Abstract
Purpose
Phthalic acid esters (PAEs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are of global concern because of their serious environmental impacts. The identification of zones contaminated with PAEs and PAHs in the soil is urgently needed to provide a basis for land use and remediation.
Materials and methods
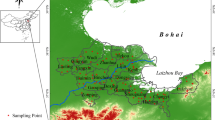
Zhejiang Province was used as a typical example to identify contaminated zones by measuring the concentrations of PAEs and PAHs in gridded soil with a 1/6° latitude by 1/4° longitude resolution. Based on the concentrations and spatial distributions of PAEs and PAHs in superficial soil in Zhejiang, the estimation of inventory, and the assessment of ecological risk, the contaminated zones and possible sources of these two groups of pollutants were identified.
Results and discussion
High spatial variability of PAE concentrations in the surface soils was observed in Zhejiang Province. The areas with high PAE concentrations were in the middle region of Zhejiang where highly urbanized and industrialized. The spatial distribution of PAH in the surface soil of Zhejiang appeared to be uneven. High PAH concentrations in the soil of Zhejiang were mainly measured in plains areas and can be linked to the development of industry and multiple emission sources.
Conclusions
PAE pollution mainly originated from centralized plastic manufacturing, plastic product use, and plastic waste recycling. PAH contamination was linked to the combustion of fuels in vehicle engines and industrial discharge from a cluster of low-capacity boilers. These results can provide a database and reliable reference information for land use and remediation in other agroindustrial ecotone areas.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data and materials used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bi XH, Sheng GY, Tan JH, Tang XL, Fu JM (2004) Phase partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)in the atmosphere. Acta Sci Circumst 24:101–106
Blair JD, Ikonomou MG, Kelly BC, Surridge B, Gobas FAPC (2009) Ultra-trace determination of phthalate ester metabolites in seawater, sediments, and biota from an urbanized marine inlet by LC/ESI-MS/MS. Environ Sci Technol 43:6262–6268
Bucheli TD, Blum F, Desaules A, Gustafsson O (2004) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, black carbon, and molecular markers in soils of Switzerland. Chemosphere 56:1061–1076
Cai QY, Mo CH, Wu QT, Katsoyiannis A, Zeng QY (2008a) The status of soil contamination by semivolatile organic chemicals (SVOCs) in China: a review. Sci Total Environ 389:209–224
Cai QY, Mo CH, Wu QT, Zeng QY (2008b) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in the soil-radish (raphanus sativus) system with sewage sludge and compost application. Bioresource Technol 99:1830–1836
Chen P, Liang J (2021) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in green space soils in Shanghai: source distribution and risk assessment. J Soils Sediments 21(2):967–977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02838-2
Chen R, Lv JG, Zhang W, Liu S, Feng JM (2015) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) pollution in agricultural soil in Tianjin, China: a spatio-temporal comparison study. Environ Earth Sci 74:2743–2748
Chou K, Wright RO (2006) Phthalates in food and medical devices. J Med Toxicol 2:126–135
Dankova R, Jarosova A (2012) Polakova S (2012) The monitoring of dibutyl phthalate and di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate in moravian agricultural soil. Mendelnet 35:736–747
Essumang DK, Kowalski K, Sogaard EG (2011) Levels, distribution and source characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in topsoils and roadside soils in Esbjerg, Denmark. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:438–443
Fromme H, Kuchler T, Otto T, Pilz K, Muller J, Wenzel A (2002) Occurrence of phthalates and bisphenol A and F in the environment. Water Res 36:1429–1438
Gereslassie T, Workineh A, Liu XN, Yan X, Wang J (2018) Occurrence and ecological and human health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from Wuhan, central China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:2751
Gibson R, Wang MJ, Padgett E, Beck AJ (2005) Analysis of 4-nonylphenols, phthalates, and polychlorinated biphenyls in soils and blosolids. Chemosphere 61:1336–1344
Gómez-Hens A, Aguilar-Caballos MP (2003) Social and economic interest in the control of phthalic acid esters. Trend Anal Chem 22:847–857
