow rainfall harvesting planting and its effect on soil erosion and soil quality in sloping farmland. Agron J 113:863–877
Xiong JB, Yu RH, Ejazul I, Zhu FH, Zha JF, Muhammad IS (2020) Effect of biochar on soil temperature under high soil surface temperature in coal mined arid and semiarid regions. Sustainability 12:8238–8247
Yu PF, Li TX, Fu Q, Liu D, Hou RJ, Zhao H (2021) Effect of biochar on soil and water loss on sloping farmland in the black soil region of northeast China during the spring thawing period. Sustainability 13(3):1460
Zhang CC, Wang YQ, Sha MA (2021) Controlling gully- and revegetation-induced dried soil layers across a slope-gully system. Sci Total Environ 755(2):142444
Zhang DK, Wang Q, Li G, Li XL, Sample DJ (2019a) Optimum ridge width and suitable mulching material for sainfoin production with ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting in semiarid regions of China. Arid Land Res Manag 33(3):274–296
Zhang DX, Pan GX, Wu G, Kibue GW, Li LQ, Zhang XH, Zheng JW, Zheng JF, Cheng K, Joseph S, Liu XY (2015) Biochar helps enhance maize productivity and reduce greenhouse gas emissions under balanced fertilization in a rainfed low fertility inceptisol. Chemosphere 142:106–133
Zhang FB, Huang CH, Yang MY, Zhang JQ, Shi WY (2019b) Rainfall simulation experiments indicate that biochar addition enhances erosion of loess-derived soils. Land Degrad Dev 30(18):2272–2286
Zhang QQ, Song YF, Wu Z, Yan XY, Gunina A, Kuzyakov Y, Xiong ZQ (2020a) Effects of six-year biochar amendment on soil aggregation, crop growth, and nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies in a rice-wheat rotation. J Clean Prod 242:118435
Zhang ZX, Whish JPM, Bell LW, Nan ZB (2017) Forage production, quality and water-use-efficiency of four warm-season annual crops at three sowing times in the Loess Plateau region of China. Eur J Agron 84:84–94
Zhang DK, Wang Q, Zhou XJ, Liu QL, Wang XY, Zhao XL, Zhao WC, He CG, Li XL, Li G, Chen J (2020b) Suitable furrow mulching material for maize and sorghum production with ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting in semiarid regions of China. Agr Water Manage 228:105928
Zhao H, Xiong YC, Li FM, Wang RY, Qiang SC, Yao TF, Mo F (2012) Plastic film mulch for half growing-season maximized WUE and yield of potato via moisture temperature improvement in a semi-arid agroecosystem. Agr Water Manage 104(2):68–78
Zhao WC, Wang Q, Wang XY, Zhao XL, Zhang DK, Zhou XJ, Mai XH, Chen J (2021) Runoff prediction of rainwater harvesting ridge based on modified SCS-CN model. J Soil Water Conserv 35(2):96–105 (Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to Maureen M. Vance, Ex-Manager Adult Reading Assistance Scheme, Christchurch, New Zealand, for improving the English in this paper.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42061050 and 41661059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Simon Pulley
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Mak-Mensah, E., Wang, Q. et al. Effects of ridge-furrow rainwater-harvesting with biochar application on sediment control and alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) fodder yield increase in semiarid regions of China. J Soils Sediments 22, 1885–1899 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03179-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03179-y