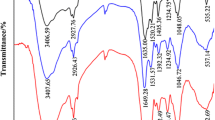
Abstract
Purpose
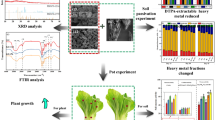
Agricultural soil contamination by heavy metals is a serious environmental problem, and developing feasible and effective soil remediation technologies is a top priority. In this study, a microbial consortium dominated by sulfur-oxidizing bacteria was constructed to enhance Cd and Zn removal from contaminated soil.
Materials and methods
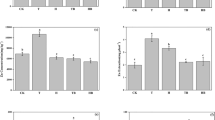
During treatments, changes in pH and Eh and the removal efficiencies of Cd and Zn were investigated. Fractionation of Cd and Zn, soil fertility indexes, and the microbial community were also analyzed before and after bioleaching.
Results and discussion
The results show that under the same conditions, the best removal efficiencies for Cd and Zn were observed in the bioleaching group compared to other treatments (acid leaching and sulfur treatment). When the sulfur concentration was 15 g/kg, 79.3% of Cd and 45.2% of Zn were removed, while undissolved Cd and Zn mainly remained in the residual fraction, accounting for 93.1% and 84.0% of their remaining totals, respectively. After remediation, the bioleaching group showed a reduction of the total phosphorus and available potassium, with a decrease of 53.7% and 41.2%, respectively. Furthermore, the exogenous microbes in the inoculum had a competitive advantage and became the dominant population at the end of the run.
Conclusions
The consortium obtained in this study can effectively improve remediation processing and be used to remediate heavy metal-contaminated soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao SD (2000) Soil agrochemical analysis. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Beenackers A, Van Swaaij WPM (1993) Mass transfer in gas–liquid slurry reactors. Chem Eng Sci 48:3109–3139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(93)80199-Z
Bisone S, Blais J, Drogui P, Mercier G (2012) Toxic metal removal from polluted soil by acid extraction. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:3739–3755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1145-1
Bisone S, Blais J, Mercier G (2013) Counter-current metal leaching and precipitation for soil remediation. Soil Sediment Contam 22:856–875. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2013.770445
Chou C, Han C, Chang J, Lay J (2011) Co-culture of Clostridium beijerinckii L9, Clostridium butyricum M1 and Bacillus thermoamylovorans B5 for converting yeast waste into hydrogen. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:13972–13983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.03.067
Cui Y, Dong Y, Li H, Wang Q (2004) Effect of elemental sulphur on solubility of soil heavy metals and their uptake by maize. Environ Int 30:323–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00182-X
Deng X, Chai L, Yang Z, Tang C, Tong H, Yuan P (2012) Bioleaching of heavy metals from a contaminated soil using indigenous Penicillium chrysogenum strain F1. J Hazard Mater 233:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.06.054
El Hazek MN, Ahmed FY, El Kasaby MA, Attia RM (2008) Sulfuric acid leaching of polymetallic Abu Zeneima gibbsite-shale. Hydrometallurgy 90:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2007.09.009
Gao J, Zhang C, Wu X, Wang H, Qiu G (2007) Isolation and identification of a strain of Leptospirillum ferriphilum from an extreme acid mine drainage site. Ann Microbiol 57:171–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175203
Gao J, Zhao J, Dong C, Wu L, Hu P (2018) Remediation of metal-contaminated paddy soils by chemical washing with FeCl3 and citric acid. J Soils Sediments 18:1020–1028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1759-4
Ghavidel A, Rad SN, Alikhani HA, Sharari M, Ghanbari A (2018) Bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge, direct action of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans or only the impact of pH? J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 20:1179–1187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-017-0680-7
Giller KE, Witter E, Mcgrath SP (1998) Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1389–1414. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00270-8
Gu J, Zhou Q (2002) Cleaning up through phytoremediation: a review of Cd contaminated soils. Ecol Sci 21:352–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-002-0038-4
Gurung A, Oh S (2013) Use of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria for assessment of chromium-contaminated soil. Environ Earth Sci 70:139–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2110-4
Kumar RN, Nagendran R (2009) Fractionation behavior of heavy metals in soil during bioleaching with Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J Hazard Mater 169:1119–1126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.069
Li B, Chen Y, Liu Q, Hu S, Chen X (2011) Complete genome analysis of Sulfobacillus acidophilus strain TPY, isolated from a hydrothermal vent in the Pacific Ocean. J Bacteriol 193:5555–5556. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05684-11
Li B, Zhang X, Guo F, Wu W, Zhang T (2013a) Characterization of tetracycline resistant bacterial community in saline activated sludge using batch stress incubation with high-throughput sequencing analysis. Water Res 47:4207–4216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.021
Li Y, Gao R, Yang R, Wei H, Li Y, Xiao H, Wu J (2013b) Using a simple soil column method to evaluate soil phosphorus leaching risk. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 41:1100–1107. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201200372
Li L, Hou M, Cao L, Xia Y, Shen Z, Hu Z (2018) Glutathione S-transferases modulate Cu tolerance in Oryza sativa. Environ Exp Bot 155:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.07.007
Liu X, Tao Y, Wen G, Kong F, Zhang X, Hu Z (2016) Influence of soil and irrigation water pH on the availability of phosphorus in struvite derived from urine through a greenhouse pot experiment. J Agric Food Chem 64:3324–3329. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00021
Liu L, Li W, Song W, Guo M (2018) Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: principles and applicability. Sci Total Environ 633:206–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.161
Lombardi AT, Garcia O Jr (2002) Biological leaching of Mn, Al, Zn, Cu and Ti in an anaerobic sewage sludge effectuated by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and its effect on metal partitioning. Water Res 36:3193–3202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00008-8
Ma Y, Li X, Mao H, Wang B, Wang P (2018) Remediation of hydrocarbon—heavy metal co-contaminated soil by electrokinetics combined with biostimulation. Chem Eng J 353:410–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.131