Guan H, Wang JS, Wan HF, Li PX, Yang GY (2007) PAEs pollution in soils from typical agriculture area of Leizhou Peninsula. J Agro-Environ Sci 26:622–628
Guo DM, Wu Y (2011) Detemination of phthalic acid esters of soil in south of Xinjiang cotton fields. Arid Environ Monit 25:76–79
He L, Gielen G, Bolan NS, Zhang X, Qin H, Huang H, Wang H (2015) Contamination and remediation of phthalic acid esters in agricultural soils in China: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 35:519–534
Jia H, Li YF, Wang D, Cai D, Yang M, Ma J, Hu J (2009a) Endosulfan in China 1-gridded usage inventories. Environ Sci Pollut R 16:295–301
Jia H, Sun Y, Li YF, Tian C, Wang D, Yang M, Ding Y, Ma J (2009b) Endosulfan in China 2-emissions and residues. Environ Sci Pollut R 16:302–311
Jiang JH, Ding LF (2007) The concentration, bioaccumulation and environmental impacts of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in organism in sea. Environ Pollut Control 29:394–397
Jiang YF, Wang XT, Wang F, Jia Y, Wu MH, Sheng GY, Fu JM (2009) Levels, composition profiles and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soil of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 75:1112–1118
Kaewlaoyoong A, Vu CT, Lin C, Liao CS, Chen JR (2018) Occurrence of phthalate esters around the major plastic industrial area in southern Taiwan. Environ Earth Sci 77:1–11
Khan S, Cao Q (2012) Human health risk due to consumption of vegetables contaminated with carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Soils Sediments 12:178–184
Kong S, Ji Y, Liu L, Chen L, Zhao X, Wang J, Bai Z, Sun Z (2012) Diversities of phthalate esters in suburban agricultural soils and wasteland soil appeared with urbanization in China. Environ Pollut 170:161–168
Kovats N, Hubai K, Sainnokhoi TA, Teke G (2021) Biomonitoring of polyaromatic hydrocarbon accumulation in rural gardens using lettuce plants. J Soils Sediments 21:106–117
Latini G (2005) Monitoring phthalate exposure in humans. Clin Chim Acta 361:20–29
Lau E, Gan SY, Ng HK (2012) Distribution and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface soils from five different locations in Klang Valley, Malaysia. B Environ Contam Tox 88:741–746
Li XH, Ma LL, Liu XF, Fu S, Cheng HX, Xu XB (2006) Phthalate ester pollution in urban soil of Beijing, People’s Republic of China. B Environ Contam Tox 77:252–259
Li KK, Ma D, Wu J, Chai C, Shi YX (2016) Distribution of phthalate esters in agricultural soil with plastic film mulching in Shandong Peninsula, east China. Chemosphere 164:314–321
Li Y, Yan HQ, Li XQ, Ge J, Cheng JJ, Yu XY (2020) Presence, distribution and risk assessment of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in suburban plastic film pepper-growing greenhouses with different service life. Ecotox Environ Safe 196:110551
Lin Z, Zhang J, Cui H, Zhang L, Chen G (2010) Determination of phthalate esters in soil by microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography coupled with accelerated solvent extractionlen. J Sep Sci 33:3717–3725
Liu BL, Li M, Hua XY, Dong DM, Dong WH (2013) Distribution and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons residues in different types of topsoil collected from Jilin Province, China. Asian J Chem 25:8957–8960
Liu XW, Shi JH, Bo T, Zhang H, Wu W, Chen QC, Zhan XM (2014) Occurrence of phthalic acid esters in source waters: a nationwide survey in China during the period of 2009–2012. Environ Pollut 184:262–270
Long ER, Macdonald DD, Smith SL, Calder FD (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manage 19:81–97
Lu XH, Gu AN, Zhang YW, Chu XY, Hu XF (2020) Accumulation of PAHs of the soils and assessment of their health risks at a village with plastic manufacturing in Taizhou, Zhejiang Province, Southeast China. J Soils Sediments 20:705–713
Luo XJ, Chen SJ, Yu M, Mai BX, Sheng GY, Fu JM (2008) Distribution and partition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water from the Pearl River estuary. Huanjing Kexue 29:2385–2391
Ma LL, Chu SG, Xu XB (2003a) Organic contamination in the greenhouse soils from Beijing suburbs, China. J Environ Monitor 5:786–790
Ma LL, Chu SG, Xu XB (2003b) Phthalate residues in greenhouse soil from Beijing suburbs, People’s Republic of China. B Environ Contam Tox 71:394–399
Mo CH, Cai QY, Tang SR, Zeng QY, Wu QT (2009) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in vegetables from nine farms of the Pearl River Delta, south China. Arch Environ Con Tox 56:181–189
Peijnenburg W, Struijs J (2006) Occurrence of phthalate esters in the environment of the Netherlands. Ecotox Environ Safe 63:204–215
