Abstract
Purpose
Determine the multiple responses of earthworm biomarkers to antimony persistent exposure in soil.
Methods
Under antimony treatment levels (exogenous nominal contents) of 15, 30, 60, and 120 mg/kg, the biological health status of earthworm Eisenia andrei after 14, 21, and 28 days of exposure was evaluated via the response of soluble protein, superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), malondialdehyde (MDA), metallothionein (MT), and their driven Biomarker Response Index (BRI).
Results
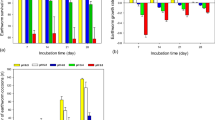
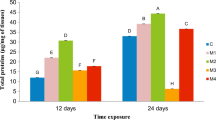
Overall, the protein contents decreased by 11.50 ~ 45.67%, the contents of MDA and MT augmented by 16.22 ~ 241.18% and 6.18 ~ 117.93%, and the activities of SOD, CAT, and POD increased by 38.99 ~ 536.36%, 27.65 ~ 105.99%, and 4.91 ~ 90.49%. The results of BRI indicated that antimony contents above 60 mg/kg always caused a severe alteration on earthworm health status.
Conclusion
The exponential relationship between BRI and antimony content ([BRI] = 1 + 3·e−0.0152·c) theoretically suggested a severe alteration when the content exceeded 45.54 mg/kg after 28 days of exposure. This study provides biological toxicity-based evidence for assessment of soil antimony.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, and Signal Transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Baek Y-W, Lee W-M, Jeong S-W, An Y-J (2014) Ecological effects of soil antimony on the crop plant growth and earthworm activity. Environ Earth Sci 71:895–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2492-y
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Calisi A, Grimaldi A, Leomanni A, Lionetto MG, Dondero F, Schettino T (2016) Multibiomarker response in the earthworm Eisenia fetida as tool for assessing multi-walled carbon nanotube ecotoxicity. Ecotoxicology 25:677–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1626-x
Chen X, Wang X, Ji R (2015) Bioaccumulation and oxidative stresses of cadmium in earthworm in a paddy soil (Chinese Edition). J Agro-Environ Sci 34:1464–1469. http://dx.doi.org/10.11654/jaes.2015.08.005
Dedeke GA, Owagboriaye FO, Adebambo AO, Ademolu KO (2016) Earthworm metallothionein production as biomarker of heavy metal pollution in abattoir soil. Appl Soil Ecol 104:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.02.013
Fei JC, Min XB, Wang ZX, Pang ZH, Liang YJ, Ke Y (2017) Health and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in an antimony mining region: a case study from South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:1–14
Geng L, Yang Z, Xu Z (2020) Effects of antimony contamination in soil on the nutrient composition of three green leafy vegetables. J Soils Sediments 20:2217–2224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02577-4
Hackenberger DK, Stjepanovic N, Loncaric Z, Hackenberger BK (2018) Acute and subchronic effects of three herbicides on biomarkers and reproduction in earthworm Dendrobaena veneta. Chemosphere 208:722–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.047
Hagger JA, Jones MB, Lowe D, Leonard DRP, Owen R, Galloway TS (2008) Application of biomarkers for improving risk assessments of chemicals under the Water Framework Directive: A case study. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1111–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.03.040
He M, Wang X, Wu F, Fu Z (2012) Antimony pollution in China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.009
Huang B, Long J, Li J, Ai Y (2021) Effects of antimony contamination on bioaccumulation and gut bacterial community of earthworm Eisenia fetida. J Hazard Mater 416:126110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126110
Indika H, Meththika V, Jochen B (2017) Antimony as a global dilemma: geochemistry, mobility, fate and transport. Environ Pollut 223:545–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.057
Kaegi JHR, Schaeffer A (1988) Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 27:8509–8515. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00423a001
Kuperman RG, Checkai RT, Simini M, Phillips CT, Speicher JA, Barclift DJ (2006) Toxicity benchmarks for antimony, barium, and beryllium determined using reproduction endpoints for Folsomia candida, Eisenia fetida, and Enchytraeus crypticus. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:754–762. https://doi.org/10.1897/04-545R.1
Leveque T, Capowiez Y, Schreck E, Mazzia C, Auffan M, Foucault Y, Austruy A, Dumat C (2013) Assessing ecotoxicity and uptake of metals and metalloids in relation to two different earthworm species (Eiseina hortensis and Lumbricus terrestris). Environ Pollut 179:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.03.066
Li J, Zheng B, He Y, Zhou Y, Chen X, Ruan S, Yang Y, Dai C, Tang L (2018) Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 156:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.024
Li L, Yang D, Song Y, Shi Y, Huang B, Yan J, Dong X (2017) Effects of bifenthrin exposure in soil on whole-organism endpoints and biomarkers of earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 168:41–48
Li X, Wang M, Chen W, Jiang R (2019) Evaluation of combined toxicity of Siduron and cadmium on earthworm (Eisenia fetida) using Biomarker Response Index. Sci Total Environ 646:893–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.380
Lin Z, Zhen Z, Wu Z, Yang J, Zhong L, Hu H, Luo C, Bai J, Li Y, Zhang D (2016) The impact on the soil microbial community and enzyme activity of two earthworm species during the bioremediation of pentachlorophenol-contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 301:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.034
Nannoni F, Protano G (2016) Chemical and biological methods to evaluate the availability of heavy metals in soils of the Siena urban area (Italy). Sci Total Environ 568:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.208
Nusair SD, Abu Zarour YS (2016) Molecular and cellular response of earthworm Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae) to PCDD/Fs exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:902–910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7893-5