Mann SS, Ritchie G (1993) The influence of pH on the forms of cadmium in four west Australian soils. Soil Res 31:255–270. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR9930255
Ministry of Natural Resources (2014) Research report on land consolidation and rehabilitation of China. Social Sciences Academic Press, Beijing
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth T (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8
Nareshkumar R, Nagendran R, Parvathi K (2008) Bioleaching of heavy metals from contaminated soil using Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans: effect of sulfur/soil ratio. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1539–1546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9639-5
Pathak A, Dastidar MG, Sreekrishnan TR (2009) Bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge: a review. J Environ Manage 90:2343–2353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.005
Poonpakdee C, Tzeng JH, Weng CH, Lin YT (2018) Assessment of potassium speciation in soil using traditional single leaching and modified sequential extraction processes. J Soils Sediments 18:610–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1773-6
Rafiq MT, Aziz R, Yang X, Xiao W, Rafiq MK, Ali B, Li T (2014) Cadmium phytoavailability to rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in representative Chinese soils. A model to improve soil environmental quality guidelines for food safety. Ecotox Environ Safe 103:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.10.016
Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monitor 1:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/A807854H
Reuss J, Christophersen N, Seip H (1986) A critique of models for freshwater and soil acidification. Water Air Soil Pollut 30:909–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-3385-9_94
Rousk J, Bååth E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4:1340. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.58
Rüşen A, Topçu MA (2017) Investigation of zinc extraction from different leach residues by acid leaching. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1365-4
SEPAC (2004) The technical specification for soil environmental monitoring. Environmental Press of China, Beijing
Štyriaková I, Štyriak I, Balestrazzi A, Calvio C, Faè M, Štyriaková D (2016) Metal leaching and reductive dissolution of iron from contaminated soil and sediment samples by indigenous bacteria and Bacillus isolates. Soil Sediment Contam 25:519–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2016.1170102
Sun Y, Li Y, Xu Y, Liang X, Wang L (2015) In situ stabilization remediation of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) co-contaminated paddy soil using bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 105:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.12.031
Tang J, He J, Qiu Z, Xin X (2019) Metal removal effectiveness, fractions, and binding intensity in the sludge during the multiple washing steps using the combined rhamnolipid and saponin. J Soils Sediments 19:1286–1296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2106-0
Wan X, Lei M, Chen T (2016) Cost–benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 563:796–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.080
Wang Y, Li Q, Hui W, Shi J, Lin Q, Chen X, Chen Y (2008) Effect of sulphur on soil Cu/Zn availability and microbial community composition. J Hazard Mater 159:385–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.029
Wang M, Zhang Q, Yang Z, Zhang A, Xie X (2014) Soil pH changes in the paddy field during the drying and rewetting cycles in the ningxia irrigation area of the yellow river basin. J Nucl Agric Sci 28:720–726. https://doi.org/10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2014.04.0720
Wang Y, Li F, Song J, Xiao R, Luo L, Yang Z, Chai L (2018) Stabilization of Cd-, Pb-, Cu-and Zn-contaminated calcareous agricultural soil using red mud: a field experiment. Environ Geochem Health 40:2143–2153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0089-9
Xu R, Zhao A, Yuan J, Jiang J (2012) pH buffering capacity of acid soils from tropical and subtropical regions of China as influenced by incorporation of crop straw biochars. J Soils Sediments 12:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-012-0483-3
Yang ZH, Zhang Z, Chai LY, Wang Y, Liu Y, Xiao RY (2016) Bioleaching remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils using Burkholderia sp. Z-90. J Hazard Mater 301:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.047
Yin B, Zhou L, Yin B, Chen L (2016) Effects of organic amendments on rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth and uptake of heavy metals in contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 16:537–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1181-8
Zeng W, Wu C, Zhang R, Hu P, Qiu G, Gu G, Zhou H (2009) Isolation and identification of moderately thermophilic acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacterium and its bioleaching characterization. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 19:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(08)60256-3
Zeng J, Gou M, Tang Y, Li G, Sun Z, Kida K (2016) Effective bioleaching of chromium in tannery sludge with an enriched sulfur-oxidizing bacterial community. Bioresour Technol 218:859–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.051
Zhang X, Xia H, Li Z, Zhuang P, Gao B (2010) Potential of four forage grasses in remediation of Cd and Zn contaminated soils. Bioresour Technol 101:2063–2066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.065
Zhang S, Yang Z, Wu B, Wang Y, Wu R, Liao Y (2014) Removal of Cd and Pb in calcareous soils by using Na2EDTA recycling washing. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 42:641–647. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201200634
Zupanc V, Kastelec D, Lestan D, Grcman H (2014) Soil physical characteristics after EDTA washing and amendment with inorganic and organic additives. Environ Pollut 186:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.11.027
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41706221), China Ocean mineral resources R&D association program (Grant No. DY135-B2), and Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (Grant No. 2017J05063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Claudio Bini
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Y., Cheng, H., Zhou, W. et al. Enhancing Zn and Cd removal from heavy metal-contaminated paddy soil using an artificial microbial consortium. J Soils Sediments 22, 218–228 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03066-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-03066-y