Plaza-Bolanos P, Padilla-Sanchez JA, Garrido-Frenich A, Romero-Gonzalez R, Martinez-Vidal JL (2012) Evaluation of soil contamination in intensive agricultural areas by pesticides and organic pollutants: south-eastern Spain as a case study. J Environ Monitor 14:1182–1189
Selvaraj KK, Sundaramoorthy G, Ravichandran PK, Girijan GK, Sampath S, Ramaswamy BR (2015) Phthalate esters in water and sediments of the Kaveri River, India: environmental levels and ecotoxicological evaluations. Environ Geochem Hlth 37:83–96
Sosa D, Hilber I, Faure R, Bartolome N, Fonseca O, Keller A, Bucheli TD, Escobar A (2019) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in urban and semi-urban soils of Havana. Cuba J Soils Sediments 19:1328–1341
Srivastava A, Sharma VP, Tripathi R, Kumar R, Patel DK, Mathur PK (2010) Occurrence of phthalic acid esters in Gomti River sediment, India. Environ Monit Assess 169:397–406
Sun J, Pan L, Tsang DCW, Li Z, Zhu L, Li X (2018) Phthalate esters and organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils and vegetables from fast-growing regions: a case study from eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:34–42
Sushkova SN, Minkina T, Deryabkina I, Mandzhieva S, Zamulina I, Bauer T, Vasilyeva G, Antonenko E, Rajput V (2018) Influence of PAH contamination on soil ecological status. J Soils Sediments 18:2368–2378
Tang L, Tang XY, Zhu YG, Zheng MH, Miao QL (2005) Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environ Int 31:822–828
Tao G, Liang C (2008) Analysis on development tendency of domestic and global plasticizer market. Plast Sci Technol 36:78–81
Tran B, Teil MJ, Blanchard M, Alliot F, Chevreuil M (2015) Fate of phthalates and BPA in agricultural and non-agricultural soils of the Paris area (France). Environ Sci Pollut R 22:11118–11126
Vikelsoe J, Thomsen M, Carlsen L (2002) Phthalates and nonylphenols in profiles of differently dressed soils. Sci Total Environ 296:105–116
Wang W, Zhang Y, Wang S, Fan CQ, Xu H (2012) Distributions of phthalic esters carried by total suspended particulates in Nanjing, China. Environ Monit Assess 184:6789–6798
Wang Z, Li H, Liu S (2019) Different distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) between Sphagnum and Ledum peat from an ombrotrophic bog in Northeast China. J Soils Sediments 19:1735–1744
Wen Z, Huang X, Gao D, Liu G, Fang C, Shang Y, Du J, Zhao Y, Lv L, Song K (2018) Phthalate esters in surface water of Songhua River watershed associated with land use types, northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:7688–7698
Wezel AP, van Vlaardingen P, Posthumus R, Crommentuijn GH, Sijm D (2000) Environmental risk limits for two phthalates, with special emphasis on endocrine disruptive properties. Ecotox Environ Safe 46:305–321
Wu SW (2010) Zhejiang recycled plastics industry base is gratifying. Resour Recycl 94:26–28
Xia XH, Yang LY, Bu QW, Liu RM (2011) Levels, distribution, and health risk of phthalate esters in urban soils of Beijing, China. J Environ Qual 40:1643–1651
Xie ZY, Ebinghaus R, Temme C, Caba A, Ruck W (2005) Atmospheric concentrations and air-sea exchanges of phthalates in the North Sea (German Bight). Atmos Environ 39:3209–3219
Xie Z, Ebinghaus R, Temme C, Lohmann R, Caba A, Ruck W (2007) Occurrence and air-sea exchange of phthalates in the arctic. Environ Sci Technol 41:4555–4560
Xu G, Li FH, Wang QH (2008) Occurrence and degradation characteristics of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in typical agricultural soils of China. Sci Total Environ 393:333–340
Yuan SY, Liu C, Liao CS, Chang BV (2002) Occurrence and microbial degradation of phthalate esters in Taiwan river sediments. Chemosphere 49:1295–1299
Yuan GL, Wu LJ, Sun Y, Li J, Li JC, Wang GH (2015) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils of the central Tibetan Plateau, China: distribution, sources, transport and contribution in global cycling. Environ Pollut 203:137–144
Zavgorodnyaya YA, Chikidova AL, Biryukov MV, Demin VV (2019) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric particulate depositions and urban soils of Moscow, Russia. J Soils Sediments 19:3155–3165
Zeng F, Cui K, Xie Z, Wu L, Liu M, Sun G, Lin Y, Luo D, Zeng Z (2008) Phthalate esters (PAEs): emerging organic contaminants in agricultural soils in peri-urban areas around Guangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 156:425–434
Zeng F, Cui K, Xie Z, Wu L, Luo D, Chen L, Lin Y, Liu M, Sun G (2009) Distribution of phthalate esters in urban soils of subtropical city, Guangzhou, China. J Hazard Mater 164:1171–1178