Obiakor MO, Tighe M, Wang Z, Ezeonyejiaku CD, Pereg L, Wilson SC (2017) The relative sensitivity of freshwater species to antimony(III): implications for water quality guidelines and ecological risk assessments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:25276–25290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0168-y
OECD (1984) Earthworm acute toxicity tests vol Test no. 207. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
Piva F, Ciaprini F, Onorati F, Benedetti M, Fattorini D, Ausili A, Regoli F (2011) Assessing sediment hazard through a weight of evidence approach with bioindicator organisms: A practical model to elaborate data from sediment chemistry, bioavailability, biomarkers and ecotoxicological bioassays. Chemosphere 83:475–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.064
Sanchez-Hernandez JC, Notario del Pino J, Capowiez Y, Mazzia C, Rault M (2018) Soil enzyme dynamics in chlorpyrifos-treated soils under the influence of earthworms. Sci Total Environ 612:1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.043
Scheuhammer AM, Cherian MG (1986) Quantification of metallothioneins by a silver -saturation method. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 82:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008x(86)90277-2
Sinkakarimi MH, Solgi E, Hosseinzadeh Colagar A (2020) Interspecific differences in toxicological response and subcellular partitioning of cadmium and lead in three earthworm species. Chemosphere 238:124595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124595
Świątek ZM, Bednarska AJ (2019) Energy reserves and respiration rate in the earthworm Eisenia andrei after exposure to zinc in nanoparticle or ionic form. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:24933–24945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05753-3
Tirado-Ballestas I, Caballero K, Olivero-Verbel J (2020) Toxicological effects of bituminous coal dust on the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae). Ecotoxicology 29:1422–1430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02263-8
Wang X, He M, Xie J, Xi J, Lu X (2010) Heavy metal pollution of the world largest antimony mine-affected agricultural soils in Hunan province (China). J Soils Sediments 10:827–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0196-4
Wang X, Li F, Yuan C, Li B, Liu T, Liu C, Du Y, Liu C (2019a) The translocation of antimony in soil-rice system with comparisons to arsenic: alleviation of their accumulation in rice by simultaneous use of Fe(II) and NO3. Sci Total Environ 650:633–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.054
Wang X, Zhu X, Peng Q, Wang Y, Ge J, Yang G, Wang X, Cai L, Shen W (2019b) Multi-level ecotoxicological effects of imidacloprid on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 219:923–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.001
Wang Y (2018) Experimental techniques for ecological remediation of soil pollution. Science Press of China
Wang Y, Yang Z, Wang T, Geng L (2019c) Analysis and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of Taipu river basin. Environ Eng 37:18–22
Xiao E, Krumins V, Dong Y, Xiao T, Ning Z, Xiao Q, Sun W (2016) Microbial diversity and community structure in an antimony-rich tailings dump. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:7751–7763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7598-1
Xu Z, Yang Z, Zhu T, Shu W (2021) Toxicity of soil antimony to earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savingy) before and after the aging process. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111278
Yang X, Li Y, Wang X (2020) Effects of ciprofloxacin exposure on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114287
Yuvaraj A, Govarthanan M, Karmegam N, Biruntha M, Kumar DS, Arthanari M, Tripathi S, Ghosh S, Kumar P, Kannan S, Thangaraj R (2020) Metallothionein dependent-detoxification of heavy metals in the agricultural field soil of industrial area: earthworm as field experimental model system. Chemosphere 267:129240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129240
Zhang B, Sheng X, Liu X (1996) Determination of metallothionein by silver saturation assay. Pharm Biotechnol 3:31–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-0934(98)00115-3
Zhang X, Liu T, Li F, Li X, Du Y, Yu H, Wang X, Liu C, Feng M, Liao B (2021) Multiple effects of nitrate amendment on the transport, transformation and bioavailability of antimony in a paddy soil-rice plant system. J Environ Sci 100:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.07.009
Zhao S, He L, Lu Y, Duo L (2017) The impact of modified nano-carbon black on the earthworm Eisenia fetida under turfgrass growing conditions: Assessment of survival, biomass, and antioxidant enzymatic activities. J Hazard Mater 338:218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.035
Zhong Q, Li L, He M, Ouyang W, Lin C, Liu X (2021) Toxicity and bioavailability of antimony to the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) in different agricultural soils. Environ Pollut 291:118215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118215
Zhou D, Ning Y, Liu J, Deng J, Liu Y (2016) Effects of oxidative stress reaction for the Eisenia fetida with exposure in Cd2+. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1–11
Funding
This study was funded by Shanghai Science and Technology Development Foundation (033919457).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Thank earthworms for their sacrifice. All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Maria Manuela Abreu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Xu, Z., Shu, W. et al. Evaluation of soil antimony stress on the biological health status of earthworm Eisenia andrei using Biomarker Response Index. J Soils Sediments 22, 1999–2008 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03153-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03153-8