Zeng LJ, Huang YH, Chen XT, Chen XH, Mo CH, Feng YX, Lu HX, Xiang L, Li YW, Li H, Cai QY, Wong MH (2020) Prevalent phthalates in air-soil-vegetable systems of plastic greenhouses in a subtropical city and health risk assessments. Sci Total Environ 743:140755
Zhang ZH, Lu L, He GX, Peng XY, Zhu L, Wang XW, Jiao X (2011a) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compounds in topsoil of Beijing, China. Ecol Environ Sci 20:668–675
Zhang LF, Yang WL, Dong L, Huang YR, Shi SX, Zhang T, Zhou L (2011b) Pollution characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in agricultural surface soil from the southern Jiangsu Province, China. J Agro-Environ Sci 30:2202–2209
Zhang A, Liu W, Yuan H, Zhou S, Su Y, Li YF (2011c) Spatial distribution of hexachlorocyclohexanes in agricultural soils in Zhejiang Province, China, and correlations with elevation and temperature. Environ Sci Technol 45:6303–6308
Zhang LF, Dong L, Ren LJ, Shi SX, Zhou L, Zhang T, Huang YR (2012) Concentration and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in the surface water of the Yangtze River Delta, China. J Environ Sci 24:335–342
Zhang Y, Liang Q, Gao RT, Hou HB, Tan WB, He XS, Zhang H, Yu MD, Ma LN, Xi BD, Wang XW (2015) Contamination of phthalate esters (PAEs) in typical wastewater-irrigated agricultural soils in Hebei, north China. Plos One 10:e0137998
Zhang ZM, Zhang HH, Zhang J, Wang QW, Yang GP (2018) Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risks of phthalate esters in the seawater and sediment of Changjiang River estuary and its adjacent area. Sci Total Environ 619:93–102
Zhao SL, Yang GY, Zhang TB, Huang NS, Zhu ZY (2009) Characteristics of pathalic acid esters in soils in typical cities of Pearl River Delta. Ecol Environ Sci 18:128–133
Zhou WW, Li J, Hu J, Zhu ZZ (2018) Distribution, sources, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils of the central and eastern areas of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Huanjing Kexue 39:1413–1420
Zuazagoitia D, Garcia-Arrona R, Millan E (2011) Evaluation of soil contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Gipuzkoa (northern Spain). Soil Sediment Contam 20:525–534
Funding
This study was supported by Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (LGF21B070006) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21976160, 41877494).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mingzhe Lv: Writing draft preparation, Methodology and Assembly of data; Wei Gao: Contributed to Map information and analysis of data; Jiacheng Li: Manuscript preparation; Xintao Ye: Sampling; Tianwei Xu: Revised the manuscript; Lu Liu: Revised the manuscript; Shanshan Zhou: Critical revision of the article; Jianqiang Sun: Critical revision of the article; Anping Zhang: Research concept and design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This work does not involve potential conflicts of interest research involving human participants and/or animals. Our institution’s committee on research gave approval for this study, and all participants gave informed consent.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that this manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The authors confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors. The author agrees to publication in the Journal of Soils and Sediments and also to publication of the article in English by Springer in Springer’s corresponding English-language journal. The copyright transfer covers the exclusive right to reproduce and distribute the article, including reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, microform, electronic form (offline, online), or any other reproductions of similar nature. After submission of the agreement signed by the corresponding author, changes of authorship or in the order of the authors listed will not be accepted by Springer.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Disclaimer
All the funding bodies played a major role in the collection of research samples and analysis and testing of samples.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Xiuping Jia
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, M., Gao, W., Li, J. et al. Identification of zones contaminated with phthalates and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by concentrations in gridded soil with 1/6° latitude by 1/4° longitude resolution: a case study of Zhejiang, China. J Soils Sediments 22, 67–78 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03075-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03075-x